Mobile Backend With Docker, Kubernetes, and Microservices
Docker and Kubernetes enable scalable, resilient mobile backends with auto-scaling and monitoring. CI/CD, caching, and Istio enhance performance and security.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMobile applications always demand highly scalable, available, and fault-tolerant backend systems. Traditional monolithic architectures often struggle with performance bottlenecks, slow deployments, and scalability limitations. To overcome these challenges, a microservices-based architecture deployed using Docker and Kubernetes provides a robust solution.
This article covers the following points:
- The challenges of monolithic architectures and how microservices solve them.
- How to containerize microservices using Docker.
- Deploying and scaling services with Kubernetes.
- Implementing auto-scaling, monitoring, and logging for production readiness.
By the end of this article, you will understand how to design, deploy, and scale a mobile backend that can handle high traffic and ensure a seamless user experience.
Challenges of Monolithic Architectures in Mobile Backends
A monolithic architecture is a single unified application where all features reside within a single codebase and database.
Limitations of Monolithic Systems
| challenge | explanation |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Monolithic applications scale as a whole, leading to inefficient resource utilization. |
| Slow Deployments | Any change, even a minor one, requires redeploying the entire application. |
| Complex Maintenance | Large codebases become difficult to manage as the application grows. |
| Fault Tolerance | A single failure can crash the entire system. |
Why Microservices?
A microservices architecture decomposes an application into small, independent services that communicate via APIs. Each service can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Benefits of Microservices for Mobile Backends
- Independent scaling – Services scale individually based on demand
- Faster deployments – Each microservice can be updated without affecting others
- Fault isolation – A failure in one service does not impact the entire system
- Technology flexibility – Each service can use the best-fit programming language and database
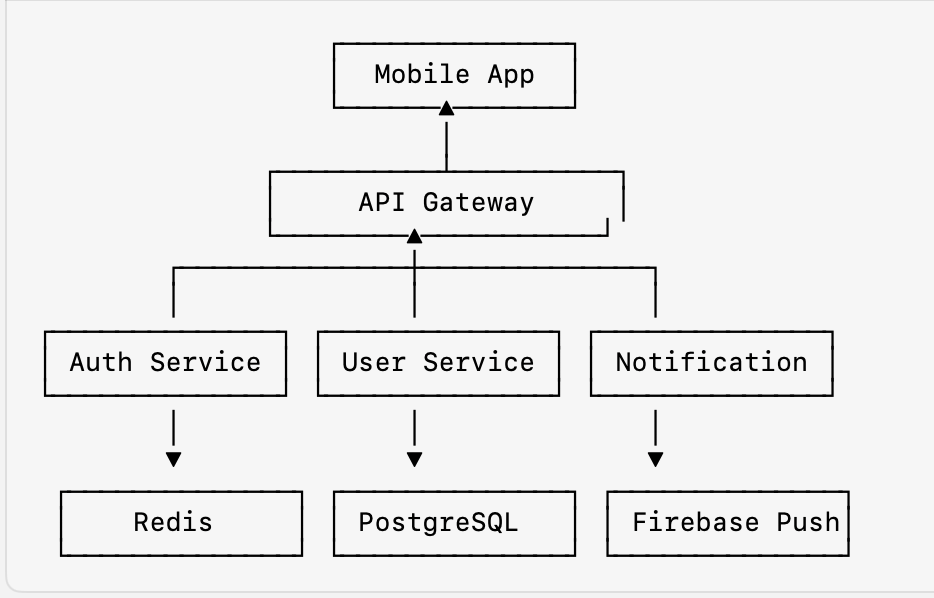
System Architecture Overview
A scalable mobile backend follows a microservices-based architecture, containerized using Docker and orchestrated using Kubernetes.
Components of a Scalable Mobile Backend
- API gateway – Manages client requests and routes them to appropriate microservices
- Authentication service – Handles user authentication and authorization
- User service – Manages user profiles, preferences, and data
- Notification service – Sends push notifications and in-app alerts
- Database layer – Stores structured and unstructured data
High-Level Architecture Diagram
Containerizing Microservices With Docker
What Is Docker?
Docker is a containerization platform that packages applications and their dependencies into portable units called containers.
Advantages of Docker in Microservices
- Consistency – Ensures applications run the same in development, testing, and production
- Isolation – Each microservice runs in its own environment, preventing conflicts
- Rapid deployment – Containers start quickly, improving deployment efficiency
Dockerizing a Microservice (User Service Example – Node.js + Express)
# Use official Node.js image
FROM node:18
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Copy files and install dependencies
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
# Copy application files
COPY . .
# Expose application port
EXPOSE 3000
# Start the service
CMD ["node", "server.js"]Docker Compose (for Local Development)
version: '3.8'
services:
user-service:
build: .
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- DATABASE_URL=postgres://user:pass@db:5432/users
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: postgres
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: pass
POSTGRES_DB: usersRun:
docker-compose up -dDeploying Microservices With Kubernetes
What Is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes (K8s) is a container orchestration system that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Key Kubernetes Features
- Auto-scaling – Scales services based on demand.
- Load balancing – Distributes traffic across multiple instances.
- Self-healing – Automatically restarts failed containers.
Deploying a Microservice on Kubernetes
Kubernetes Deployment for User Service
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: user-service
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: user-service
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: user-service
spec:
containers:
- name: user-service
image: myrepo/user-service:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 3000Expose Service With Load Balancer
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: user-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 3000
selector:
app: user-serviceDeploy:
kubectl apply -f user-service.yaml
kubectl get pods
kubectl get servicesAuto-Scaling Microservices With Kubernetes
Kubernetes supports Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), which adjusts the number of pods based on CPU utilization.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: user-service-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: user-service
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70Apply:
kubectl apply -f hpa.yamlMonitoring and Logging With Prometheus and Grafana
Why Monitoring?
Monitoring helps detect performance bottlenecks, track resource utilization, and identify failures.
Prometheus Configuration
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-config
data:
prometheus.yml: |
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kubernetes'
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9090']Deploy Prometheus and Grafana:
kubectl apply -f prometheus-config.yaml
helm install grafana grafana/grafanaConclusion and Next Steps
In this article, we explored how to design, build, and deploy a scalable, resilient, and efficient mobile backend using Docker, Kubernetes, and Microservices.
We started by identifying the limitations of monolithic architectures, such as scalability issues, slow deployments, and system-wide failures. Then, we introduced microservices as a solution, enabling independent scaling, faster deployments, fault isolation, and technology flexibility.
We containerized our microservices using Docker, ensuring that applications run consistently across different environments. Then, we leveraged Kubernetes to orchestrate and manage these containers, benefiting from auto-scaling, self-healing, and load balancing.
Additionally, we implemented Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) in Kubernetes to dynamically adjust the number of running instances based on CPU utilization. This ensures that our backend remains responsive and cost-efficient, even during high-traffic spikes.
To improve observability and performance monitoring, we integrated Prometheus and Grafana, enabling real-time monitoring, alerting, and data visualization. These tools help in identifying performance bottlenecks and ensuring system reliability.
Key Takeaways
- Microservices architecture enhances modularity, scalability, and flexibility.
- Docker containers enable portability and consistency across environments.
- Kubernetes provides automated deployment, self-healing, and scalability.
- Auto-scaling with Kubernetes HPA ensures efficient resource utilization.
- Monitoring with Prometheus & Grafana improves system reliability and performance.
Next Steps: Enhancing Your Mobile Backend
Now that we have a robust, scalable backend, there are several ways to further enhance its capabilities:
- Implement CI/CD pipelines. Automate the deployment process with GitHub Actions, Jenkins, or GitLab CI/CD. This will enable faster releases with minimal manual intervention.
- Enhance security. Use Istio Service Mesh for authentication, traffic encryption, and service-to-service security policies. Implement RBAC (role-based access control) to restrict access to Kubernetes resources.
- Database optimization. Optimize database queries and caching mechanisms to reduce latency and improve response times. Consider using Redis or Memcached for faster data retrieval.
- Multi-cloud deployment. Deploy across multiple cloud providers (AWS, GCP, Azure) for better fault tolerance and disaster recovery.
- Advanced logging and tracing. Use ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or Jaeger for distributed tracing to track API request flows across microservices.
Implementing these next-level optimizations ensures your mobile backend remains scalable, secure, and high-performing as your user base grows.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments