IoT in Healthcare: Use Cases, Trends, Advantages, and Disadvantages
Learn more about the state of IoMT, or the Internet of Medical Things.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIt is hard to overestimate the place of IoT in healthcare these days. Smart devices, wearables, and the overall level of connectivity and innovations in modern medical equipment have changed the industry forever. And definitely for the better. In this piece, you’ll find a comprehensive answer to the majority of questions you can have about the state of IoT in healthcare in 2019.
A Place of IoT in Healthcare
To say that modern medicine is striving would be a moderate expression. The progress accelerates every day ‘without any remorse’, transforming all known medical practices. Global healthcare evolves based on the latest achievements of the planet’s greatest minds and amazing prospects of autonomous, self-learning tech solutions.
Along with such rapid development, however, comes a strict necessity to keep up with the pace. The good thing is that all medical fields are either looking to or already go hand in hand with advanced technologies – from diagnostics to therapeutics, from pediatrics to complex surgery.
Technologies are numerous – artificial intelligence, machine learning – you name it. But what particular tech concept or combination of concepts can provide sufficient monitoring and managing powers such an evergrowing, global niche requires? The answer may be found in the Internet of Things or IoT. Despite the concept’s relatively young age, it’s already become closely entangled with healthcare. So much that it’s commonly coined as the Internet of Medical Things.
Extensive centralization and interconnection capacities the IoT tech provides are difficult to overestimate. It brings health monitoring, remote treatment, hospital physical and digital infrastructure organization to a whole new level. But let’s ponder on IoT powers in healthcare in a bit more detail.
IoT Applications in Healthcare
The Internet of Things allows setting up a centralized network of interconnected devices that can generate and exchange data within a single framework. All that data can also be tracked and gathered in real time, which provides a passive accumulation of analytics materials. In terms of enhancement for medical facilities, this means that a regular hospital can be turned into a smart hospital.

It is an advanced facility where everything is tracked and managed simultaneously while all the data is collected in a centralized database. Such tech features open a myriad of possibilities to improve the convenience, efficiency, and even budget-saving options of modern hospitals.
The advantages of IoT applications in healthcare don’t end there. The technology has a very diverse field of application in medicine. Let’s take a look at some major implementations.
IoT Use Cases in Healthcare
Remote Patient Monitoring
In 2018, NHS England — an ‘executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care’ announced that it’s willing to support a remote diabetes treatment solution. The statement was made on World Diabetes Day 2018. The solution is a Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM). A device that is the size of a penny which monitors blood glucose level non-stop after it’s inserted in a patient’s arm.
The monitoring data can be easily accessed via your Android or iOS device. Mass-market instances of such products are Freestyle Libre and Eversense. Such smart health monitoring devices bring huge value to the research and treatment of diabetics.

The Eversense continuous glucose monitoring sensor can be implanted in the patient’s arm and lasts up to 90 days.
And in many other cases, remote capabilities (also called telehealth) may make the need to visit your local hospital practically obsolete. An excellent resolution for patients suffering from mobility issues.
Going deeper into the remote subject, the IoT network can connect and track practically any sensor inserted into a human body for medical purposes. This will help prevent cardiac arrests (MoMe Kardia from InfoBionic), all sorts of seizures, and provide medical help for critical patients just in time.
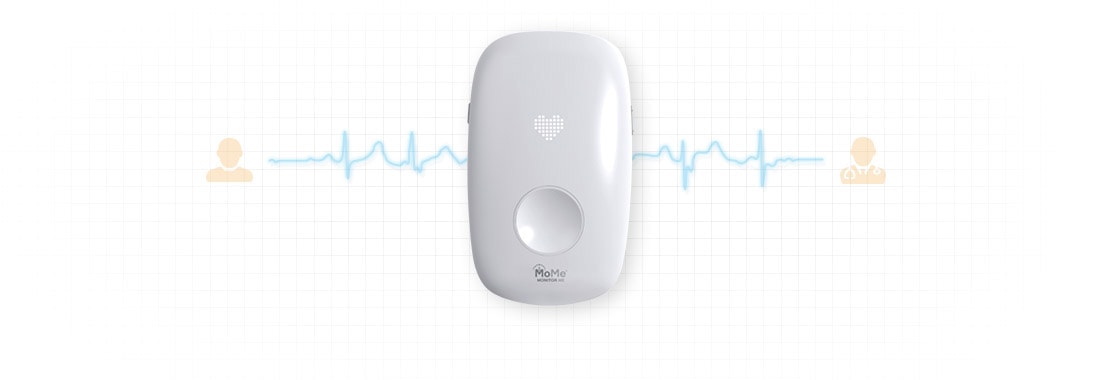
InfoBionic’s wearable cardinal tracker streams ECG and motion data to the doctor in real time.
Tracked Ingestible Sensors
The World Health Organization conducted a study in 2003 to find out that about 50 percent of prescribed medicines aren’t taken the right way or completely ignored. A prominent example of resolving this issue is the ingestible sensors solution developed by Proteus. These tiny sensors take place of a prescription and send a signal a receiving device upon dissolution in the stomach. An amazing advanced creation, Proteus’ ‘smart pills’ will surely help reduce the rates of incorrect, senseless consumption of highly important medical prescriptions. Now, this is what one can call a truly advanced drug management.

While being an advanced piece of medical technology, Porteus Smart Pills have the same tiny size as the actual pills.
There are also smart pills that feature tiny cameras, which allow conveniently visualizing the inside environment of one’s organism. PillCam from Medtronic is one example.

Mobile Health
Also called mHealth, it’s the way of watching and taking care of one’s health via mobile can be a true life-saver for modern patients, practically all of whom use smartphones regularly. Mobile health is an emerging field that contributes heavily to both critical medical situations and regular treatment instances. As we’ve already mentioned in the ‘Remote patient monitoring’ section, mobile apps can serve as the management means for health tracking devices.

In the image above, this is only a small portion of startups who are trying to gain market share with their mobile app. Source: www.cbinsights.com
Such apps can be used as your full-blown healthcare hub where you can access valuable medical info, analyze your organism behavior trends, manage other body-inserted IoT sensors, and contact your doctor with a single tap.
This is an especially valuable solution for underdeveloped countries of the world where people can’t afford regular visits to hospitals yet, most probably, have smartphones. And governments, in turn, get a capability to see how the population is doing in terms of health, accumulating massive statistics.
There are many apps already available on the market, ranging in functionality and purpose:
- Medication management apps;
- Fitness apps
- Body, activity, & sleep tracking apps
- Pregnancy monitoring apps
- Individual health recording apps
The list may go on. You can check it all out yourself on your OS-compatible mobile application market.
Smart Hospitals
The dissatisfaction with flawed, difficult-to-manage hospital infrastructures is a common issue of a vast majority of the planet’s countries (even the developed ones). Colossal loads of paperwork, long and frustrating lines, and working overload most nurses and doctors experience — this is where the problem stems.

Practically all such situations can be turned around with the integration of IoT solutions. Huge, cumbersome paper registers can be replaced with an automated, centralized database, which can be additionally enhanced in terms of reliability with blockchain and smart contracts; a single management system can receive submissions, help optimally control queues, and track staff members via their smartphones; all the equipment can also be remotely monitored and managed (e.g., shut down in unprecedented cases).
Such innovations can help greatly reduce in-house costs for hospitals, preserve forests, and make both patients’ and medical staff’s lives easier. The overall productivity will also increase due to the automated smart solutions’ capability to immediately recognize health issues which would otherwise take months of live doctor diagnostics.
Enhanced Chronic Disease Treatment
With IoT-powered wearables, sensors, data analytics, and mobile opportunities, battling chronic diseases become more efficient and accessible. The thing is, recurring health issues must be monitored and analyzed over long periods of time. That way, trends in the disease fluctuations can be defined and juxtaposed in order to be most efficiently treated.
All that tech allows doing just that, with many additional capabilities provided by the integration of blockchain and AI on top of that. This is very important when it comes to health issues as difficult to understand and underexplored as the chronic ones.
Challenges of IoT in Healthcare
As much as the Internet of Medical Things seems to be revolutionary and highly-efficient, there are still some major challenges of IoT in healthcare this tech concept must overcome down the road. With large, game-changing integrations such as this one, there comes along a myriad of technical difficulties and adaptation issues. The main include:
- Underdeveloped initiatives. Many IoMT initiatives directed at battling chronic diseases or other issues still need time to grow and develop. This technological niche as a whole must grow a lot in order to start providing regular enhancement results.
- Possible lack of available memory. IoT sensors and devices can general colossal amounts of data, all of which is important and needs to be analyzed. This poses a question of huge data repositories that must hold all those volumes of info for indefinite terms.
- Difficulties with regular updates. With so many hardware solutions comes as much software for powering and managing it all. This software must be timely updated in order to run smoothly and stay at its latest version. And here’s where constant updates will require lots of effort and might spawn many technical issues.
- Personal sensitive data security. An IoT-powered medicine is a hardware-backed system that functions through the Internet. And online systems get hacked and breached. This spawns a chance of important private data being potentially undermined.
- Global healthcare regulations. The IoMT still has to be approved by global healthcare regulatory bodies worldwide. This will take time and may keep many innovations at bay just because of some formalities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IoT in Healthcare
Considering the above-mentioned challenges of IoT in healthcare, there are, indeed, downsides as well as benefits when it comes to the medical IoT.
Advantages of IoT in Healthcare
The ‘all-consuming’ connection of health devices and data centralization brings many significant benefits to the table, such as:
- All-around technological enhancement. Rendering hospital visits unnecessary, passively accumulating and deeply analyzing important health data, etc. We’ve already pondered on all these advanced tech capacities galore enough. The IoMT provides space for fantastic long-term innovations.
- Cost savings. One of the greatest advantages of IoT in healthcare is that efficient autonomous systems will cost less to manage and ‘employ’ in the long run. Things are even better when it comes to patient cost savings due to fewer hospital journeys as well as accelerated diagnostics and treatment.
- Accessibility. Doctors can view all the necessary data on command and check real-time patient conditions without leaving their office.
Disadvantages of IoT in Healthcare
Alternatively, some downsides that come along with the massive implementation of the IoT in healthcare include:
- Privacy can be potentially undermined. As we’ve already mentioned, systems get hacked. Lots of attention will need to be focused on data security, which requires significant additional spendings.
- Unauthorized access to centralization. There is a chance that dishonest interlopers may access centralized systems and realize some cruel intentions.
- Global healthcare regulations. International health administrations are already issuing guidelines that must be strictly followed by governmental medical establishments integrating the IoT in their workflow. These may restrict possible capacities to some extent.
IoT Trends in Healthcare of 2019
In 2019, there can be defined several IoMT trends implemented by majorities of startups worldwide.
- Wearables continue to top the market. Major mobile technology providers like Apple and Android are enhancing and updating their authentic wearables, adding them with more health tracking features. And the rest of the world isn’t shy to follow the tendency, spawning numerous various-purpose mini devices.
- Surgical robotics become a common reality. AI-powered, robotic surgical means show to be more precise than real doctors on more than one occasion. There are still limitations and risks involved, but the technology is definitely in the spotlight and is looking to become more widespread in the nearest future.
- Integration of other prominent technologies with the IoT expands the horizon. AI, AR, Machine Learning, Big Data, blockchain, and smart contracts – all of that fuel up and expands the IoT powers even further. AI is already better and far more precise in predicting, for one instance, women’s breast cancer.
Future of IoT in Healthcare
Full-blown smart hospitals by 2020, mHealth as a regular, common thing on a global scale, and reduced physical visits to hospitals – this is only an approximate picture of the IoMT success. With that being said, as young as the concept is, it isn’t really regarded to be that novel by progressive hospitals of the now. Most of them are either implementing major IoT techniques and capabilities or already have enhanced parts that are in their calibration stage.
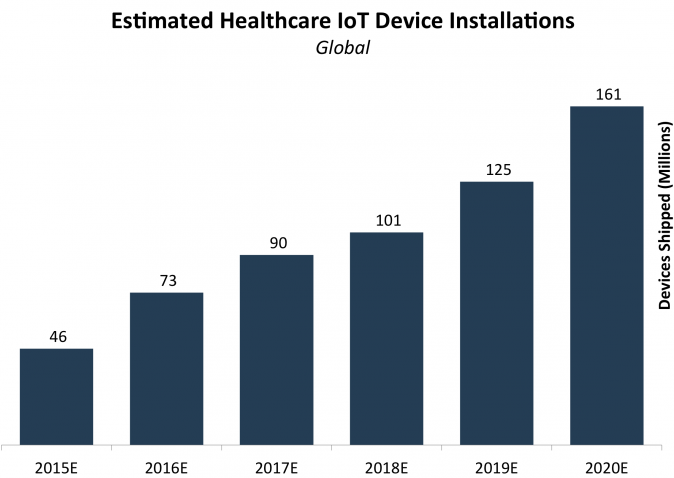
It is estimated that the install base of IoT devices in healthcare will be more than 161 million units by the end of 2020. Source: Business Insider
According to some independent predictions, almost 90 percent of healthcare establishments and organization worldwide will be employing the IoT as a regular in-house tool by the end of 2019. So, the ‘now’ of the healthcare IoT is pretty vivid, with its future looking even brighter.
Summary
Let us emphasize once more that the IoT can be nothing short of a revolution in the field as important on the global scale as healthcare. there are still many difficulties, peculiarities, and technological obstacles to overcome. And even though there are, currently, downsides as well as advantages to the concept, things seem to go very well for this technological innovation.
We are pretty confident that if you ask most medical professionals about their opinion on the subject, they will say that full IoMT integration and adaptation is the only logical way of development for advanced medicine of the future.
With that being said, enjoy the life-saving, health-improving fruits of the massive technological progress.
Published at DZone with permission of Victor Osetskyi, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments