Istio Circuit Breaker With Outlier Detection
The basic intent of outlier detection is to stop sending requests to an unhealthy instance and give it time to recover.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhile architecting distributed cloud applications, you should assume that failures will happen and design your applications for resiliency. A microservices ecosystem is going to fail at some point or the other and hence you need to learn to embrace failures. In short, design your microservices with failure in mind.
Problem Statement
In a K8s environment, services run inside a pod and dynamically autoscale based on load. To make your services highly available, you might be running multiple instances of your service. But how do you handle scenarios where one of your service instances becomes slow or unresponsive? In such a scenario, you should not send traffic to that instance. But how do you automatically identify this issue at runtime and change your routing rules to exclude this service instance?
Outlier Detection
Outlier Detection is an Istio Resiliency strategy to detect unusual host behavior and evict the unhealthy hosts from the set of load balanced healthy hosts inside a cluster. It automatically tracks the status of each individual host and checks metrics like consecutive errors and latency associated with service calls. If it finds outliers, it will automatically evict them.
Ejection/eviction implies that the host is identified as unhealthy and won't be used to cater to user requests as part of the load balancing process. If a request is sent to a service instance and it fails (returns a 50X error code), then Istio ejects the instance from the load balanced pool for a specified duration. This is configured as the sleep window.
This entire process increases the overall availability of the services by making sure that only healthy pods participate in catering user requests.

Read more about Envoy Outlier Detection here:
https://www.envoyproxy.io/docs/envoy/latest/intro/arch_overview/outlier
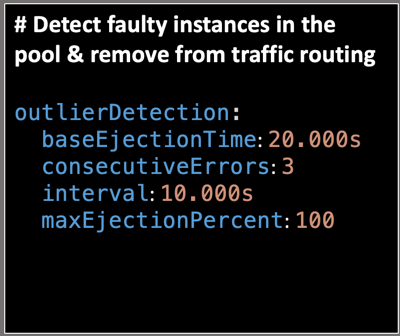
With the below settings, the dependent service is scanned every 10 seconds and if there are any hosts that fail more than 3 times with a 5XX error code it will be ejected from the load balanced pool for 20 seconds.
Read more about Outlier Detection here.
- BaseEjectionTime - The maximum ejection duration for a host. For example, the host will be ejected for 20 seconds before it is evaluated again for processing requests.
- ConsecutiveErrors - Number of errors before a host is ejected from the connection pool. For example, if you have three consecutive errors while interacting with a service, Istio will mark the pod as unhealthy.
- Interval - The time interval for ejection analysis. For example, the service dependencies are verified every 10 seconds.
- MaxEjectionPercent - The max percent of hosts that can be ejected from the load balanced pool. For example, setting this field to 100 implies that any unhealthy pods throwing consecutive errors can be ejected and the request will be rerouted to the healthy pods.
Outlier detection will be enabled until the load balancing pool has the minimum number of healthy hosts associated.
While creating a DestinationRule, you can mention the Circuit Breaker fields inside the TrafficPolicy section. Sample DestinationRule below:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: serviceB
spec:
host: serviceB
subsets:
- labels:
version: v1
name: serviceB-v1
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http: {}
tcp: {}
loadBalancer:
simple: RANDOM
outlierDetection:
baseEjectionTime: 20s
consecutiveErrors: 3
interval: 10s
maxEjectionPercent: 100
- labels:
version: v2
name: serviceB-v2
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http: {}
tcp: {}
loadBalancer:
simple: RANDOM
outlierDetection:
baseEjectionTime: 20s
consecutiveErrors: 3
interval: 10s
maxEjectionPercent: 100The below video demonstration from RedHat shows the Istio Outlier Detection functionality in action:
Red Hat Developer Istio Video Series: Number 2 - Istio Pool Ejection
With outlier detection, the application is now self-healing, so if you encounter errors from one service instance you can automatically eject the instance out of the pool so that it doesn't receive any requests. There is no service downtime with this approach and errors are not thrown to consumers.
Conclusion
Istio improves the reliability and availability of services in the mesh. The basic intent of outlier detection is to stop sending requests to the unhealthy instance and give it time to recover. In the meantime, the requests are redirected to the healthy instances such that the consumers are not impacted. The entire implementation of outlier detection is transparent to the application and involves no changes to the application code.
Published at DZone with permission of Samir Behara, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments