Mule API: Experience, Process, System
This article explains how to define and understand the basic API layers in Mule.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article explains how to define and understand the basic API layers in Mule. I have prepared this demo to explain the layer differences and their implementations. This example is mainly for beginners.
The purpose of this tutorial is to process a valid CSV file and store it into a database. The Experience API lets you expose the API to the end user. The Process API lets you validate the file extension as .csv or not. A system API will carry out the system level processes, such as validating the file contents and processing them to the database.
API Projects Definitions
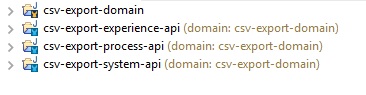
Experience API
The Experience API is defined to expose the end user to the API. So, we should define and implement the high-level logic in the API. The purpose of this API is to interact with the Process API and process the output to the end user with the process status.
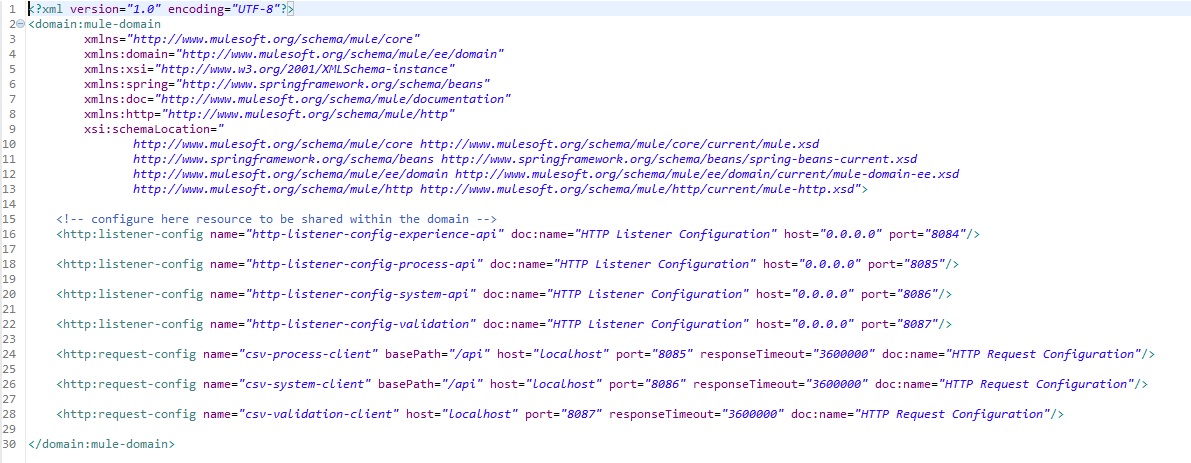
Step 1: Define the global definitions for the http connectors in the "csv-export-domain" project.
Step 2: Define the RAML definition for the Experience API.


Step 3: To generate the flow, right-click on the api.raml file and choose "Mule -> Generate Flows from REST API."
Step 4: Once the api.xml generates the call, see the Process API flow.
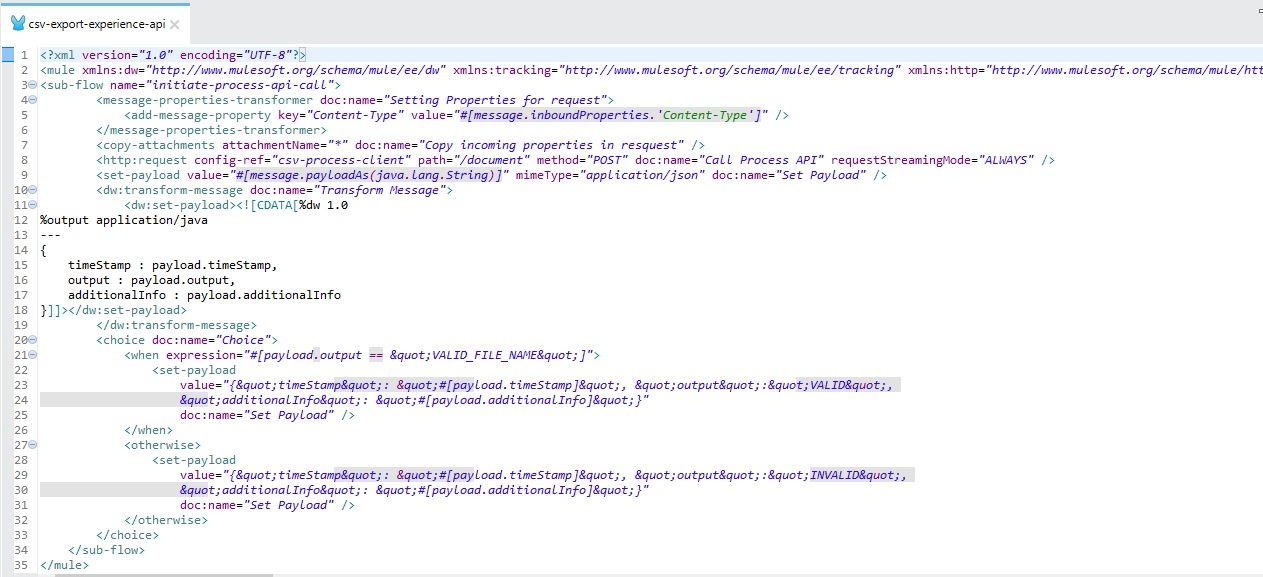
Step 5: Define "initiate-process-api-call" flow for the Process API call. Here is the xml view of the flow.
Process API
In the Process API, we are doing file extension validation. Except for the .csv file, this API will not process any files. Once the validation is successful, extract the contents of the CSV file and send them to the System API for further processing.
Step 6: Define the RAML definition for the Process API.
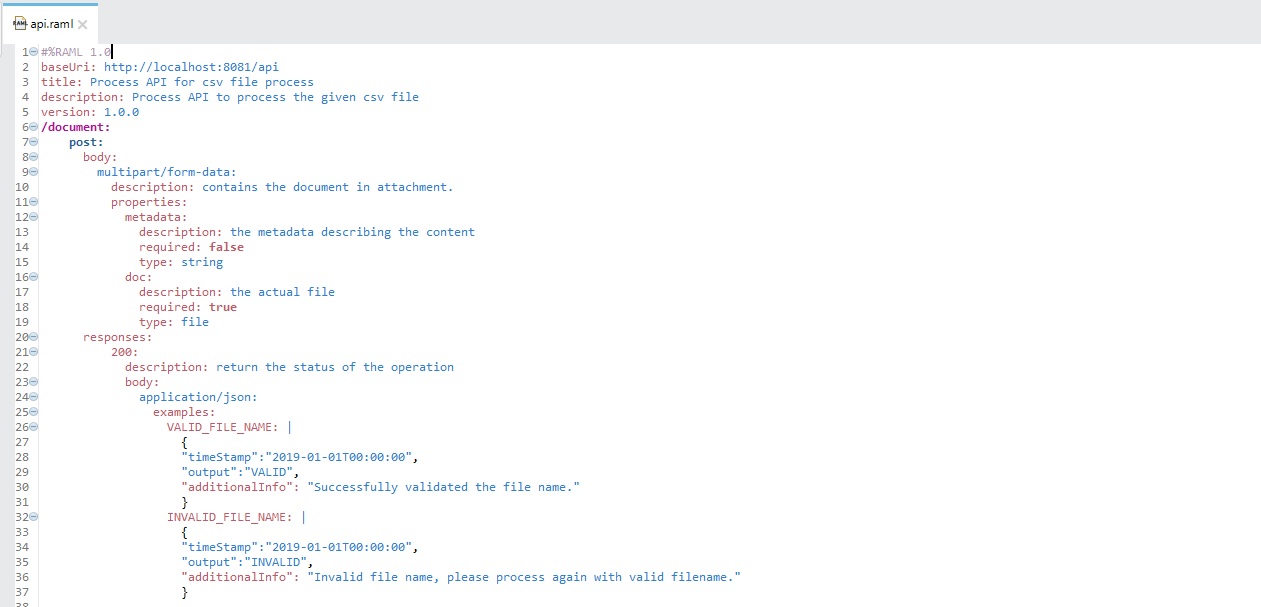

Step 7: Repeat step 3 and call the System API call.
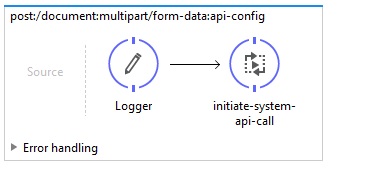
Step 8: Define the "initiate-system-api-call" flow for the Process API call. Here is the xml view of the flow.
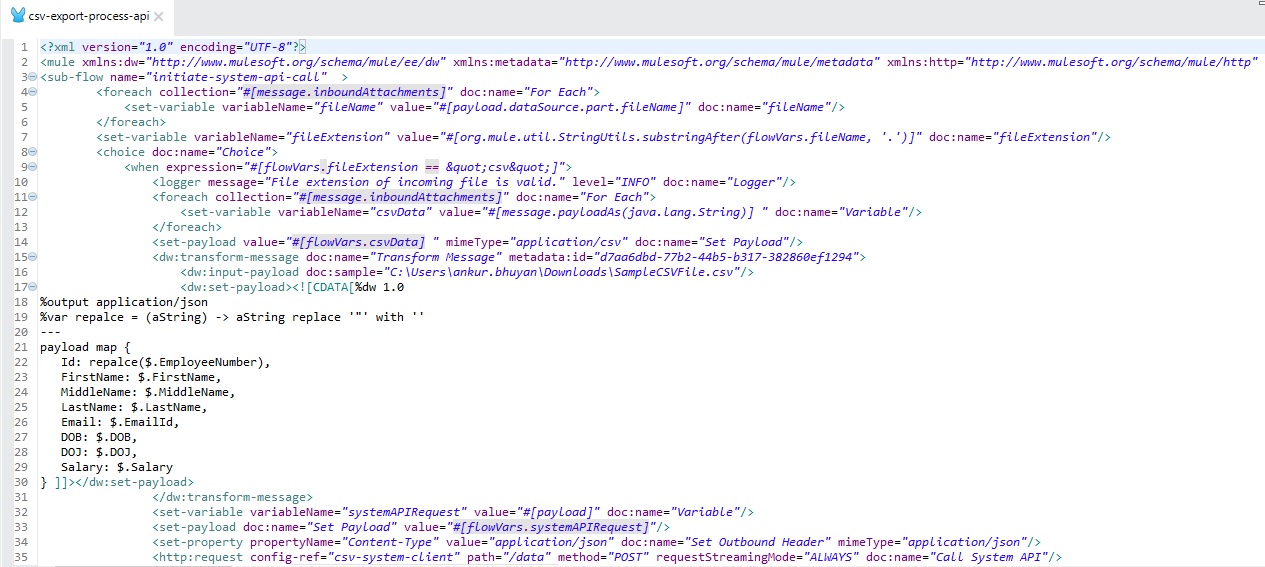
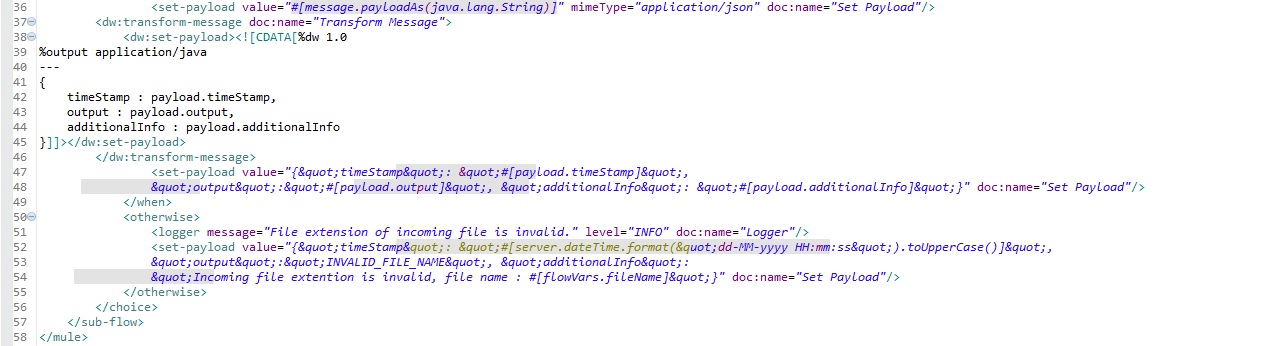
System API
The System API is for low-level processes. Once we get the JSON input from the Process API, we will validate the content one by one with the Mule validator. If any validation fails, the API will get the actual reason for the validation and reject the flow and pass the reason to the Experience API through the Process API. If the validation of all the content succeeds, process the data for the database to insert/update the record.
Step 9: Define the RAML definition for the System API.
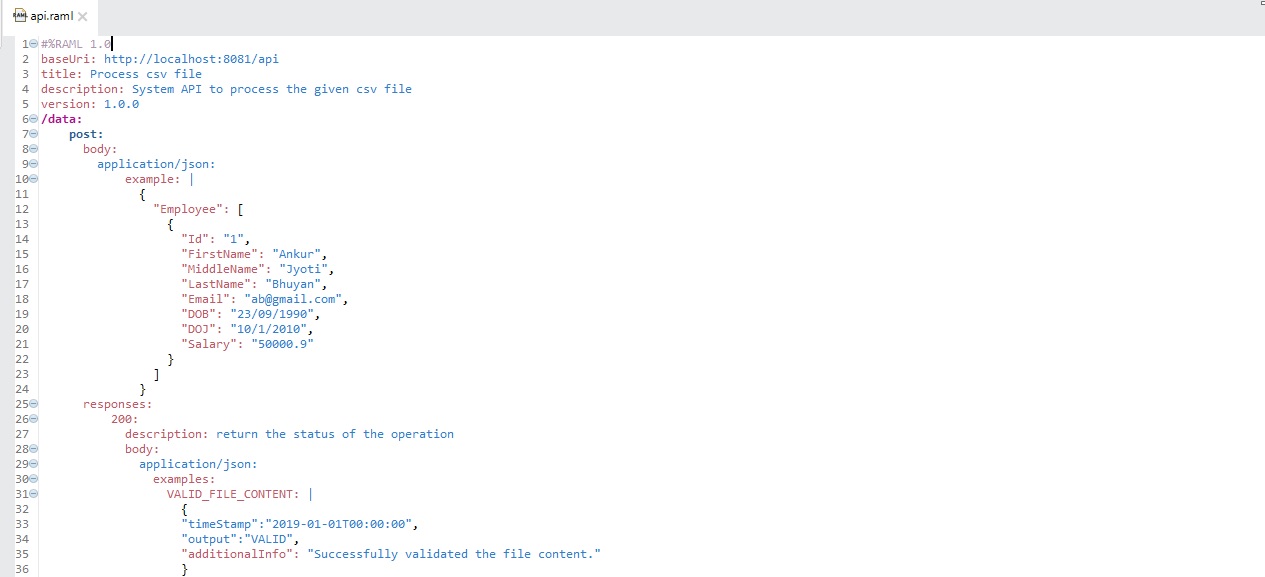
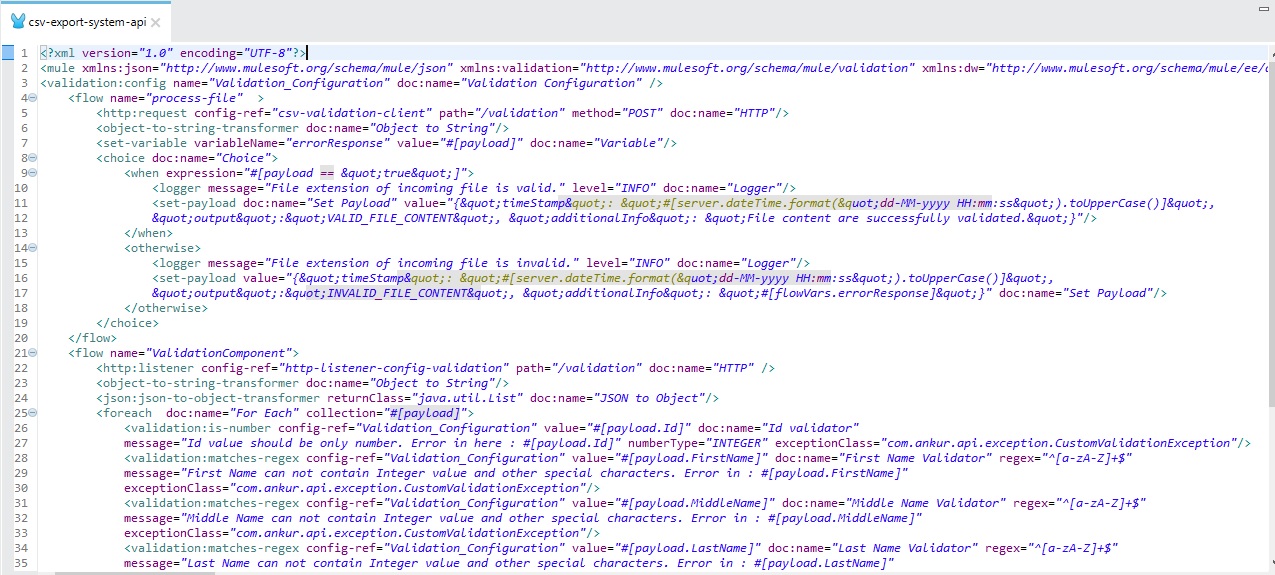
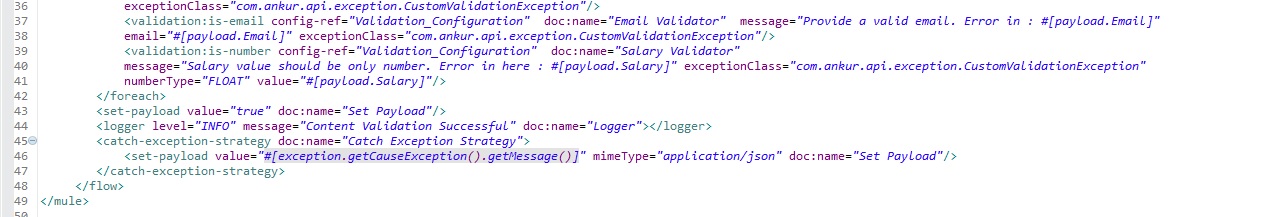
Step 7: Repeat step 3 and call the "process-file" flow of the System API for content validation and store it into the database (the database part is not complete here).
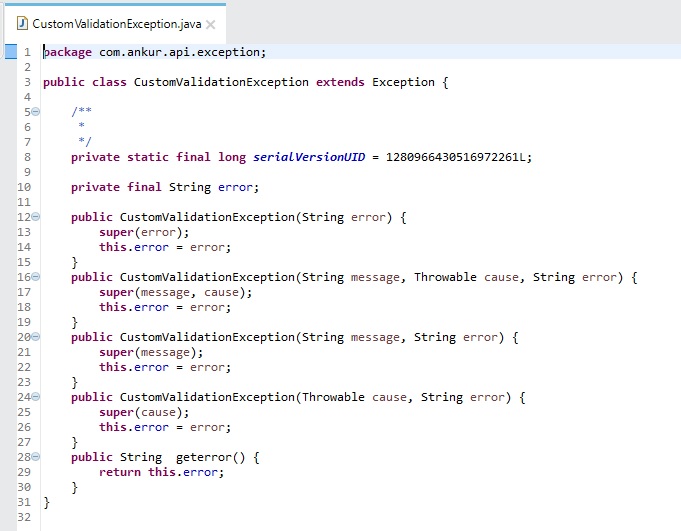
CustomValidationException.java: This custom exception class lets you catch the exception thrown by the validator flow.
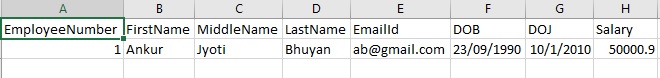
Sample CSV File
Valid content:
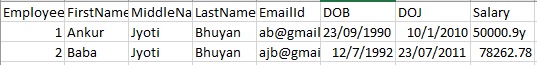
Invalid Content:
Let me know your thoughts in the comments.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments