OpenVPN With Radius and Multi-Factor Authentication
This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide to install an OpenVPN server with Radius and multi-factor authentication for additional security.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSetting up a VPN server to allow remote connections can be challenging if you set this up for the first time. In this post, I will guide you through the steps to set up your own VPN Server and connect to it using a VPN Client.
Additionally, I will also show how to set up a free Radius server and a plugin to implement multi-factor authentication for additional security.
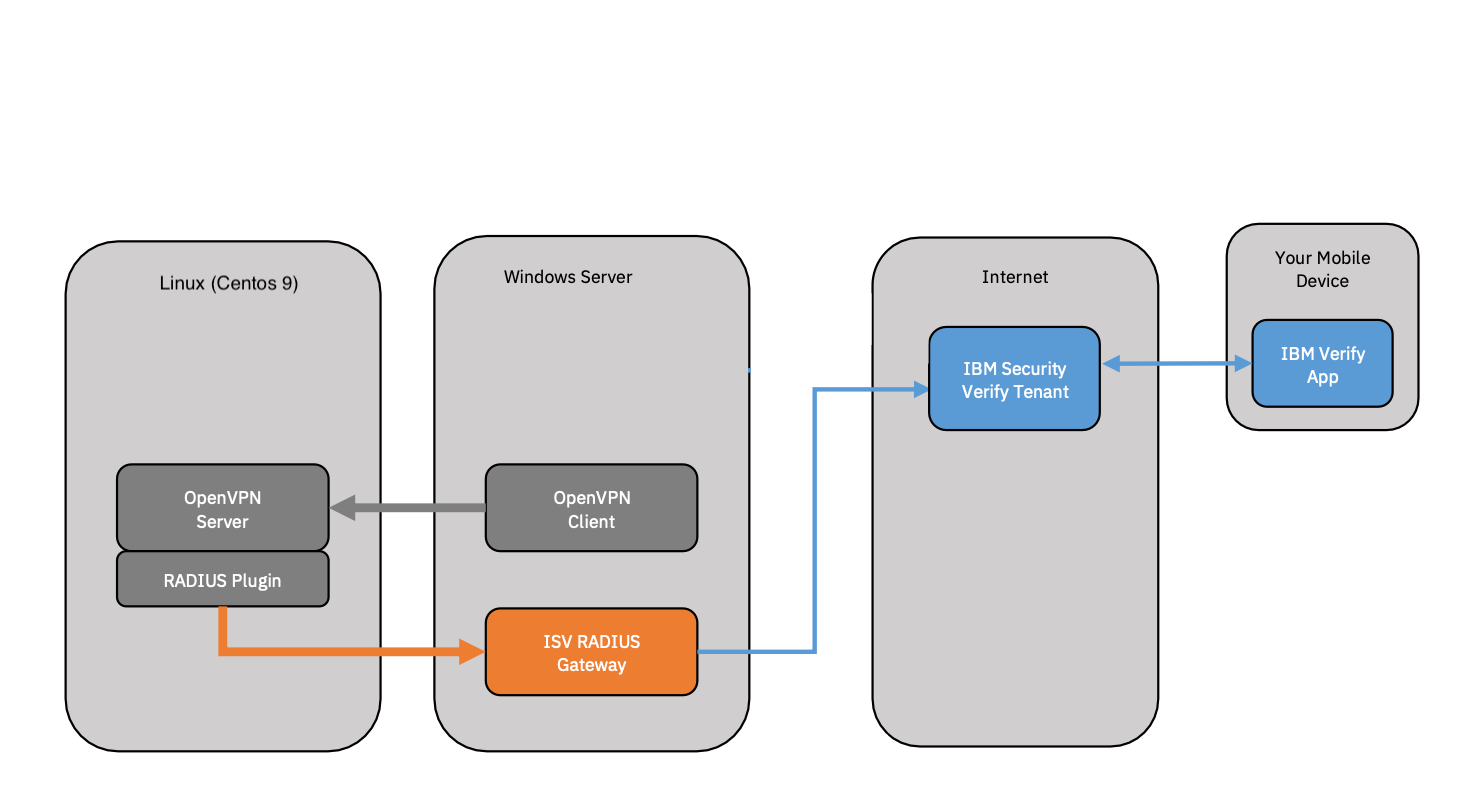
1. Installation OpenVPN Server on Linux (Using a Centos Stream 9 Linux)
# yum update
# curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/angristan/openvpn-install/master/openvpn-install.sh
# chmod +x openvpn-install.sh
# ./openvpn-install.shAccept defaults for installation of OpenVPN and, in the end, provide a Client name e.g. demouser. I have chosen a passwordless client, but if you want, you can also add an additional password to protect your private key.
Client name: demouser
Do you want to protect the configuration file with a password?
(e.g. encrypt the private key with a password)
1) Add a passwordless client
2) Use a password for the client
Select an option [1-2]: 1
...
...
The configuration file has been written to /root/demouser.ovpn.
Download the .ovpn file and import it in your OpenVPN client.Finally, a client configuration file is ready to be imported into the VPN Client.
2. Installation of OpenVPN Client for Windows
Download the OpenVPN Client software.
Install the OpenVPN Client:

Once the installation is finished, we can import the configuration file demouser.ovpn which was generated on the OpenVPN server, but before importing, we need to modify the IP address of our OpenVPN server within this file:
client
proto udp
explicit-exit-notify
remote 192.168.0.150 1194
dev tun
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
...Normally the remote IP by default will be the address of your public IP which is normal if you have your VPN server on your local network and need remote access from outside this network. You can leave the public IP address in the config, but then you will have to open up the correct port and set the routing on your internet access point.

Finally, we can test the VPN connection. The first time the connection will probably fail as the firewall on the OpenVPN Linux server is blocking the access. To quickly test this, we can just disable the firewall using the command:
# systemctl stop firewalldAlternatively, configure Linux firewall for OpenVPN connectivity:
# sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=openvpn
# sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=openvpn
# sudo firewall-cmd --add-masquerade
# sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-masquerade
# sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=1194/udp
# sudo firewall-cmd --reloadNow the connection should work:

On the windows client, you should now also get an additional VPN adapter configured with a default IP address of 10.8.0.2 (this subnet is defined within the file /etc/openvpn/server.conf).

3. How To Use Radius With OpenVPN
First, we will install the IBM Security Verify Gateway for Radius on a Windows machine.
This package can be downloaded from the IBM Security AppExchange (you will need to use your IBMid to log in).

Extract and run the installation using setup_radius.exe.
Edit the Radius configuration file c:\Program Files\IBM\IbmRadius\IbmRadiusConfig.json:
- Find the clients section in the configuration file.
- The default file has three example client definitions. Delete these definitions and replace them with the single definition shown above.
- This definition will match any Radius client connecting from the network used by the test machines. The secret authenticates the client.
Save the file and close the editor.
{
"address":"::",
"port":1812,
/*
"trace-file":"c:/tmp/ibm-auth-api.log",
"trace-rollover":12697600,
*/
"ibm-auth-api":{
"client-id":"???????",
"obf-client-secret":"???????", /* See IbmRadius -obf "the-secret" */
"protocol":"https",
"host":"???????.verify.ibm.com",
"port":443,
"max-handles":16
},
"clients":[
{
"name": "OpenVPN",
"address": "192.168.0.0",
"mask": "255.255.0.0",
"secret": "Passw0rd",
"auth-method": "password-and-device",
"use-external-ldap": false,
"reject-on-missing-auth-method": true,
"device-prompt": "A push notification has been sent to your device:[%D].",
"poll-device": true,
"poll-timeout": 60
}
]
}Complete the fields client-id, obf-client-secret and host with the correct information to point to your IBM Verify Saas API.
Before we can do this, we will need to set up API access in IBM Verify Saas.
Login to your environment or go for a trial account if you don’t have one.
From the main menu, select Security > API Access > Add API client
Create a new API Client :
- Specify the entitlements by selecting the check bow from the list:
- Authenticate any user
- Read authenticator registrations for all users
- Read users and groups
- Read second-factor authentication enrollment for all users
- Click next on the following screens and finally give the API client a name: e.g.
MFA-Client
A Client ID and Secret will automatically be created for you. Use this information to complete the Radius config. Use the c:\Program Files\IBM\IbmRadius\IbmRadius.exe -obf command to generate the obfuscated secret value.
Finally, configure the IBM Radius service to startup automatically and start the service:

Test Radius Authentication using the Radius tool : NTRadPing
You should get a push notification on the IBM Verify app on the mobile device.
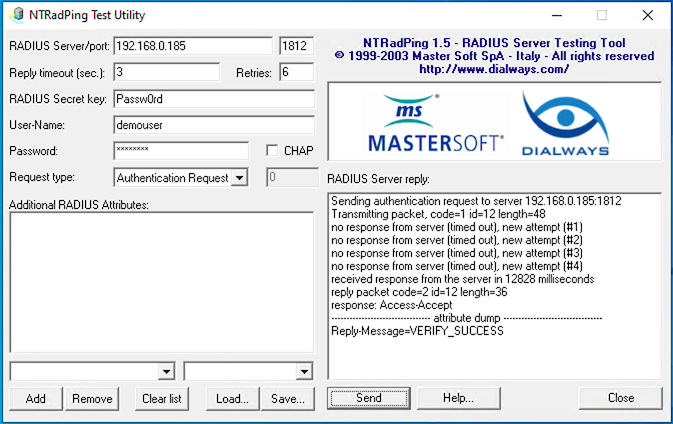
(Make sure you test with a userid that is known in IBM Verify Saas and is enrolled for OTP)
4. Install OpenVPN Radius Plugin
- Log in to the Linux OpenVPN server and launch the following commands:
# wget https://www.nongnu.org/radiusplugin/radiusplugin_v2.1a_beta1.tar.gz
# tar -xvf radiusplugin_v2.1a_beta1.tar.gz
# cd radiusplugin_v2.1a_beta1
# yum install libgcrypt libgcrypt-devel gcc-c++
# make- Copy the Radius plugin files to
/etc/openvpn
# cp /root/radiusplugin_v2.1a_beta1/radiusplugin.cnf /etc/openvpn
# cp /root/radiusplugin_v2.1a_beta1/radiusplugin.so /etc/openvpn
- Edit the file
/etc/openvpn/server.confand add the following line to activate the Radius plugin:
plugin /etc/openvpn/radiusplugin.so /etc/openvpn/radiusplugin.cnf - Edit the file
/etc/openvpn/radiusplugin.cnfand modify the ip address of the Radius server and set the sharedsecret toPassw0rd(this is the secret that was also configured on the Radius server side). Make sure to setnonfatalaccounting=truebecause the Radius server does not support Radius accounting.
...
NAS-IP-Address=<IP Address of the OpenVPN Server>
...
nonfatalaccounting=true
...
Server
{
# The UDP port for RADIUS accounting.
acctport=1813
# The UDP port for RADIUS authentication.
authport=1812
# The name or ip address of the RADIUS server.
name=<IP Address of the RADIUS Server>
# How many times should the plugin send the if there is no response?
retry=1
# How long should the plugin wait for a response?
wait=60
# The shared secret.
sharedsecret=Passw0rd
}Save the file and restart the OpenVPN server using the command :
# systemctl restart openserver-server@server.service- Finally, edit the OpenVPN client file
demouser.ovpnand add a lineauth-user-pass:
client
proto udp
auth-user-pass
explicit-exit-notify
remote 192.168.0.150 1194
dev tun
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
...This will allow the user to enter a username and password when initiating the VPN connection. These credentials will be authenticated against the IBM Verify Saas directory, and this should result in a challenge request on the IBM Verify Mobile app. The wait=60 will allow the plugin to wait for a response from the user who has to respond to the challenge using the IBM Verify App on his phone.
If you prefer to use a TOTP challenge instead, you can modify the Radius configuration file on Windows (IBMRadiusConfig.json) and set the auth-method to password-and-totp. Then you can open the client VPN connection and use 123456:password instead of the normal password.
Published at DZone with permission of Yves Debeer. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments