Nullable Types and Null Coalescing Operator in C#
In this post, we go over what nullable types and null coalescing operators are and how to use them in your C#-based code.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis is a fundamental concept in C# programming. Here I am going to explain nullable types, the null coalescing operator in C#, and how we can use this operator in LINQ.
The data types in C# are divided into two main categories: Value Type and Reference Type.
A value type variable cannot be null, but we can assign a null value in the reference type variable.
Let' check what will happen when we assign null to a value type.
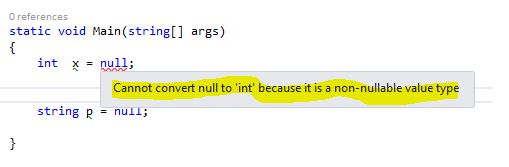
So when I am trying to assign a null value to an integer it is showing the following error: "Cannot Convert null to 'Int' because it is a non-nullable value type."
This is a common type of error we usually face while coding. There are two ways to solve this problem.
Nullable<int> x = null;
- int ? x = null;
- The above shows two ways to convert a non-nullable value type to nullable value type in C#. From this, we conclude that: A type is said to be nullable if it can be assigned a value or can be assigned null, which means the type has no value whatsoever. By default, all reference types, such as strings, are nullable, but all value types, such as Int32, are not.
- There are two members of a nullable type. 1: HasValue:
HasValueis of type boolean value. It is set to true when the variable contains a non-null value.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int? x = 5;
if(x.HasValue)
{
Console.WriteLine("contain not nullable value.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("contain Null value.");
}
Console.ReadLine();
} So the output will contain a non-nullable value.
2. Value: Value is of Boolean type. It contains the data stored in the nullable type.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int? x = 5;
if(x.HasValue)
{
Console.WriteLine(x.Value.ToString());
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("contain Null value.");
}
Console.ReadLine(); Here the output will be -5.
This is all about Nullable types in C#. Now I am going to discuss the Null Coalescing operator in C#.
Null-Collation
Null-collation(??) is an important operator in C#. As per the MSDN definition: The ?? operator is called the null-coalescing operator and is used to define a default value for nullable value types or reference types. It returns the left-hand operand if the operand is not null; otherwise, it returns the right operand. The C# Null Coalescing Operator (??) is a binary operator that simplifies checking for null values. It is used to assign a default value to a variable when the value is null.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string name = null;
string myname = name ?? "Laxmi";
Console.WriteLine(myname);
Console.ReadLine();
}
} 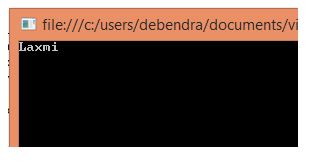 The output here is Laxmi. This is because the variable name is null and the null Coalescing operator checks for a null value. If it is null, then it will assign the default value.
The output here is Laxmi. This is because the variable name is null and the null Coalescing operator checks for a null value. If it is null, then it will assign the default value.
In property also we can use a null Coalescing operator like this.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NullCollation
{
class employee
{
}
class Program
{
static string _name;
static string Name
{
get
{
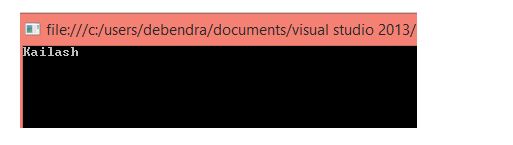
return _name ?? "Kailash";
}
set
{
_name = value;
}
}
public int age { get; set; }
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(Name);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
} 
Now I am showing you how this operator is used in LINQ.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NullCollation
{
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int age { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
public string gender { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Employee> li = new List<Employee>();
li.Add(new Employee { Id = 1, age = 19, name = "Ritesh", gender = "M" });
li.Add(new Employee { Id = 2, age = 20, name = "sujit", gender = "M" });
li.Add(new Employee { Id = 3, age = 23, name = "Kabir", gender = "F" });
li.Add(new Employee { Id = 4, age = 3, name = null, gender = "F" });
li.Add(new Employee { Id = 5, age = 24, name = "Kamlesh", gender = "M" });
li.Add(new Employee { Id = 6, age = 28, name = "Manoj", gender = "M" });
var Data = from emp in li where emp.Id == 4 select new { Name = emp.name ?? "No name" };
foreach (var obj in Data)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj.Name);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
} 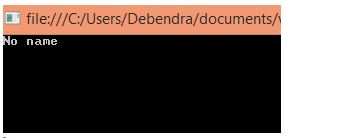
So in this way, we can use the null Coalescing operator in LINQ Queries.
Published at DZone with permission of Debendra Dash. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments