Low-Code Development: Why It Is Important and Why It Can't Replace Traditional Approach
In today's dynamic and fast-paced business ecosystem, a traditional development approach is often time-consuming and requires a lot of investment.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOn the flip side of the coin, many digital trends have boomed recently as of COVID-19, including the simplified interfaces that can help users quickly build and launch custom apps with minimal hand-coding. These factors, along with the fact that every company strives to streamline and automate its processes, allowed low code and no-code platforms to flourish.
The popularity of low-code application development has gained decent traction these days — according to Gartner, low-code is forecast to comprise over 65% of application development by 2024.
Nevertheless, low code solutions aren't as great as you might think. In this short guide, we want to highlight this methodology's key features and pitfalls.
What Is Low-Code Development?
As the name implies, low-code is a software development methodology where you can create apps with little coding. That said, low code automation tools are visual-driven Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) designed for rapid application development. This inclusive approach was created in response to ever-augmenting business requirements and the shortage of skilled experts.
Unlike traditional development that requires highly-skilled experts to handle all the code, low-code methodologies allow users to create apps with less manual coding through a graphical user interface (GUI) and its built-in drag-and-drop tooling. Thanks to the drag&drop technology, you can seamlessly add and move various elements, such as buttons, images, icons, text, maps, video, etc.
At the same time, low-code is different from no-code — while low-code still requires knowledge of technologies and frameworks, no-code enables users to build apps with almost no hand-coding. But let's keep the no-code approach for later.
Usually (even based on modern agile techniques), it takes a while before you can end up with a fully-functioning product. On the other hand, low-code allows users to skip a few development cycles and get right to an MVP that can be tested with real users. Low-code platforms help businesses acquire early adopters, validate an idea, and ensure faster development and delivery.
How Is Using Low-Code Different From Traditional Development?
In stark contrast to low-code solutions, traditional development is 100% coding, from start to finish; it is also called custom software development. It wouldn't be fair to say that people are torn between these two options, but there are enough enthusiasts on both sides.
Below are the main practical differences between low-code and traditional development.
Low-Code vs. Traditional Development
| LOW-CODE | TRADITIONAL | |
|---|---|---|
| Tools | Drag-and-drop development environments | Manual coding |
| Coding knowledge and skill | Minimum knowledge and experience | Advanced |
| Speed | In a matter of weeks | In a matter of months |
| Level of customization | Limited (depends on the platform) | Unlimited |
| Scope | Built for specific business needs (one at a time) | Full-scale development |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Cost | Relatively low, you only need to pay for access and minimal labor | Higher, since the app is created from scratch |
| App performance | Standard | High (assuming you're working with a competent development team) |
How Does Low-Code Simplify the Development Process?
Beyond the basics, no two low-code tools are the same. So, let's take a specific example: how does low-code simplify the development lifecycle for a website? A popular low-code website builder is Zoho. Unlike traditional web development, there is no need for developers to write the code from scratch. Instead, users can choose from 190+ pre-designed layout templates, which Zoho calls "sections." While the platform doesn't require the knowledge of HTML or CSS, those who are skilled in either of them can use a code editor and customize existing themes by adding custom codes. So, low-code platforms provide building blocks that specialists can assemble into finished workflows and applications. They are in no direct competition with developers.
Leading platforms
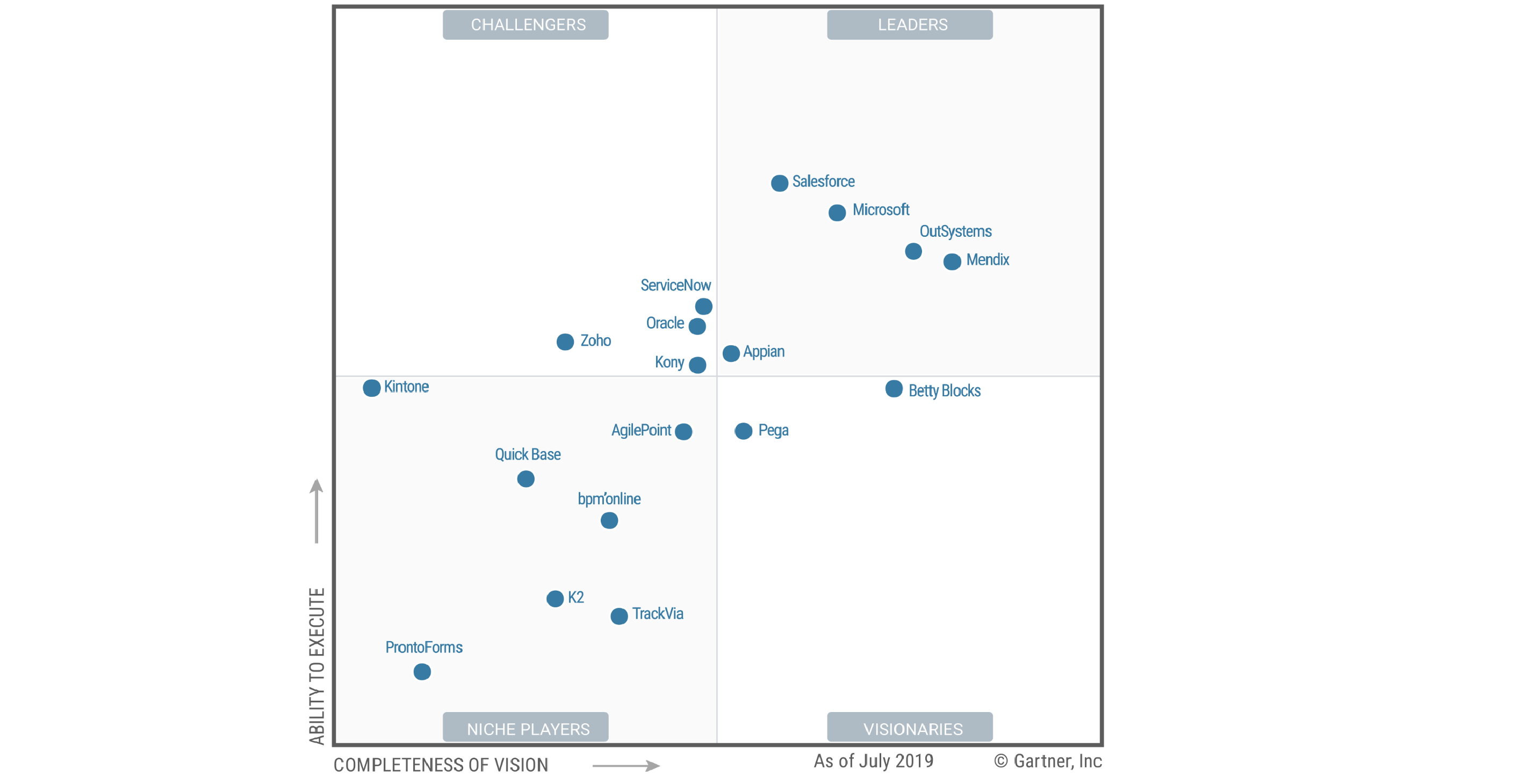
Several leading low-code application platforms (LCAP) are on the market, like Mendix low code software, OutSystems, and Appian.
The best low code development platforms should provide comprehensive tooling to support testing, building, and deploying applications. For instance, Mendix includes everything from conception and development to deployment and operation services. According to them, it allows users to create ten times faster with 70% fewer resources.
Why Is Low-Code Popular?
"The future of coding is no coding at all." - Chris Wanstrath CEO of GitHub
Citizen developers and non-tech-savvy users can utilize low-code/no-code platforms to build custom-designed products while avoiding some hand-coding tasks. On top of that, seasoned experts and software providers can also use low-code solutions as supplementary tools in addition to their traditional toolset.
Low code can enhance the entire workflow and propel your IT teams' productivity by equipping them with powerful tools for quick and smooth app creation. Now, let's look at this development technique's major benefits.
Improved Speed
You can create solutions for several platforms in one go and demonstrate to investors or stakeholders a fully-functioning MVP within the shortest time possible.
Resources Saving
If you are about to start a new big project, you don't have to wait for your experts to finish their projects. With low code, you can save your time and the company's resources by getting things done more quickly and at a lower cost compared to a traditional approach.
Low risk and High ROI
Low-code platforms are backed by the best industry standards and security practices: cross-platform support, data integration, and up-to-date security algorithms are built-in features. Hence, you can focus on more important business tasks while ensuring your entire workflow is highly protected and customized.
Easy Deployment
Most often than not, the launch day is all about unexpected problems and new emergency bugs. With low code, you can roll all changes back to a stable version with just a single click and fix the issues early on.
Lifecycle Support and Seamless Integration
Low code platforms support the entire application development lifecycle from idea to exit, including DevOps and CI/CD. Besides, the low code platform APIs allow for external integration with tools to support project management, DevOps, testing, and CICD pipelines.
What Are the Cons of Low-Code?
"Low-code isn't the future of code. It certainly has a place in the future and will be leveraged to make many applications. It will not replace other ways of creating software because low-code breaks down when the solution's complexity increases. We saw the same thing with Visual Basic in the '90s. VB was valuable, and a lot of software was written in VB. In the end, it was complexity required by some applications that caused VB to break down and no longer be a good solution. Low code will be the same." - Thomas Stiehm CTO of Coveros
At first glance, low code software is a perfect solution for app development, but there are multiple drawbacks as well.
Business Logic Complication
Low code tools like Mendix are an excellent option for the automation of simple processes or prototyping. However, once the prototyping stage is passed, the business logic becomes more complex eventually. To develop a project any further, you'll need an expert team. Today's low code platforms are not perfect yet, so it's not good to rely on them in the long run. Otherwise, you risk jeopardizing your business.
Limited Functionality
In a low code development tool, the number of functions that you can implement is limited. It is a quick way to build applications, but you do not have many options if you want to try out something different.
For sure, drag & drop functionality features can be useful under certain circumstances. But when you need a unique feature that's not available, you will need some custom code. Sometimes integrating this custom code can also cost a lot more than a completely customized solution built from scratch.
No Technical Background Myth
You still need a robust technical background to use low-code tools despite the name. Furthermore, you first need to examine basic low-code development requirements and technologies, which by themselves take time to learn and adapt to.
Security Limitations
Low-code solutions indeed have in-build security protocols, but they still can't provide the same security level as standalone development technologies. With an application based on low-code, you have neither full control over data security nor access to source code. Hence, you can't define all the possible vulnerabilities out there.
Summary
Now that we know the major pros and cons of low-code methodology, we can understand that it is not meant to replace traditional development or professional software providers.

Instead, companies need to utilize low-code practices to strengthen a traditional approach and fill gaps. When combined, low-code and traditional techniques can ensure faster and more productive application development.
Low-code solutions are not for everyone. And especially at their current level of customization and complexity, they are not a substitute for a developer. Furthermore, there is no indication that low-code platforms will be able to understand advanced and detailed applications as well as real developers. Ultimately, low code development tools work best as tools for reducing software developers' workloads.
With this in mind, low code significantly enhances speed-to-market and improves the overall business efficiency when used in tandem with traditional methods. However, no silver bullet can turbo-boost your business, so it's vital to consider multiple options and get professional advice.
Published at DZone with permission of Anastasiia Komendantova. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments