Microservices With Spring Boot - Part 5 - Using Eureka Naming Server
In this final part of our microservices architecture series, we will learn to enable a Eureka Naming Server and allow the microservices to communicate with it.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this series, let's learn the basics of microservices and microservices architectures. We will also start looking at a basic implementation of a microservice with Spring Boot. We will create a couple of microservices and get them to talk to each other using Eureka Naming Server and Ribbon for Client Side Load Balancing.
This is part 5 of this series. In this part, we will focus on enabling Eureka Naming Server and have the microservices communicate with it.
Microservices with Spring Boot
- Part 1 - Getting Started with Microservices Architecture
- Part 2 - Creating Forex Microservice
- Part 3 - Creating Currency Conversion Microservice
- Part 4 - Using Ribbon for Load Balancing
- Current Part - Part 5 - Using Eureka Naming Server
You will learn:
- What is the need for a Naming Server?
- What is Eureka?
- How does a Naming Server enable location transparency between microservices?
Microservices Overview
In Parts 2 and 3, we created two microservices and established communication between them.
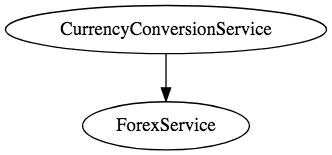
In Part 4, we used Ribbon to distribute load between the two instances of Forex Service. However, we are hardcoding the URLs of both instances of the Forex Service in CCS. That means that every time there is a new instance of FS, we would need to change the configuration of CCS. That's not cool.
In this part, we will use Eureka Naming Server to fix this problem.
Tools you will need:
- Maven 3.0+ is your build tool
- Your favorite IDE. We use Eclipse.
- JDK 1.8+
Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Our GitHub repository has all the code examples.
Bootstrapping Eureka Naming Server With Spring Initializr
Creating a Eureka Naming Server with Spring Initializr is a cake walk. Spring Initializr is a great tool for bootstrapping your Spring Boot projects. You can create a wide variety of projects using Spring Initializr.
The following steps have to be done for a web services project:
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following:
- Choose
com.in28minutes.springboot.microservice.eureka.naming.serveras Group - Choose
spring-boot-microservice-eureka-naming-serveras Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project.
- Do not forget to choose Eureka in the dependencies.
Enabling Eureka
EnableEurekaServer in SpringBootMicroserviceEurekaNamingServerApplication.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class SpringBootMicroserviceEurekaNamingServerApplication {Configure the application name and port for the Eureka Server:
/spring-boot-microservice-eureka-naming-server/src/main/resources/application.properties
spring.application.name=netflix-eureka-naming-server
server.port=8761
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=falseLaunching Eureka Naming Server
Launch SpringBootMicroserviceEurekaNamingServerApplication as a Java application.
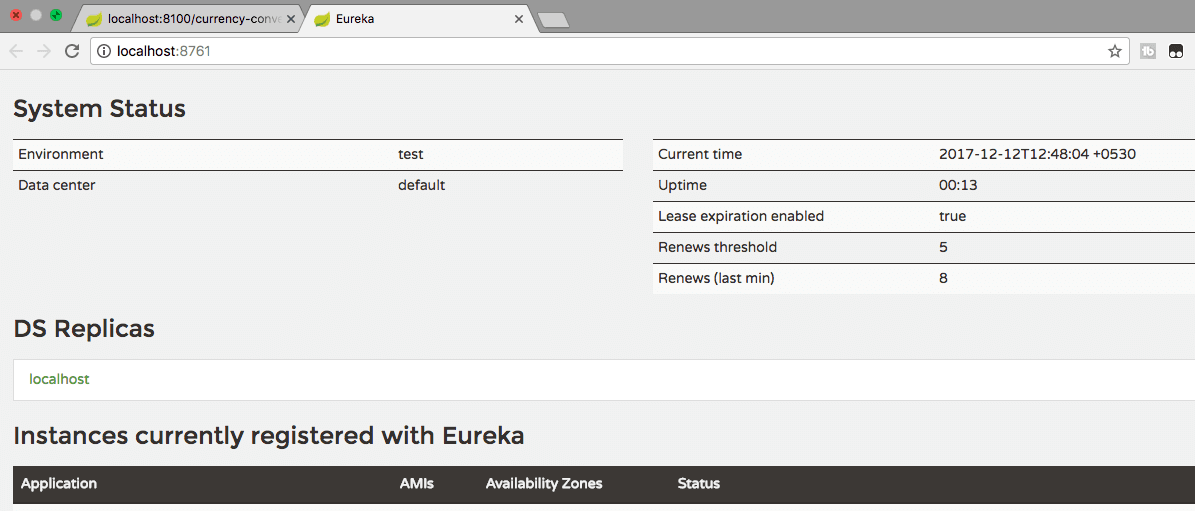
You can launch Eureka at http://localhost:8761
You will see that there are no instances connected to Eureka yet:
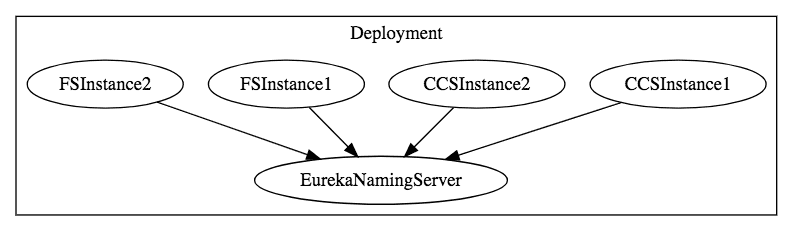
Connect FS and CCS Microservices With Eureka
Make these changes on both the microservices
Add to pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>Configure Eureka URL in application.properties:
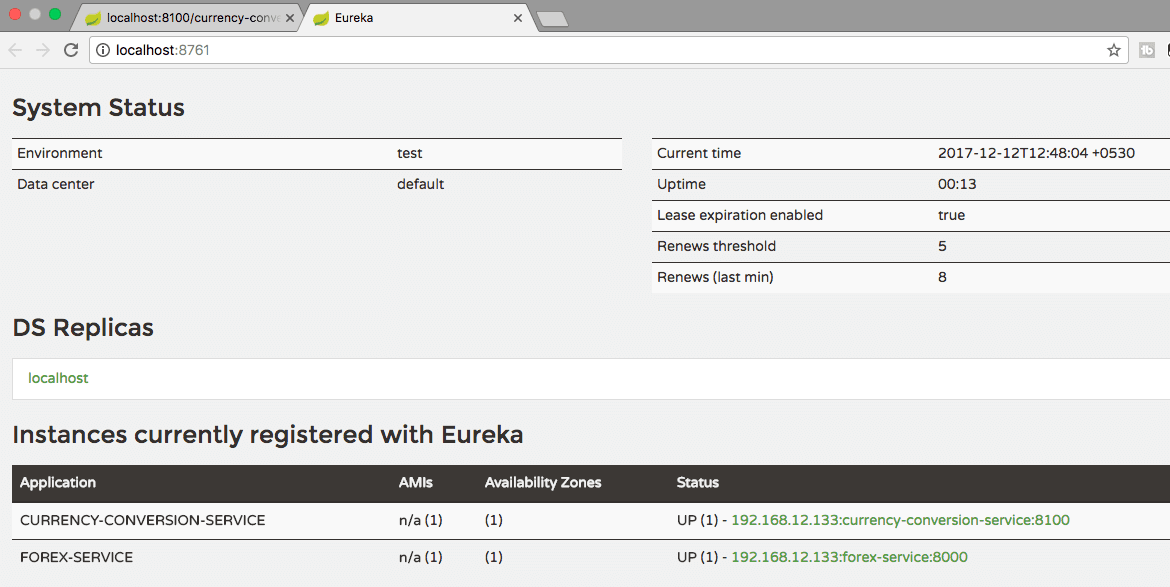
eureka.client.service-url.default-zone=http://localhost:8761/eurekaRestart all the instances of CCS and FS. You will see that the CCS and FS microservices are registered with Eureka Naming Server. That's cool!
This screenshot shows how to launch an additional instance of Forex Service on 8081. 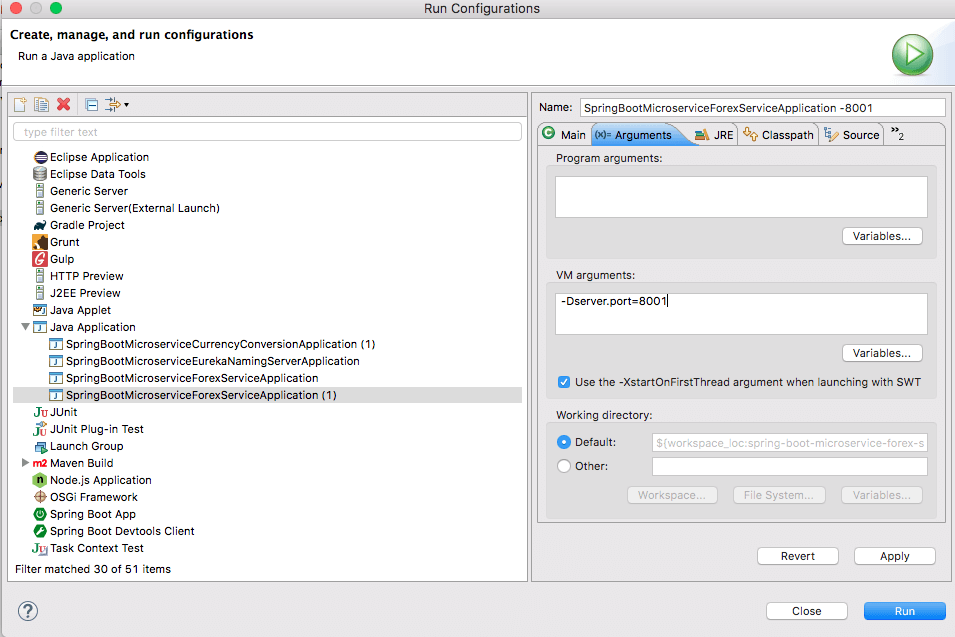
You will see that one instance of CCS and two instances of FS microservices are registered with Eureka Naming Server. 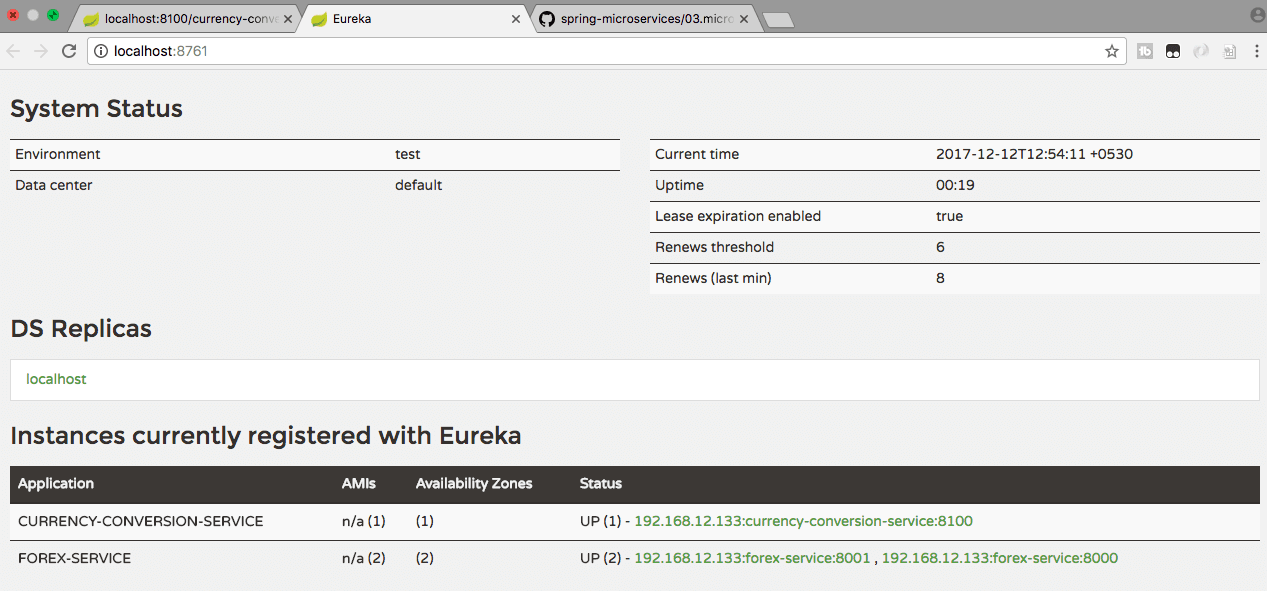
Routing Ribbon Requests Through Eureka
All that you would need to do is to remove this configuration. Remove this configuration from application.properties:
forex-service.ribbon.listOfServers=localhost:8000,localhost:8001Restart the CCS instance.
Eureka in Action
Currently, we have the following services up and running:
- Currency Conversion Microservice (CCS) on 8100
- Two instances of Forex Microservice on 8000 and 8001
- Eureka Server launched
Now you will see that the requests to CCS will be distributed between the two instances of the Forex Microservice by Ribbon through Eureka.
Request 1
GET to http://localhost:8100/currency-converter-feign/from/EUR/to/INR/quantity/10000
{
id: 10002,
from: "EUR",
to: "INR",
conversionMultiple: 75,
quantity: 10000,
totalCalculatedAmount: 750000,
port: 8000,
}Request 2
GET to http://localhost:8100/currency-converter-feign/from/EUR/to/INR/quantity/10000
{
id: 10002,
from: "EUR",
to: "INR",
conversionMultiple: 75,
quantity: 10000,
totalCalculatedAmount: 750000,
port: 8001,
}You can see that the port numbers in the two responses are different.
Exercise: Launch another instance of Forex Service on 8002. You will see that load gets automatically routed to it as well.
Cool! That's awesome, isn't it?
Summary
We have now created two microservices and established communication between them.

We are using Ribbon to distribute load between the two instances of Forex Service and Eureka as the naming server. When we launch new instances of Forex Service, you will see that load is automatically distributed to them.
The idea behind this series of five articles was to give the flavor of Spring Boot and Spring Cloud with microservices.
There is a lot more ground to cover with microservices. Until next time, cheers!
The complete code example for this project can be found in the GitHub repository.
Published at DZone with permission of Ranga Karanam, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments