Introduce a New API Quickly Using Spring Boot and Gradle
Time to market can make or break any idea or solution. Check out how quickly a RESTful API can be created by leveraging ChatGPT, Spring Boot, Gradle, and Heroku.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeFor the last five years, I’ve had the quote “Everything begins with an idea” on the wall of my office.

My wife found this product on Etsy shortly after I started developing an API collection for a fitness application. I love this statement because it captures the passion that consumes me during the creation stages of a new project. This is still my favorite aspect of being an engineer, even three decades into my career.
What I’ve learned during this time is that an idea only matters if someone has the opportunity to experience it. If an idea takes too long to become a reality, you end up with a missed opportunity as someone else beats you to the punch. This is why startups are always racing to get their ideas to market as quickly as possible.
Let’s walk through how we can make an idea a reality... quickly.
Assumptions
For this article, we’ll keep things simple. We’ll use Java 17 and Spring Boot 3 to create a RESTful API. In this example, we’ll use Gradle for our build automation.
While the service idea we plan to take to market would normally use a persistence layer, we’ll set that aside for this example and statically define our data within a repository class.
We won’t worry about adding any security for this example, simply allowing anonymous access for this proof of concept.
The Motivational Quotes API
Let’s assume our idea is a motivational quotes API. To make sure we are racing as fast as possible, I asked ChatGPT to create an OpenAPI spec for me.

Within seconds, ChatGPT provided the response:

Here’s the OpenAPI specification in YAML that ChatGPT generated:
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: Motivational Quotes API
description: An API that provides motivational quotes.
version: 1.0.0
servers:
- url: https://api.example.com
description: Production server
paths:
/quotes:
get:
summary: Get all motivational quotes
operationId: getAllQuotes
responses:
'200':
description: A list of motivational quotes
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: array
items:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Quote'
/quotes/random:
get:
summary: Get a random motivational quote
operationId: getRandomQuote
responses:
'200':
description: A random motivational quote
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Quote'
/quotes/{id}:
get:
summary: Get a motivational quote by ID
operationId: getQuoteById
parameters:
- name: id
in: path
required: true
schema:
type: integer
responses:
'200':
description: A motivational quote
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Quote'
'404':
description: Quote not found
components:
schemas:
Quote:
type: object
required:
- id
- quote
properties:
id:
type: integer
quote:
type: stringI only needed to make one manual update — making sure the id and quote properties were required for the Quote schema. And that’s only because I forgot to mention this constraint to ChatGPT in my original prompt.
With that, we’re ready to develop the new service using an API-first approach.
Building the Spring Boot Service Using API-First
For this example, I’ll use the Spring Boot CLI to create a new project. Here’s how you can install the CLI using Homebrew:
$ brew tap spring-io/tap
$ brew install spring-bootCreate a New Spring Boot Service
We’ll call the project quotes, creating it with the following command:
$ spring init --dependencies=web quotesLet’s examine the contents of the quotes folder:
$ cd quotes && ls -la
total 72
drwxr-xr-x@ 11 jvester 352 Mar 1 10:57 .
drwxrwxrwx@ 90 jvester 2880 Mar 1 10:57 ..
-rw-r--r--@ 1 jvester 54 Mar 1 10:57 .gitattributes
-rw-r--r--@ 1 jvester 444 Mar 1 10:57 .gitignore
-rw-r--r--@ 1 jvester 960 Mar 1 10:57 HELP.md
-rw-r--r--@ 1 jvester 545 Mar 1 10:57 build.gradle
drwxr-xr-x@ 3 jvester 96 Mar 1 10:57 gradle
-rwxr-xr-x@ 1 jvester 8762 Mar 1 10:57 gradlew
-rw-r--r--@ 1 jvester 2966 Mar 1 10:57 gradlew.bat
-rw-r--r--@ 1 jvester 28 Mar 1 10:57 settings.gradle
drwxr-xr-x@ 4 jvester 128 Mar 1 10:57 srcNext, we edit the build.gradle file as shown below to adopt the API-first approach.
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.4.3'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.7'
id 'org.openapi.generator' version '7.12.0'
}
openApiGenerate {
generatorName = "spring"
inputSpec = "$rootDir/src/main/resources/static/openapi.yaml"
outputDir = "$buildDir/generated"
apiPackage = "com.example.api"
modelPackage = "com.example.model"
configOptions = [
dateLibrary: "java8",
interfaceOnly: "true",
useSpringBoot3: "true",
useBeanValidation: "true",
skipDefaultInterface: "true"
]
}
group = 'com.example'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
java {
toolchain {
languageVersion = JavaLanguageVersion.of(17)
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-validation'
implementation 'org.openapitools:jackson-databind-nullable:0.2.6'
implementation 'io.swagger.core.v3:swagger-annotations:2.2.20'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher'
}
sourceSets {
main {
java {
srcDirs += "$buildDir/generated/src/main/java"
}
}
}
compileJava.dependsOn tasks.openApiGenerate
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}Finally, we place the generated OpenAPI specification into the resources/static folder as openapi.yaml.
Generate the API and Model Objects
After opening the project in IntelliJ, I executed the following command to build the API stubs and model objects.
./gradlew clean buildNow, we can see the api and model objects created from our OpenAPI specification. Here’s the QuotesAPI.java file:
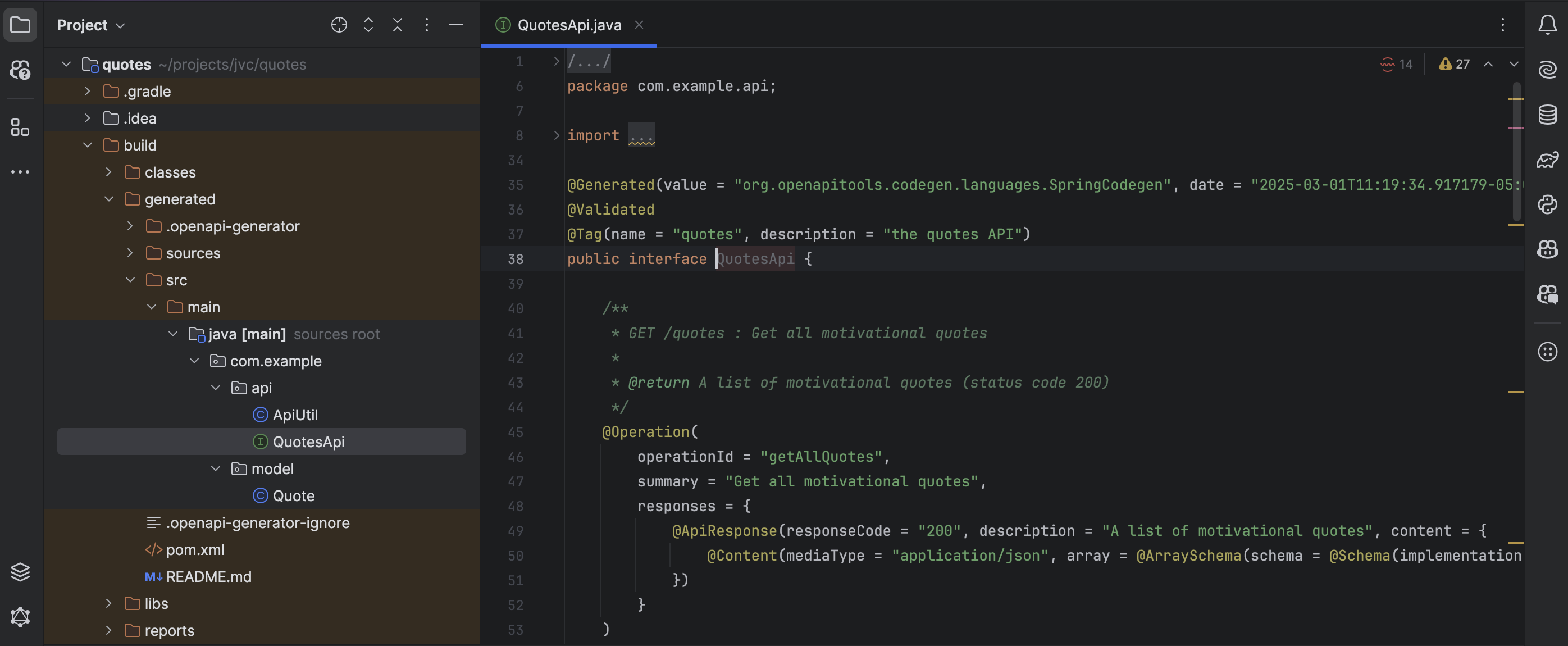
Add the Business Logic
With the base service ready and already adhering to our OpenAPI contract, we will start adding some business logic to the service.
First, we create a QuotesRepository class, which returns the data for our service. As noted above, this would normally be stored in some dedicated persistence layer. For this example, hard-coding five quotes’ worth of data works just fine, and it keeps us focused.
@Repository
public class QuotesRepository {
public static final List<Quote> QUOTES = List.of(
new Quote()
.id(1)
.quote("The greatest glory in living lies not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall."),
new Quote()
.id(2)
.quote("The way to get started is to quit talking and begin doing."),
new Quote()
.id(3)
.quote("Your time is limited, so don't waste it living someone else's life."),
new Quote()
.id(4)
.quote("If life were predictable it would cease to be life, and be without flavor."),
new Quote()
.id(5)
.quote("If you set your goals ridiculously high and it's a failure, you will fail above everyone else's success.")
);
public List<Quote> getAllQuotes() {
return QUOTES;
}
public Optional<Quote> getQuoteById(Integer id) {
return Optional.ofNullable(QUOTES.stream().filter(quote -> quote.getId().equals(id)).findFirst().orElse(null));
}
}Next, we create a QuotesService which will interact with the QuotesRepository. Taking this approach will keep the data separate from the business logic.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class QuotesService {
private final QuotesRepository quotesRepository;
public List<Quote> getAllQuotes() {
return quotesRepository.getAllQuotes();
}
public Optional<Quote> getQuoteById(Integer id) {
return quotesRepository.getQuoteById(id);
}
public Quote getRandomQuote() {
List<Quote> quotes = quotesRepository.getAllQuotes();
return quotes.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(quotes.size()));
}
}Finally, we just need to implement the QuotesApi generated from our API-first approach:
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class QuotesController implements QuotesApi {
private final QuotesService quotesService;
@Override
public ResponseEntity<List<Quote>> getAllQuotes() {
return new ResponseEntity<>(quotesService.getAllQuotes(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
@Override
public ResponseEntity<Quote> getQuoteById(Integer id) {
return quotesService.getQuoteById(id)
.map(quote -> new ResponseEntity<>(quote, HttpStatus.OK))
.orElseGet(() -> new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND));
}
@Override
public ResponseEntity<Quote> getRandomQuote() {
return new ResponseEntity<>(quotesService.getRandomQuote(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
}At this point, we have a fully functional Motivational Quotes API, complete with a small collection of responses.
Some Final Items
Spring Boot gives us the option for a web-based Swagger Docs user interface via the springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui dependency.
dependencies {
...
implementation 'org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui:2.8.5'
...
}While the framework allows engineers to use simple annotations to describe their API, we can use our existing openapi.yaml file in the resources/static folder.
We can implement this approach in the application-properties.yaml file, along with a few other minor configuration updates:
server:
port: ${PORT:8080}
spring:
application:
name: quotes
springdoc:
swagger-ui:
path: /swagger-docs
url: openapi.yamlJust for fun, let’s add a banner.txt file for use when the service starts. We place this file into the resources folder.
${AnsiColor.BLUE}
_
__ _ _ _ ___ | |_ ___ ___
/ _` | | | |/ _ \| __/ _ \/ __|
| (_| | |_| | (_) | || __/\__ \
\__, |\__,_|\___/ \__\___||___/
|_|
${AnsiColor.DEFAULT}
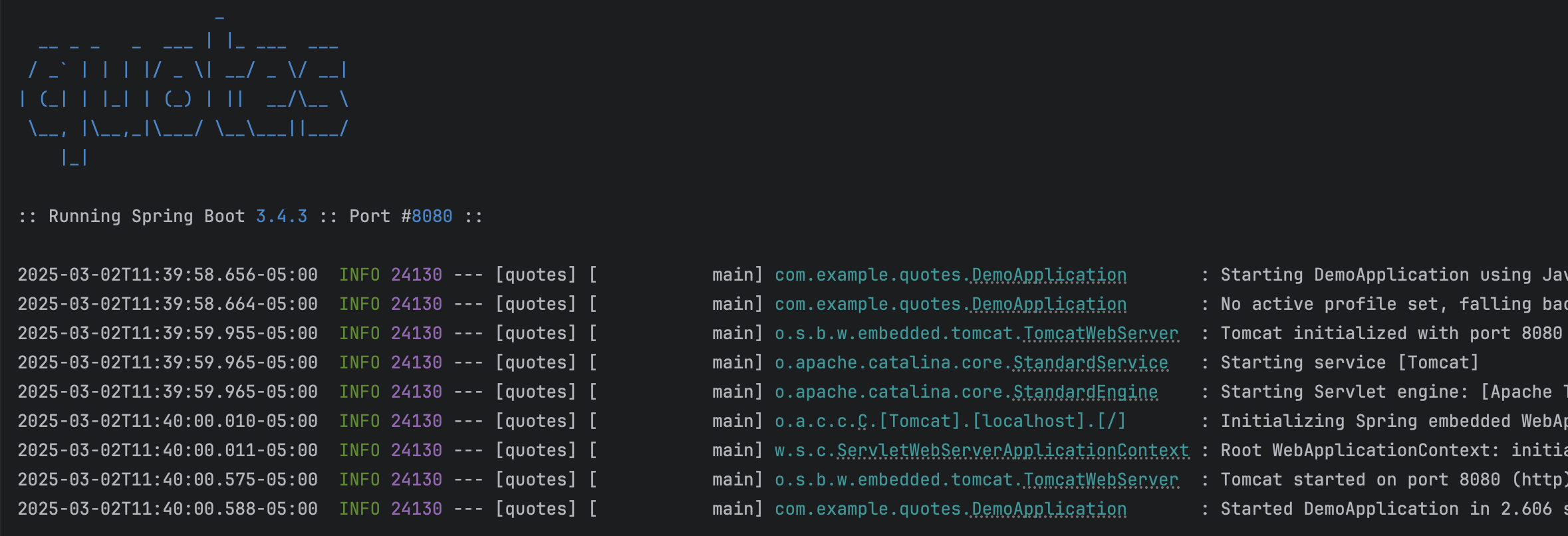
:: Running Spring Boot ${AnsiColor.BLUE}${spring-boot.version}${AnsiColor.DEFAULT} :: Port #${AnsiColor.BLUE}${server.port}${AnsiColor.DEFAULT} ::Now, when we start the service locally, we can see the banner:
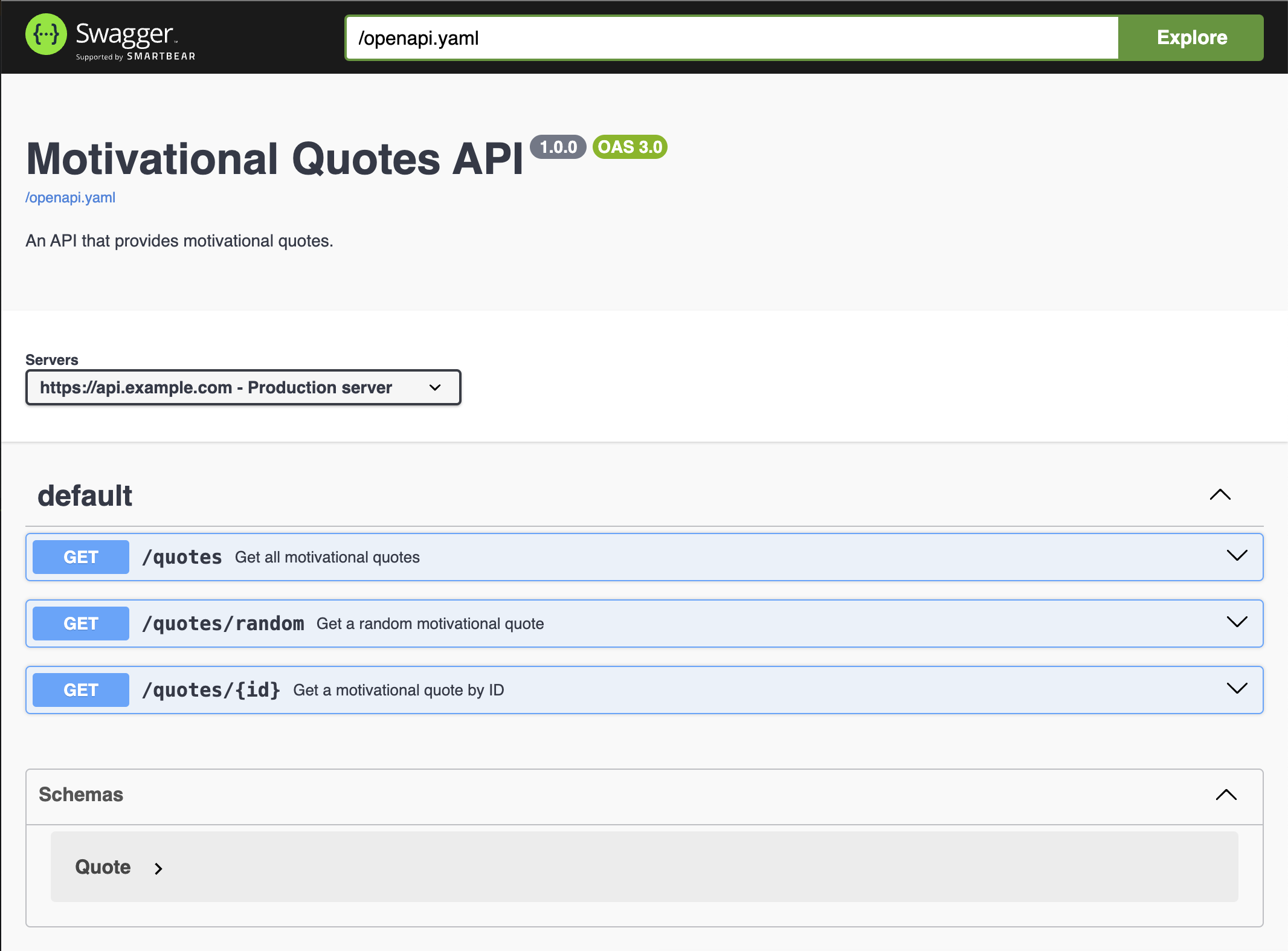
Once started, we can validate the Swagger Docs are working by visiting the /swagger-docs endpoint.
Finally, we’ll create a new Git-based repository so that we can track any future changes:
$ git init
$ git add .
$ git commit -m "Initial commit for the Motivational Quotes API"Now, let’s see how quickly we can deploy our service.
Using Heroku to Finish the Journey
So far, the primary focus for introducing my new idea has been creating an OpenAPI specification and writing some business logic for my service. Spring Boot handled everything else for me.
When it comes to running my service, I prefer to use Heroku because it’s a great fit for Spring Boot services. I can deploy my services quickly without getting bogged down with cloud infrastructure concerns. Heroku also makes it easy to pass in configuration values for my Java-based applications.
To match the Java version we’re using, we create a system.properties file in the root folder of the project. The file has one line:
java.runtime.version = 17Then, I create a Procfile in the same location for customizing the deployment behavior. This file also has one line:
web: java -jar build/libs/quotes-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarIt’s time to deploy. With the Heroku CLI, I can deploy the service using a few simple commands. First, I authenticate the CLI and then create a new Heroku app.
$ heroku login
$ heroku create
Creating app... done, vast-crag-43256
https://vast-crag-43256-bb5e35ea87de.herokuapp.com/ | https://git.heroku.com/vast-crag-43256.gitMy Heroku app instance is named vast-crag-43256 (I could have passed in a specified name), and the service will run at https://vast-crag-43256-bb5e35ea87de.herokuapp.com/.
The last thing to do is deploy the service by using a Git command to push the code to Heroku:
$ git push heroku masterOnce this command is complete, we can validate a successful deployment via the Heroku dashboard:
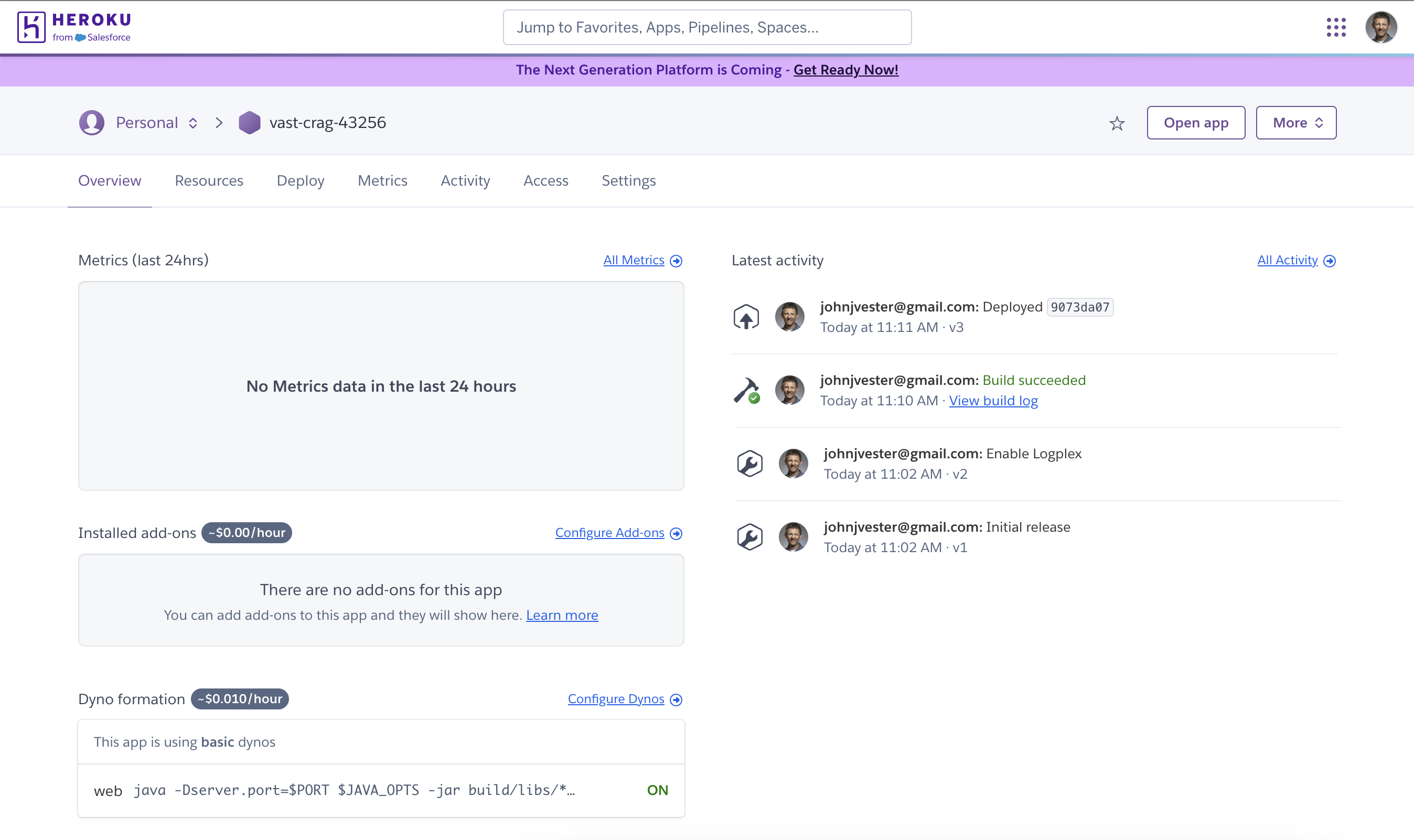
Now, we’re ready to take our new service for a test drive!
Motivational Quotes in Action
With the Motivational Quotes service running on Heroku, we can validate everything is working as expected using a series of curl commands.
First, let’s get a complete list of all five motivational quotes:
$ curl \
--location 'https://vast-crag-43256-bb5e35ea87de.herokuapp.com/quotes'
[
{
"id":1,
"quote":"The greatest glory in living lies not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall."
},
{
"id":2,
"quote":"The way to get started is to quit talking and begin doing."
},
{
"id":3,
"quote":"Your time is limited, so don't waste it living someone else's life."
},
{
"id":4,
"quote":"If life were predictable it would cease to be life, and be without flavor."
},
{
"id":5,
"quote":"If you set your goals ridiculously high and it's a failure, you will fail above everyone else's success."
}
]Let’s retrieve a single motivational quote by ID:
$ curl \
--location 'https://vast-crag-43256-bb5e35ea87de.herokuapp.com/quotes/3'{
"id":3,
"quote":"Your time is limited, so don't waste it living someone else's life."
}Let’s get a random motivational quote:
$ curl --location \
'https://vast-crag-43256-bb5e35ea87de.herokuapp.com/quotes/random'{
"id":5,
"quote":"If you set your goals ridiculously high and it's a failure, you will fail above everyone else's success."
}We can even browse the Swagger Docs, too.
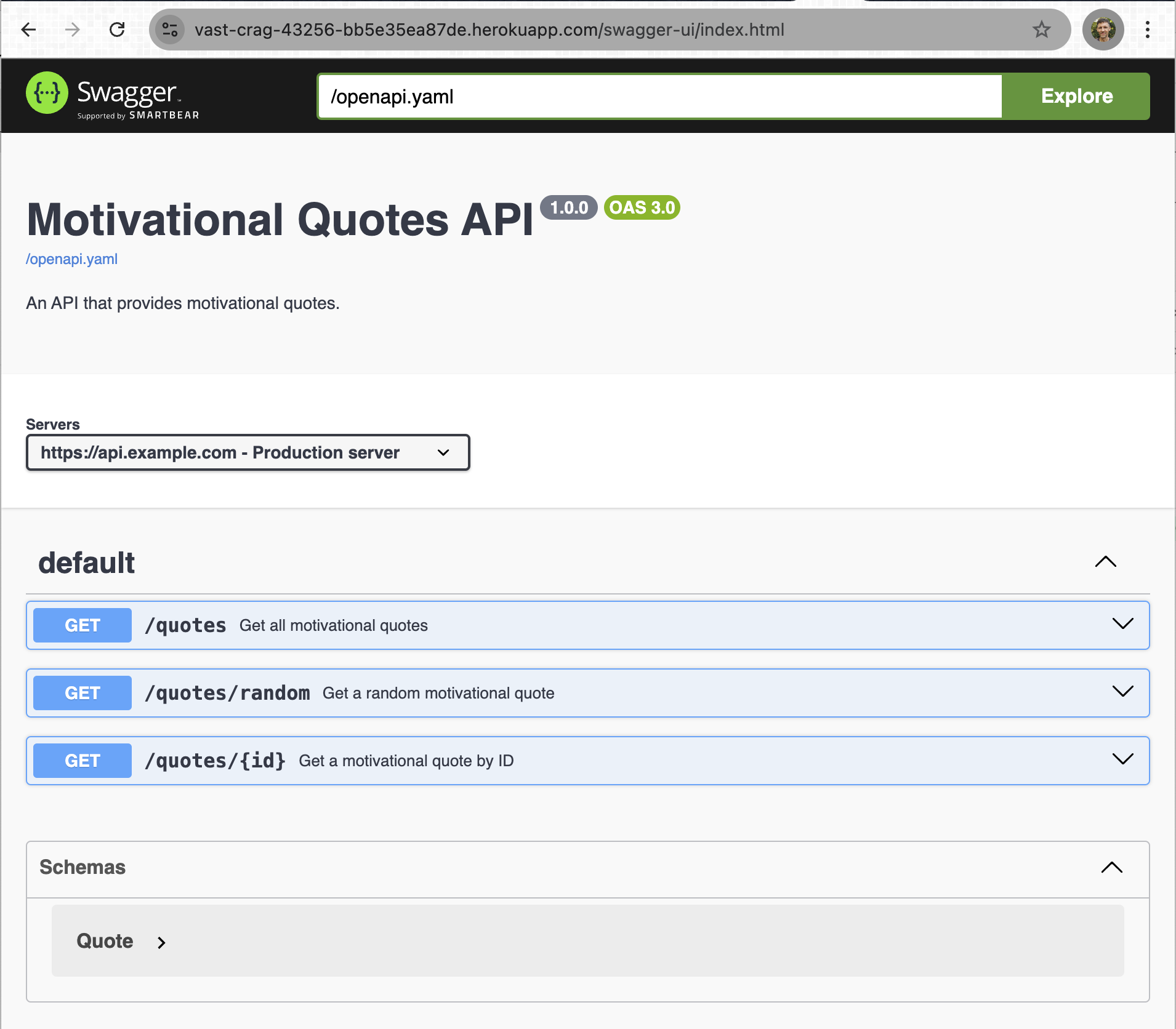
Conclusion
Time to market can make or break any idea. This is why startups are laser-focused on delivering their innovations as quickly as possible. The longer it takes to reach the finish line, the greater the risk of a competitor arriving before you.
My readers may recall my personal mission statement, which I feel can apply to any IT professional:
“Focus your time on delivering features/functionality that extends the value of your intellectual property. Leverage frameworks, products, and services for everything else.” — J. Vester
In this article, we saw how Spring Boot handled everything required to implement a RESTful API. Leveraging ChatGPT, we were even able to express in human words what we wanted our service to be, and it created an OpenAPI specification for us in a matter of seconds. This allowed us to leverage an API-First approach. Once ready, we were able to deliver our idea using Heroku by issuing a few CLI commands.
Spring Boot, ChatGPT, and Heroku provided the frameworks and services so that I could remain laser-focused on realizing my idea. As a result, I was able to adhere to my personal mission statement and, more importantly, deliver my idea quickly. All I had to do was focus on the business logic behind my idea—and that’s the way it should be!
If you’re interested, the source code for this article can be found on GitLab.
Have a really great day!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments