JWT: Using the Header and JWS Parameters
Explore the basic components of JWT — headers and JWS parameters.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis post aims to provide a quick overview of the JWT claims and meta information because they are often presented in short, three-letter instances to keep them compact.
Oversimplified JWT Definition
JWT has three basic components: [MetaInformation].[Claims].[Signature]
Sample JWT in the Image Below
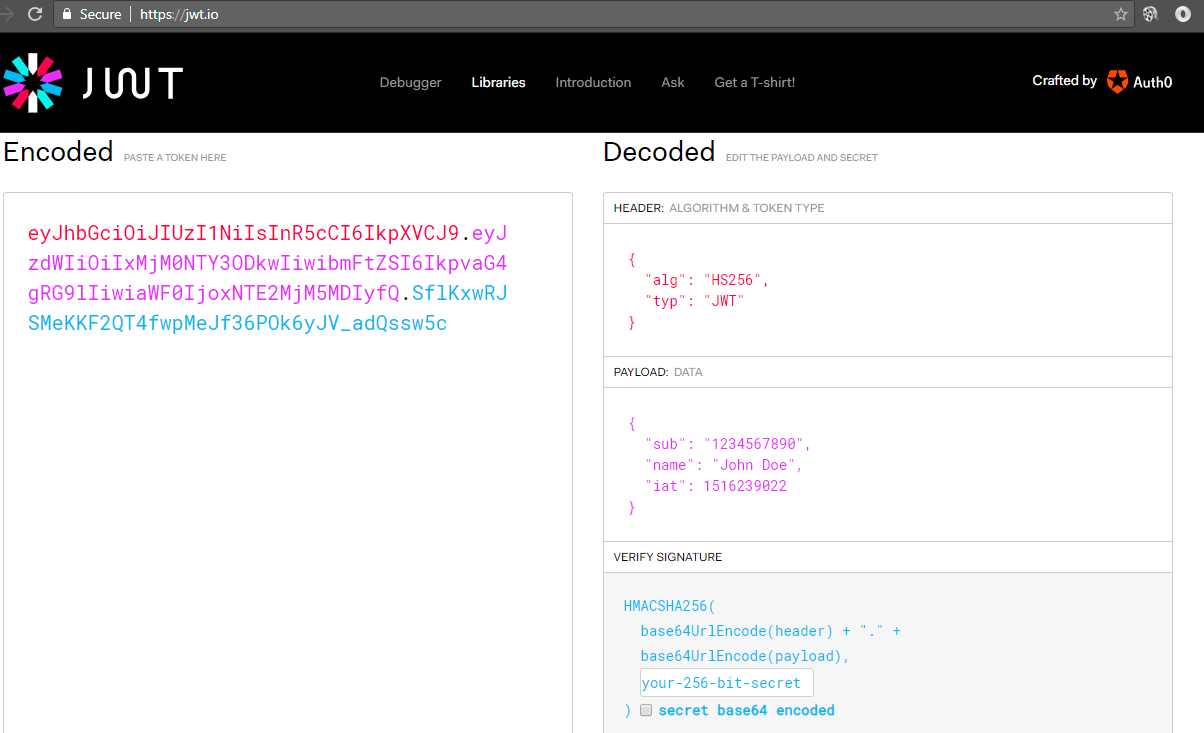
1. Base64 – The metadata (also known as the header or manifest) includes how the token is structured, signed, and so on.
2. Base64 – Claims provide the actual meaning of the token.
3. Base64 – Signature provides authenticity and integrity.
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519#section-10.1.2 describes the registered claims for JWT. An identity provider has the flexibility to add claims that are specific for the intended situations.
Exploring the JWT Header
Let’s look at the following JWT sample (base64 decoded) that has the below header information. We will explore the data section subsequently. RFC reference – https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7515#section-4.1 (JSON Web Signature)
RFC reference – https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7515#section-4.1 (JSON Web Signature)
typ
In the above example, typ indicates the token type of JWT.
alg
alg indicates the type of algorithm used to sign the JWT token. The most commonly used values are RS256 and HS256, which stands for RSA-SHA256 (asymmetric) and HMAC-SHA256 (symmetric), respectively. RS256 alg belongs to the RSA kty (read the kty section below)
x5t
x5t is the X509 certificate’s thumbprint. That is the certificate whose private key was used to sign the JWT.
kid
The kid id the key id indicating which key was used to sign the JWT token. This field is particularly useful when the public key discovery endpoint supports many keys and we need to know which key was used to sign.
In order to verify the signature of the JWT token, the verifier needs to know the public key of the public /private key pair used to sign the JTW token. Most identity providers expose this information via discovery mechanisms, such as the one below from Microsoft Azure.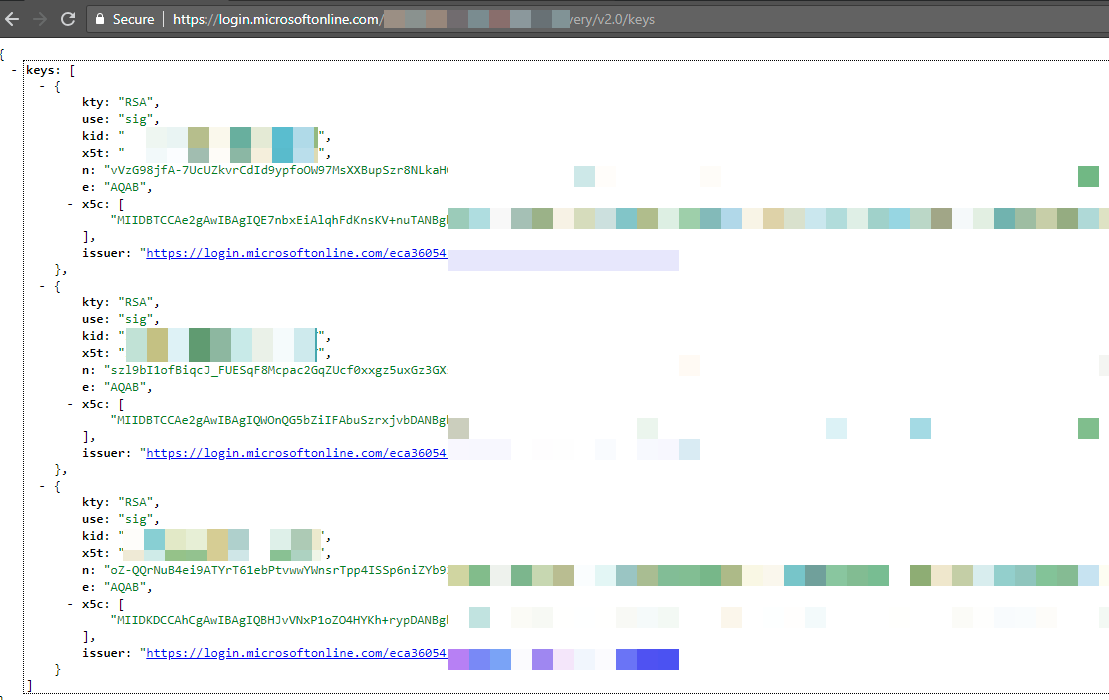 Based on the above example:
Based on the above example:
kty
If the key type is part of the algorithm family used to sign the JW, RSA and ECare some allowed via kty. RS256 and RS512 are some algorithms (alg) that belong to the RSA algorithm family (kty)
Use
Use the above information — whether the algorithm is used for enc encryption or sig signing.
X5t and kid are explained above
n is a public key component of the RSA.
e is a public key component of the RSA.
x5c is the x509 certificate chain.
Note: If the algorithm
ktyis EC (elliptic Curve), then the public components are x and y.
The next blog post will reference information from a sample JWT token in Azure AD. Stay tuned!
Credits and References
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/v1-id-and-access-tokens
- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519
- https://redthunder.blog/2017/06/08/jwts-jwks-kids-x5ts-oh-my/
- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7518
- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7515
Published at DZone with permission of Marudhamaran Gunasekaran. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments