Bridging OT and IT: IIoT Middleware for Edge and Cloud With Kafka and Flink
Explore how IIoT middleware and data streaming tools like Kafka and Flink bridge OT and IT, enabling real-time integration and smarter industrial operations.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAs industries continue to adopt digital transformation, the convergence of Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) has become essential. The OT/IT Bridge is a key concept in industrial automation to connect real-time operational processes with business-oriented IT systems ensuring seamless data flow and coordination. This integration plays a critical role in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). It enables industries to monitor, control, and optimize their operations through real-time data synchronization and improve the Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). By leveraging IIoT middleware and data streaming technologies like Apache Kafka and Flink, businesses can achieve a unified approach to managing both production processes and higher-level business operations to drive greater efficiency, predictive maintenance, and streamlined decision-making.
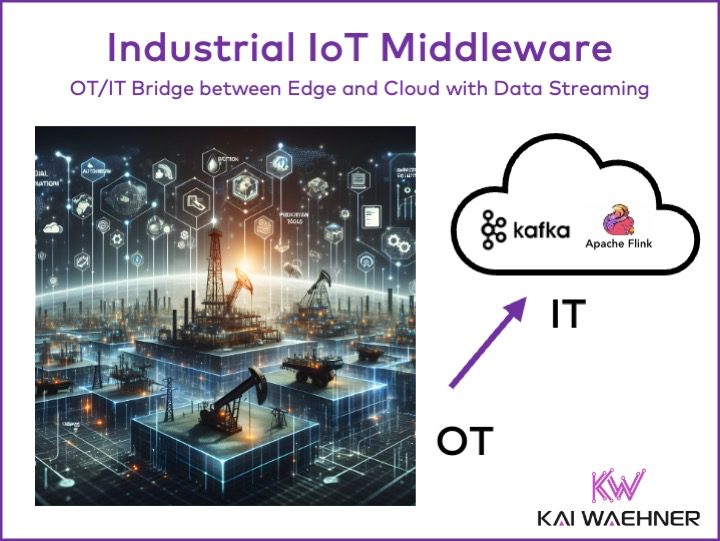
Industrial Automation — The IT/OT Bridge
An OT/IT Bridge in industrial automation refers to the integration between Operational Technology (OT) systems, which manage real-time industrial processes, and Information Technology (IT) systems, which handle data, business operations, and analytics. This bridge is crucial for modern Industrial IoT (IIoT) environments, as it enables seamless data flow between machines, sensors, and industrial control systems (PLC, SCADA) on the OT side, and business management applications (ERP, MES) on the IT side.
The OT/IT Bridge facilitates real-time data synchronization. It allows industries to monitor and control their operations more efficiently, implement condition monitoring/predictive maintenance, and perform advanced analytics. The OT/IT bridge helps overcome the traditional siloing of OT and IT systems by integrating real-time data from production environments with business decision-making tools. Data Streaming frameworks like Kafka and Flink, often combined with specialized platforms for the last-mile IoT integration, act as intermediaries to ensure data consistency, interoperability, and secure communication across both domains.
This bridge enhances overall productivity and improves the OEE by providing actionable insights that help optimize performance and reduce downtime across industrial processes.
OT/IT Hierarchy — Different Layers Based on ISA-95 and the Purdue Model
The OT/IT Levels 0-5 framework is commonly used to describe the different layers in industrial automation and control systems, often following the ISA-95 or Purdue model:
- Level 0 —Physical Process: This is the most basic level, consisting of the physical machinery, equipment, sensors, actuators, and production processes. It represents the actual processes being monitored or controlled in a factory or industrial environment.
- Level 1 —Sensing and Actuation: At this level, sensors, actuators, and field devices gather data from the physical processes. This includes things like temperature sensors, pressure gauges, motors, and valves that interact directly with the equipment at Level 0.
- Level 2 —Control Systems: Level 2 includes real-time control systems such as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS). These systems interpret the data from Level 1 and make real-time decisions to control the physical processes.
- Level 3 —Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM): This level manages and monitors production workflows. It includes systems like Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), which ensure that production runs smoothly and aligns with the business’s operational goals. It bridges the gap between the physical operations and higher-level business planning.
- Level 4 —Business Planning and Logistics: This is the IT layer that includes systems for business management, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and supply chain management (SCM). These systems handle business logistics such as order processing, materials procurement, and long-term planning.
- Level 5 —Enterprise Integration: This level encompasses corporate-wide IT functions such as financial systems, HR, sales, and overall business strategy. It ensures the alignment of all operations with the broader business goals.
In summary, Levels 0-2 focus on the OT (Operational Technology) side — real-time control and monitoring of industrial processes, while Levels 3-5 focus on the IT (Information Technology) side —managing data, logistics, and business operations.
While the modern, cloud-native IIoT world is not strictly hierarchical anymore (e.g. there is also lots of edge computing like sensor analytics), these layers are still often used to separate functions and responsibilities. Industrial IoT data platforms, including the data streaming platform, often connect to several of these layers in a decoupled hub-and-spoke architecture.
Industrial IoT Middleware
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Middleware is a specialized software infrastructure designed to manage and facilitate the flow of data between connected industrial devices and enterprise systems. It acts as a mediator that connects various industrial assets, such as machines, sensors, and controllers, with IT applications and services such as MES or ERP, often in a cloud or on-premises environment.
This middleware provides a unified interface for managing the complexities of data integration, protocol translation, and device communication to enable seamless interoperability among heterogeneous systems. It often includes features like real-time data processing, event management, scalability to handle large volumes of data, and robust security mechanisms to protect sensitive industrial operations.
In essence, IIoT Middleware is critical for enabling the smart factory concept, where connected devices and systems can communicate effectively, allowing for automated decision-making, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes in industrial settings.
By providing these services, IIoT Middleware enables industrial organizations to optimize operations, enhance Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), and improve system efficiency through seamless integration and real-time data analytics.
Relevant Industries for IIoT Middleware
Industrial IoT Middleware is essential across various industries that rely on connected equipment, sensors, or vehicles and data-driven processes to optimize operations. Some key industries where IIoT Middleware is particularly needed include:
- Manufacturing: For smart factories, IIoT Middleware enables real-time monitoring of production lines, predictive maintenance, and automation of manufacturing processes. It supports Industry 4.0 initiatives by integrating machines, robotics, and enterprise systems.
- Energy and Utilities: IIoT Middleware is used to manage data from smart grids, power plants, and renewable energy sources. It helps in optimizing energy distribution, monitoring infrastructure health, and improving operational efficiency.
- Oil and Gas: In this industry, IIoT Middleware facilitates the remote monitoring of pipelines, drilling rigs, and refineries. It enables predictive maintenance, safety monitoring, and optimization of extraction and refining processes.
- Transportation and Logistics: IIoT Middleware is critical for managing fleet operations, tracking shipments, and monitoring transportation infrastructure. It supports real-time data analysis for route optimization, fuel efficiency, and supply chain management.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, IIoT Middleware connects medical devices, patient monitoring systems, and healthcare IT systems. It enables real-time monitoring of patient vitals, predictive diagnostics, and efficient management of medical equipment.
- Agriculture: IIoT Middleware is used in precision agriculture to connect sensors, drones, and farm equipment. It helps in monitoring soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, leading to optimized farming practices and resource management.
- Aerospace and Defense: IIoT Middleware supports the monitoring and maintenance of aircraft, drones, and defense systems. It ensures the reliability and safety of critical operations by integrating real-time data from various sources.
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, IIoT Middleware connects smart vehicles, assembly lines, and supply chains. It enables connected car services, autonomous driving, and the optimization of manufacturing processes.
- Building Management: For smart buildings and infrastructure, IIoT Middleware integrates systems like HVAC, lighting, and security. It enables real-time monitoring and control, energy efficiency, and enhanced occupant comfort.
- Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceuticals, IIoT Middleware helps monitor production processes, maintain regulatory compliance, and ensure the integrity of the supply chain.
These industries benefit from IIoT Middleware by gaining better visibility into their operations. The digitalization of shop floor and business processes improves decision making and drives efficiency through automation and real-time data analysis.
Industrial IoT Middleware Layers in OT/IT
While modern, cloud-native IoT architectures don't always use a hierarchical model anymore, Industrial IoT (IIoT) middleware typically operates at Level 3 (Manufacturing Operations Management) and Level 2 (Control Systems) in the OT/IT hierarchy.
At Level 3, IIoT middleware integrates data from control systems, sensors, and other devices, coordinating operations and connecting these systems to higher-level IT layers such as MES and ERP systems. At Level 2, the middleware handles real-time data exchange between industrial control systems (like PLCs) and IT infrastructure, ensuring data flow and interoperability between the OT and IT layers.
This middleware acts as a bridge between the operational technology (OT) at Levels 0-2 and the business-oriented IT systems at Levels 4-5.
Edge and Cloud Vendors for Industrial IoT
The industrial IoT space provides many solutions from various software vendors. Let's explore the different options and their trade-offs.
Traditional “Legacy” Solutions
Traditional Industrial IoT (IIoT) solutions are often characterized by proprietary, monolithic architectures that can be inflexible and expensive to implement and maintain. These traditional platforms, offered by established industrial vendors like PTC ThingWorx, Siemens MindSphere, GE Predix, and Osisoft PI, are typically designed to meet specific industry needs but may lack the scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency required for modern industrial applications. However, while these solutions are often called "legacy," they do a solid job integrating with proprietary PLCs, SCADA systems, and data historians. They still operate the shop floor in most factories worldwide.
Emerging Cloud Solutions
In contrast to legacy systems, emerging cloud-based IIoT solutions offer elastic, scalable, and (hopefully) cost-efficient alternatives that are fully managed by cloud service providers. These platforms, such as AWS IoT Core, enable industrial organizations to quickly deploy and scale IoT applications while benefiting from the cloud’s inherent flexibility, reduced operational overhead, and integration with other cloud services.
However, emerging cloud solutions for IIoT can face challenges:
- Latency and real-time processing limitations, making them less suitable for time-sensitive industrial applications.
- High network transfer cost from the edge to the cloud.
- Security and compliance concerns arise when transferring sensitive operational data to the cloud, particularly in regulated industries.
- Depending on reliable internet connectivity, which can be a significant drawback in remote or unstable environments.
- Very limited connectivity to proprietary (legacy) protocols such as Siemens S7 or Modbus.
The IIoT Enterprise Architecture is a Mix of Vendors and Platforms
There is no black and white when comparing different solutions. The current IIoT landscape in real-world deployments features a mix of traditional industrial vendors and new cloud-native solutions. Companies like Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure still provide robust industrial platforms, while newer entrants like AWS IoT Core are gaining traction due to their modern, cloud-centric approaches. The shift toward cloud solutions reflects the growing demand for more agile and scalable IIoT infrastructures.
The reality in the industrial space is that:
- OT/IT is usually hybrid, edge-to-cloud, not just cloud
- Most cloud-only solutions do not provide the right security, SLAs, latency, cost
- IoT is a complex space. "Just" a OPC-UA or MQTT connector is not sufficient in most scenarios.
Data Streaming for Industrial IoT in the OT/IT World with Kafka and Flink
Data streaming with Apache Kafka and Flink is a powerful approach that enables the continuous flow and processing of real-time data across various systems. However, to be clear, data streaming is NOT a silver bullet. It is complementary to other IoT middleware. And some modern, cloud-native industrial software is built on top of data streaming technologies like Kafka and Flink under the hood.
In the context of Industrial IoT, data streaming plays a crucial role by seamlessly integrating and processing data from numerous IoT devices, equipment, PLCs, MES, and ERP in real-time. This capability enhances decision-making processes and operational efficiency by providing continuous insights, allowing industries to optimize their operations and respond proactively to changing conditions. The last-mile integration is usually done by complementary IIoT technologies providing sophisticated connectivity to OPC-UA, MQTT and proprietary legacy protocols like S7 or Modbus.
Apache Kafka and Flink in IT Environments
In data center and cloud settings, Kafka and Flink are used to provide continuous processing and data consistency across IT applications, including sales and marketing, B2B communication with partners, and e-commerce. Data streaming facilitates data integration, processing, and analytics to enhance the efficiency and responsiveness of IT operations and business, no matter if data sources or sinks are real-time, batch, or request-response APIs.
Apache Kafka as an OT/IT Bridge
Kafka serves as a critical bridge between Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) by enabling real-time data synchronization at scale. This integration ensures data consistency across different systems, supporting seamless communication and coordination between industrial operations and business systems.
Apache Kafka and Flink in OT Edge Applications
At the edge of operational technology, Kafka and Flink provide a robust backbone for use cases such as condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. By processing data locally and in real-time, these technologies improve the Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and support advanced analytics and decision-making directly within industrial environments.
Data Streaming With Kafka and Flink Empowers Edge-to-Cloud Industrial IoT Middleware
Data streaming plays a crucial role in bridging OT and IT in industrial automation. By enabling continuous data flow between the edge and the cloud, Kafka and Flink ensure that both operational data from sensors and machinery and IT applications like ERP and MES remain synchronized in real-time. Additionally, data consistency with non-real-time systems, like a legacy batch system or a cloud-native data lakehouse, are guaranteed out-of-the-box.
The real-time integration powered by Kafka and Flink improves the overall operational efficiency (OEE) and enables specific use cases such as enhanced predictive maintenance, condition monitoring. As industries increasingly adopt edge computing alongside cloud solutions, these data streaming tools provide the scalability, flexibility, and low-latency performance needed to drive Industrial IoT initiatives forward.
How does your OT/IT integration look today? Do you plan to optimize the infrastructure with data streaming? What does the hybrid architecture look like? What are the use cases?
Published at DZone with permission of Kai Wähner, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments