MuleSoft: Payload Annotation Usage in Java Component
Learn about how to retrieve the JSON payload in the Java component using the @Payload annotation, which controls how a message payload is passed.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free@Payload annotation controls how the current message payload is passed into a method by performing automatic transformation of the message payload to match the annotated parameter type. A parameter injection annotation that can be used on component entry points.
The primary goal of this article is to retrieve the JSON payload in the Java component using the@Payload annotation.
I created a Book POJO class under src/main/java.
package com.ss.component;
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
private double price;
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [title=" + title + ", author=" + author + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}...and a component class as:
package com.ss.component;
import org.mule.api.annotations.param.Payload;
public class MyComponent {
public Object process(@Payload Book book) {
System.out.println("Title:" + book.getTitle());
System.out.println("Author:" + book.getAuthor());
System.out.println("Price:" + book.getPrice());
return book;
}
}Develop the flow as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule
xmlns:json="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json"
xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http"
xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json/current/mule-json.xsd">
<http:listener-config name="HTTP_Listener_Configuration" host="localhost" port="9001" doc:name="HTTP Listener Configuration"/>
<flow name="component_annotationFlow">
<http:listener config-ref="HTTP_Listener_Configuration" path="/" doc:name="HTTP" allowedMethods="POST"/>
<json:json-to-object-transformer returnClass="com.ss.component.Book" doc:name="JSON to Object"/>
<component doc:name="Java">
<singleton-object class="com.ss.component.MyComponent"/>
</component>
<object-to-string-transformer doc:name="Object to String"/>
<logger message="#[payload]" level="INFO" doc:name="Logger"/>
</flow>
</mule>And here's the flow diagram: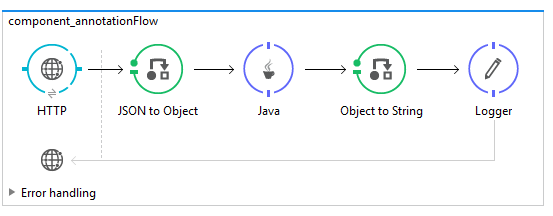
Run and deploy the flow to Anypoint runtime.
Test the flow with the POSTMAN plug-in:
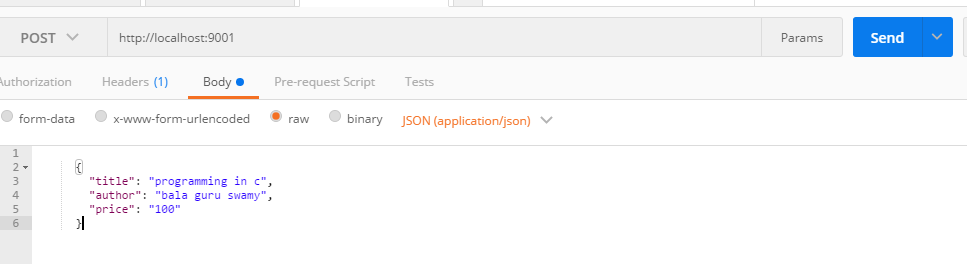
Hit the HTTP URL with a POST request with a JSON body as:
{
"title": "programming in c",
"author": "bala guru swamy",
"price": "100"
}We can observe output in the console as:
Title:
programming in c.Author:
bala guru swamy.Price:
100.
INFO 2017-03-24 16:30:11,640:
[[component_annotation].HTTP_Listener_Configuration.worker .01]
org.mule.api.processor.LoggerMessageProcessor: Book[title = programming in c, author = bala guru swamy, price = 100.0]Now, we have accessed the JSON payload in a Java component.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments