Kubernetes Auditing: Which IAM User Deleted a Namespace?
Learn how to collect audit logs that are passed through the Kubernetes API server to IBM Log Analysis to check who initiated a request and when they did so.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAs a cluster administrator, by following the simple steps in this blog post, you should be able to answer questions about Kubernetes audit logs, like who initiated a request to delete a Kubernetes resource? When did it happen? On what did it happen?
What Are Audit Logs?
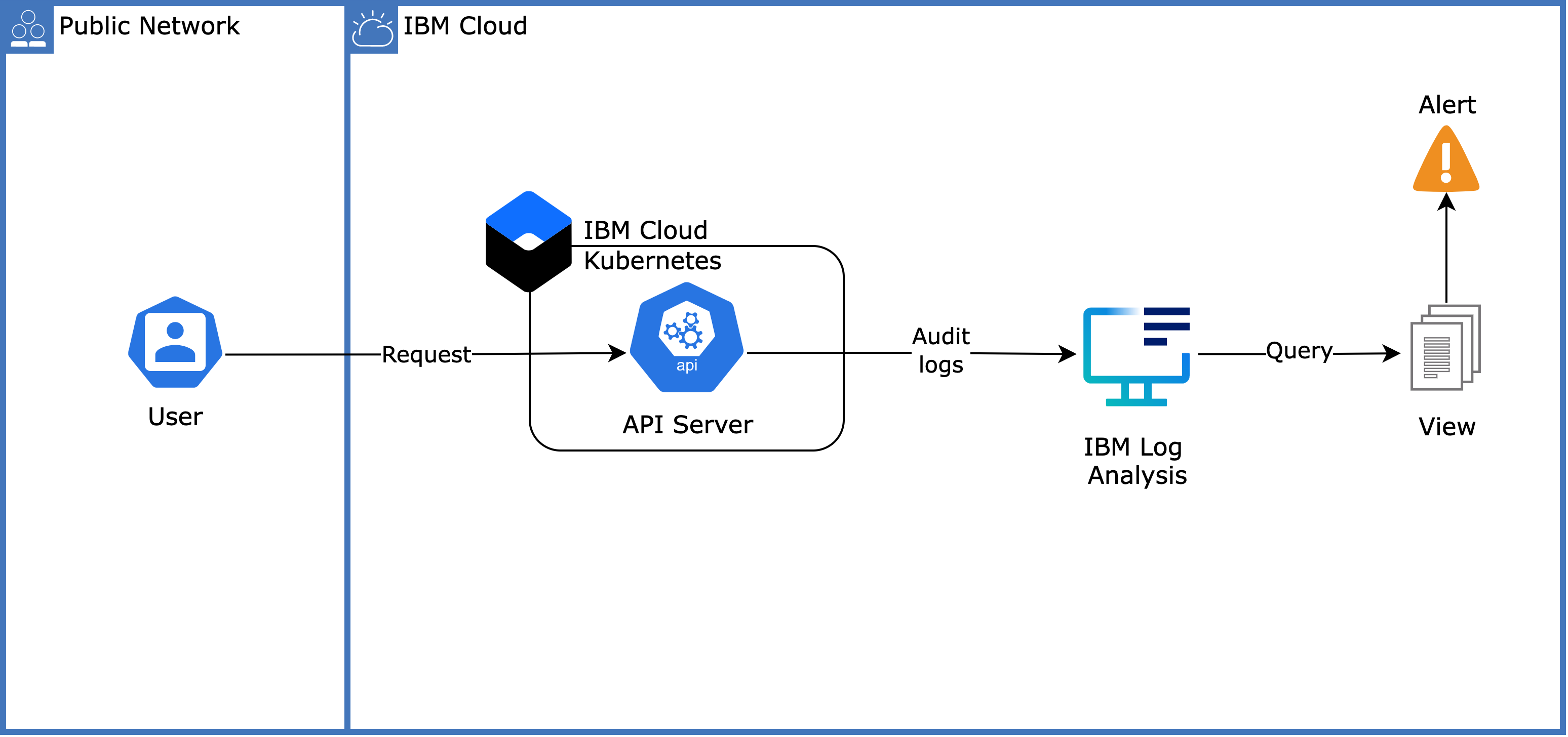
Audit logs allow you to better understand the operations that are initiated by users in your cluster, which can help you troubleshoot issues or report compliance to industry and internal standards.
Although the Kubernetes API server for your cluster is enabled for auditing by default, no auditing data is available until you set up log forwarding. You can forward audit logs for the IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service, the Kubernetes API server, and the worker nodes to a logging instance on IBM Cloud.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you completed the steps to forward the Kubernetes API audit logs to Log Analysis.
- To quickly set up a Kubernetes cluster on VPC, you can use the Terraform scripts provided in the "Multizone Kubernetes and VPC Load Balancer Setup" post.
Query and Decode the Logs
You can always enable and launch logging from your Kubernetes cluster's overview page. By now, you should see the audit logs on the IBM Log Analysis view:
- To test, set the context for your cluster without the
--adminflag:ibmcloud ks cluster config --cluster <CLUSTER ID or NAME>Note: Using the--adminflag will show the cluster-admin context and may not reveal the IAM user overriding the RBAC. - Create a namespace with the following command:
kubectl create namespace test123 - In the Log Analysis UI, enter the following query:
verb:create objectRef.name:test123 objectRef.resource:namespacesSo, by now you know which IAM user (who) created the namespace (what) and when was it created. Note: The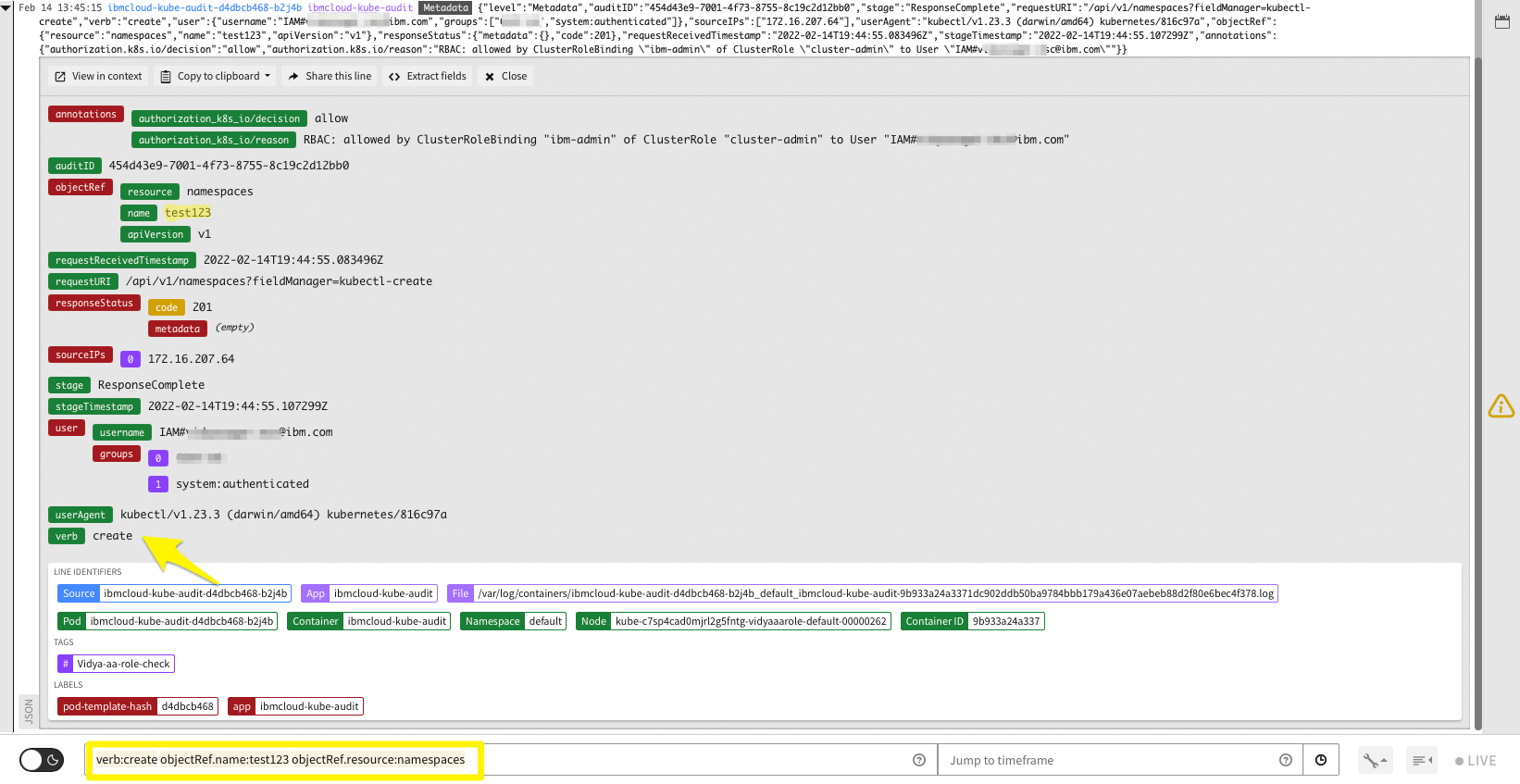
objectRef.resourcesis optional and can be any Kubernetes resource (e.g., secrets, configmaps, services, etc.). - Similarly, you can delete the namespace with the command
kubectl delete namespace test123. Then, from the audit logs, you can quickly find out who (IAM user) deleted the namespace and at what time. The query to decode who deleted the namespace will be as follows:verb:deleteobjectRef.name:test123 objectRef.resource:namespaces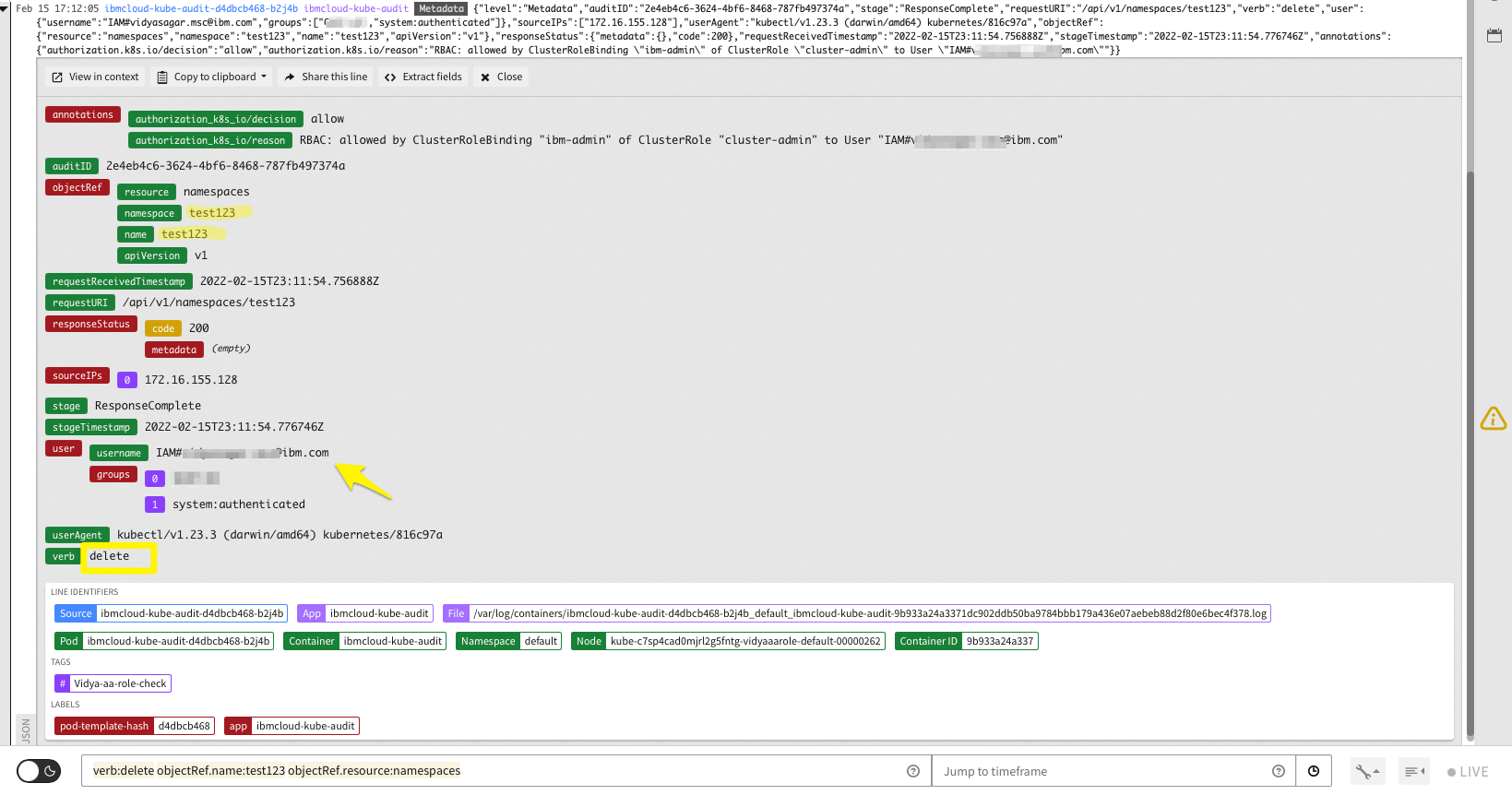
- To create a custom view out of the query:
- Click "unsaved view" > Save as new view
- Enter a name for your view
- Optionally, you can select a category and alert value
- Click "save view." Your view is listed under your selected category. If you didn't select a category, it will be listed under UNCATEGORIZED.
- To add an alert to your custom view, check the add alert to custom view section of IBM Cloud Kubernetes documentation.
Conclusion
Following the steps in the post, you learned what audit logs are, what the audit logs capture, and how to forward and collect the audit logs in IBM Log Analysis to query and decode the logs to understand the operations that are initiated by users in your cluster.
You can always control user access with IBM Cloud IAM and Kubernetes RBAC. To understand more about Kubernetes auditing and the audit policy, refer to the Kubernetes documentation.
If you have any queries, feel free to reach out to me on Twitter or on LinkedIn.
Published at DZone with permission of Vidyasagar (Sarath Chandra) Machupalli FBCS, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments