Integrating With SaaS Applications: Example Processes and 3rd-Party Platform Integration
In this article, we'll share how customers are integrating processes and 3rd-party platforms as SaaS applications in their architectures...
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIt's a starting point for the generic architecture that rises from several customer solutions that were researched.
Having completed the outline of the architectural details and the resulting logical diagram elements, it's now time to take a look as specific examples.
In this article, we'll continue building the previous examples by sharing how customers are integrating processes and 3rd-party platforms as SaaS applications in their architectures.
Architecture Scenarios
As a reminder, the architectural details covered here are base on real customer integration solutions using open source technologies.
The example scenario presented here is a generic common architecture that was uncovered researching customer solutions. It's my intent to provide an example that provides guidance and not deep technical details.
This section covers the visual representations as presented. There are many ways to represent each element in this architecture, but I've chosen icons, text, and colors that I hope are going to make it all easy to absorb. Feel free to post comments at the bottom of this post, or contact me directly with your feedback.
Now let's take a look at the details in this architecture and outline the solution.
Integrating Processes and SaaS Applications
The example shown in the figure titled Example: Third Party Platform Process Integration outlines how to integrate processes and an existing 3rd-party platform as if it's a SaaS platform.
As is often the case, organizational choices in our past have left us with legacy components in our architectures. While sometimes these are simple components to integrate with, we live and learn by applying the same abstractions to our larger platforms that might be hosting a collection of functionality in our organization.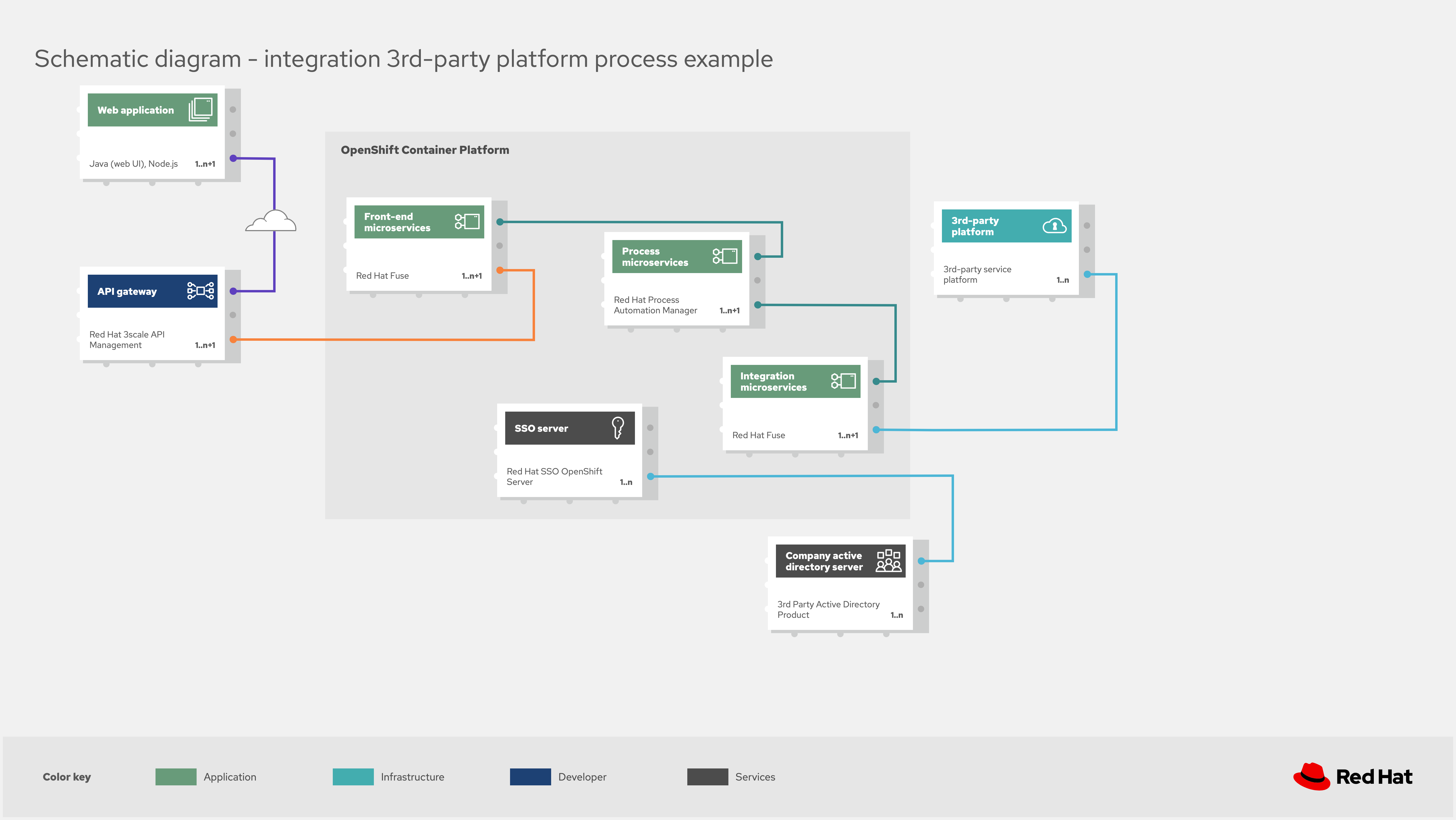
Furthermore, organizations have processes in place that become dependent on their ability to react on information from SaaS applications. Along those same lines, these processes produce information that might need to be shared with these external SaaS applications. Integrating process and SaaS applications introduce stateful complexities into the integration solution.
Let's assume this example is making use of a legacy platform hosting a myriad of specialized services that have become impossible to maintain. The amount of interfaces and maintenance has become such a burden that the organization desires to migrate away from the legacy platform, yet cannot at this time due to their dependency on those hosted services.
A logical approach is to segregate the platform as if it's a cloud or SaaS service. This allows for gradual migration of the existing services from the 3rd-party platform at your convenience, including eventual moves to offsite or cloud-based service hosting. SaaS integration with these services or applications provides many options going forward in managing the architecture.
The architecture here shows a specific part of the integration, where a front end web connection uses front-end microservices to access integration microservices that manage that generic access to the third-party platform. Note, the security aspects are left in this example to ensure that you remember to include authentication and authorization across your integration landscape.
Within the integration microservices lies the solution for processes and 3rd-party platform integration. The stateful nature of processes means that they are awaiting a trigger to start or continue their process, often based on data supplied with that trigger. On the other hand, processes can also reach a state where they wait after sending data requests to a 3rd-party platform. How does this integration communication happen?
The solution in this architecture is inside the integration microservices where messaging is used with processes posting data to message queues and listening for triggers from microservices that interact with queues receiving messages from 3rd-party platforms.
Implementation details are left up to the reader to quantify as each organization's needs and usage of specific SaaS integration with all possible third-party platforms can not be captured in a generic architecture beyond the above.
What's Next
An overview of the series on integrating SaaS applications portfolio architecture can be found here:
- An introduction
- Common architectural elements
- Example CRM integration
- Example CRM connector integration
- Example 3rd-party platform integration
- Example processes with 3rd-party platform integration
Catch up on any articles you missed by following one of the links above. This completes the series on integrating with SaaS applications. If you missed any of the previous articles, they're available in the linked list above.
Published at DZone with permission of Eric D. Schabell, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments