MapReduce Design Patterns
This article covers some MapReduce design patterns and uses real-world scenarios to help you determine when to use each one.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article discusses four primary MapReduce design patterns:
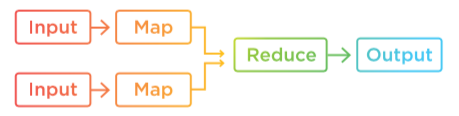
1. Input-Map-Reduce-Output
2. Input-Map-Output
3. Input-Multiple Maps-Reduce-Output 4. Input-Map-Combiner-Reduce-Output
Following are some real-world scenarios, to help you understand when to use which design pattern.
Input-Map-Reduce-Output

If we want to perform an aggregation operation, this pattern is used:

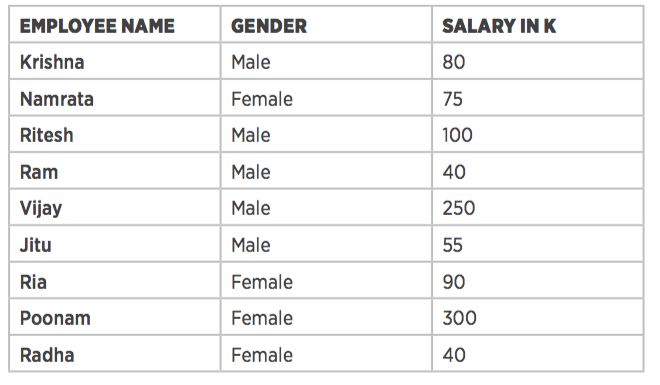
To count the total salary by gender, we need to make the key Gender and the value Salary. The output for the Map function is:
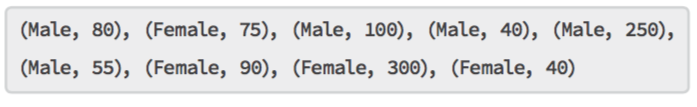
Intermediate splitting gives the input for the Reduce function:
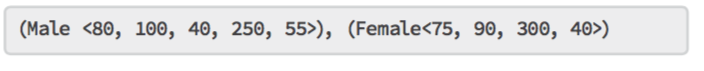
And the Reduce function output is:

Input-Map-Output

The Reduce function is mostly used for aggregation and calculation. However, if we only want to change the format of the data, then the Input-Map-Output pattern is used:

In the Input-Multiple Maps-Reduce-Output design pattern, our input is taken from two files, each of which has a different schema. (Note that if two or more files have the same schema, then there is no need for two mappers. We can simply write the same logic in one mapper class and provide multiple input files.)

This pattern is also used in Reduce-Side Join:
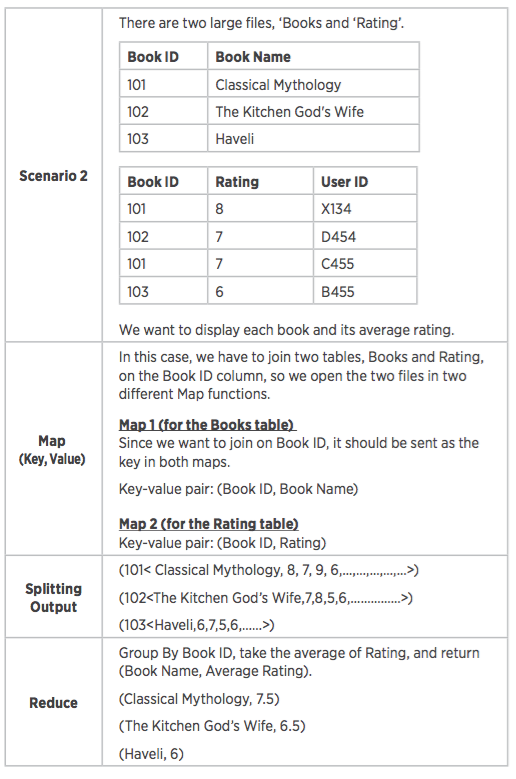
Input-Map-Combiner-Reduce-Output

Apache Spark is highly effective for big and small data processing tasks not because it best reinvents the wheel, but because it best amplifies the existing tools needed to perform effective analysis. Coupled with its highly scalable nature on commodity grade hardware, and incredible performance capabilities compared to other well known Big Data processing engines, Spark may finally let software finish eating the world.
A Combiner, also known as a semi-reducer, is an optional class that operates by accepting the inputs from the Map class and then passing the output key-value pairs to the Reducer class. The purpose of the Combiner function is to reduce the workload of Reducer.
In a MapReduce program, 20% of the work is done in the Map stage, which is also known as the data preparation stage. This stage does work in parallel.
80% of the work is done in the Reduce stage, which is known as the calculation stage. This work is not done in parallel, so it is slower than the Map phase. To reduce computation time, some work of the Reduce phase can be done in a Combiner phase.
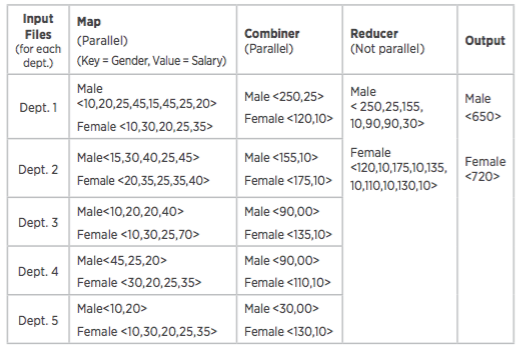
Scenario
There are ve departments, and we have to calculate the total salary by department, then by gender. However, there are additional rules for calculating those totals. After calculating the total for each department by gender:
If the total department salary is greater than 200K, add 25K to the total.
If the total department salary is greater than 100K, add 10K to the total.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments