Jenkins: Installation and Creation of Freestyle Project
It's pretty easy to get up and running with creating an instance of Jenkins and creating a freestyle project.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Overview
Jenkins is a continuous integration server that can fetch the latest code from the version control system (VCS), build it, test it, and notify developers. Jenkins can do many things apart from just being a Continuous Integration (CI) server. Originally known as Hudson, Jenkins is an open-source project written by Kohsuke Kawaguchi. As Jenkins is a java based project, before installing and running Jenkins on your machine, first, you need to install Java 8.
You may also enjoy: Getting Started With Jenkins: The Ultimate Guide
Pre-Requisites
Before you proceed to install Jenkins in your Ubuntu machine, there are some prerequisites for Jenkins to install Jenkins.
Hardware Requirements: You need a minimum of 1 GB+ of RAM and 50 GB+ of drive space to install Jenkins.
Software Requirements: Java 8, either a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) or a Java Development Kit (JDK) is fine
Note: This is not a requirement if running Jenkins as a Docker container.
Installing Jenkins
Login to Jenkins VM
1. Login to your Jenkins VM using putty.
2. Update the packages:
sudo apt-get update3. Install Java 8 Open JDK package.
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk 4. Add the Jenkins Debian repository to the system
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins-ci.org.key | sudo apt-key add -5. When the key is added, the system will return "OK." Next, we'll append the Debian package repository address to the server's sources.list:
echo deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list6. Update the packages one more time.
sudo apt-get update7. Finally, install the latest version of Jenkins with the following command.
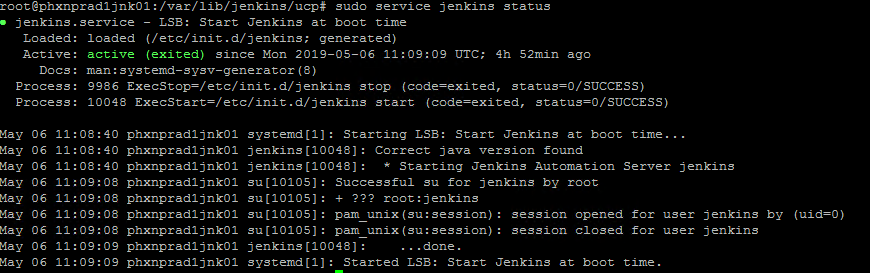
sudo apt-get install jenkins -y 8. After the installation process, the Jenkins service is automatically started. You can verify by typing the following command.
sudo service jenkins status Output should be like this:
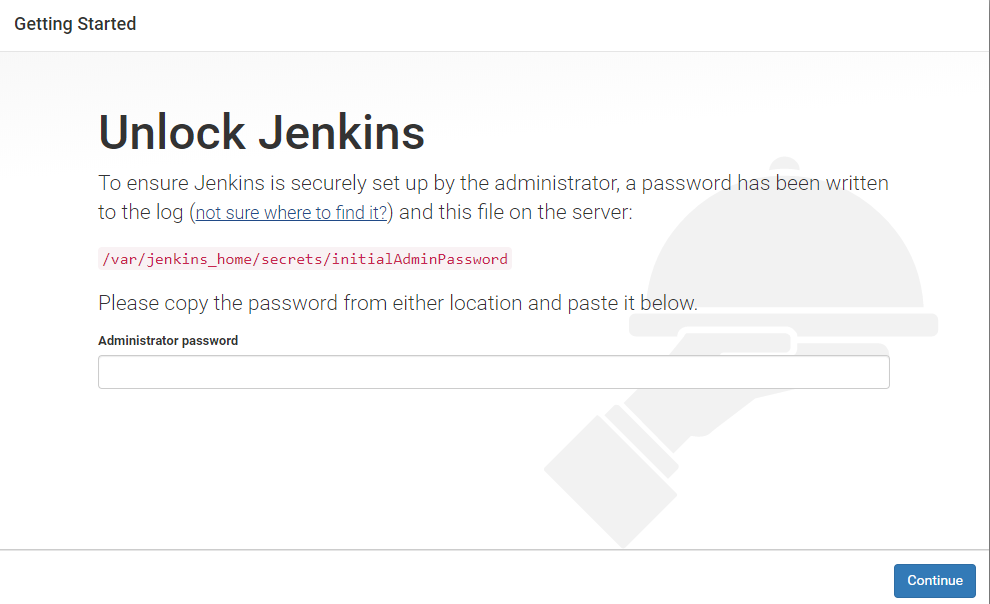
9. To set up your latest Jenkins installation, open your browser and browse the service hostname or IP address followed by port 8080. http://ip_address or domain.com:8080
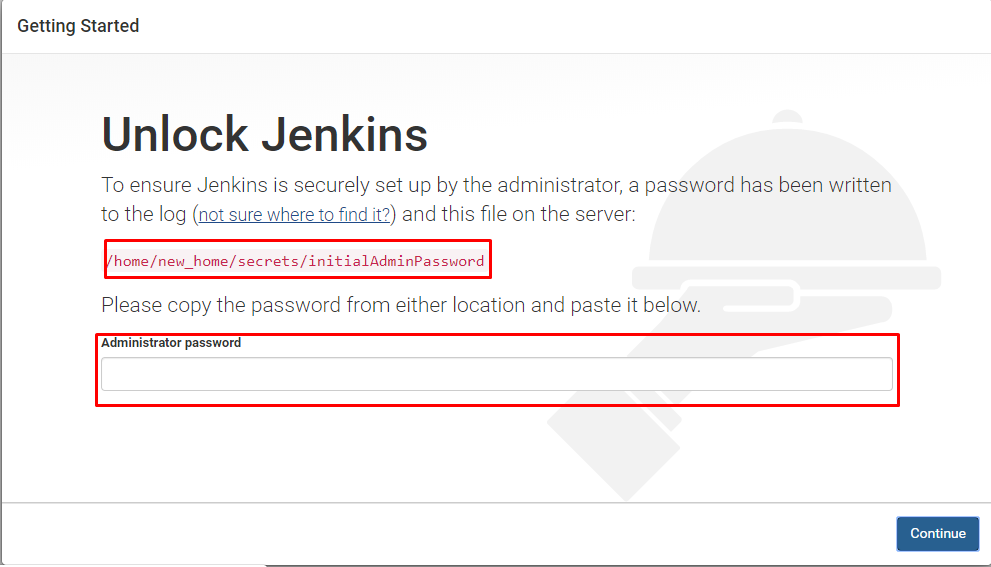
10. Open the command line and type the following command
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword 11. Jenkins installer creates an initial 32-character alphanumeric password. Copy and paste it into the browser administrator password field, then click Continue.
12. The setup wizard will ask you whether you want to install suggested plugins or you want to install specific plugins.
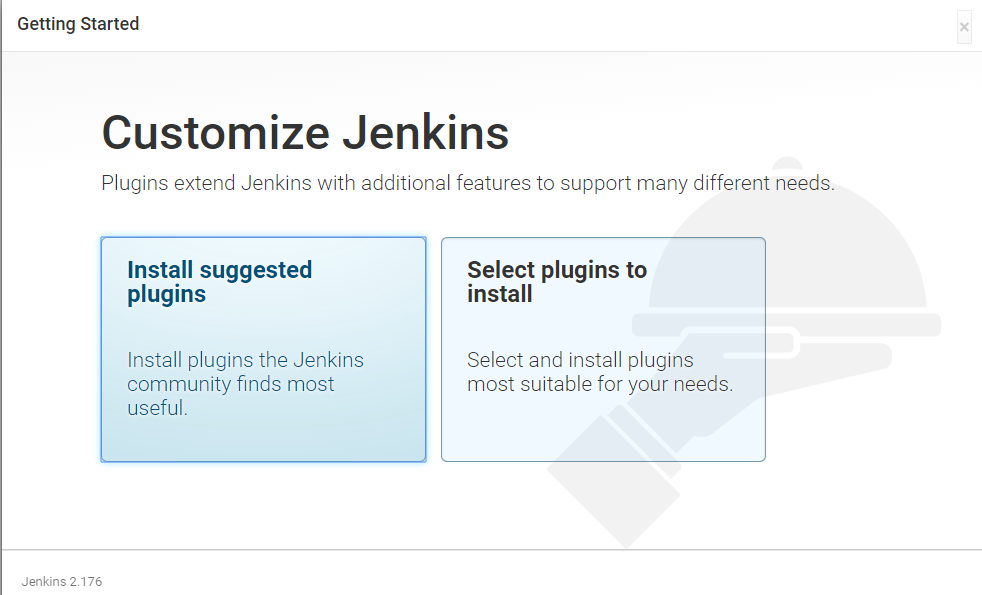
13. Click on the suggested plugins box, and the plugins installation process will start.
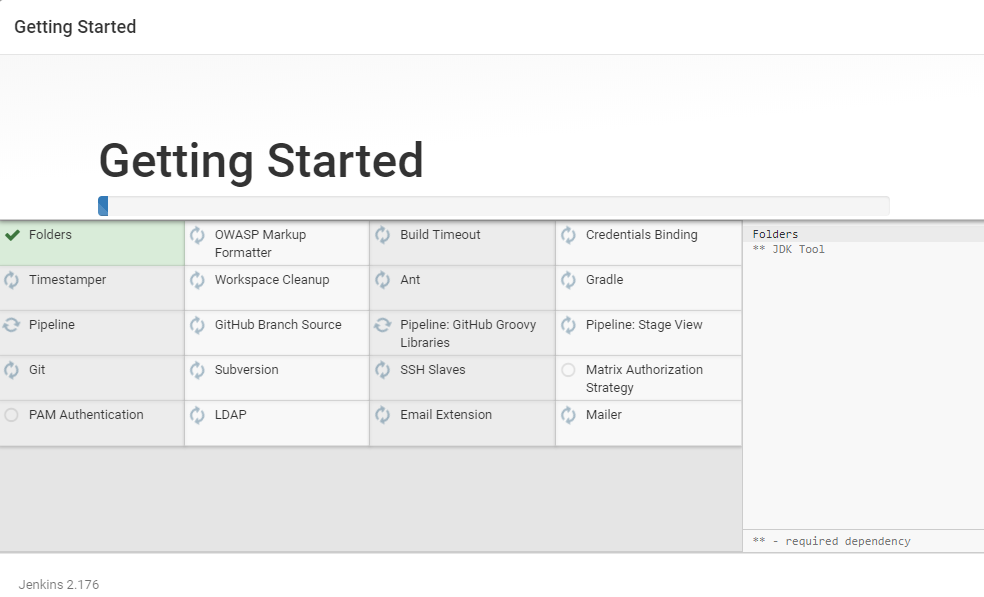
14. Once the plugins are installed, you will be prompted to set up the first admin user. Fill out all required information and click Save and Continue.
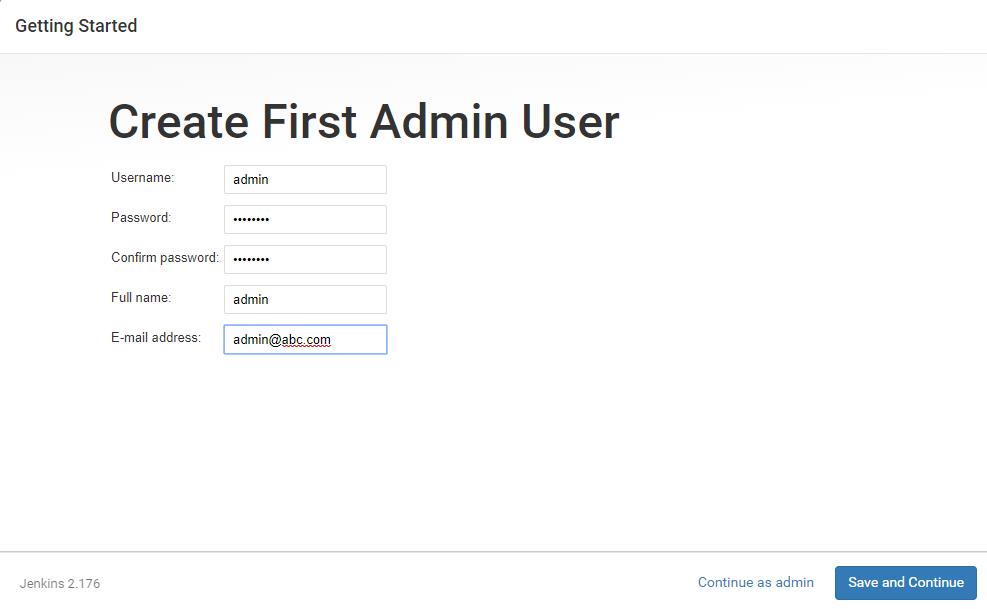
15. Next set the URL for your Jenkins instance. The URL will be generated automatically. Confirm the URL by clicking the Save and Finish button.
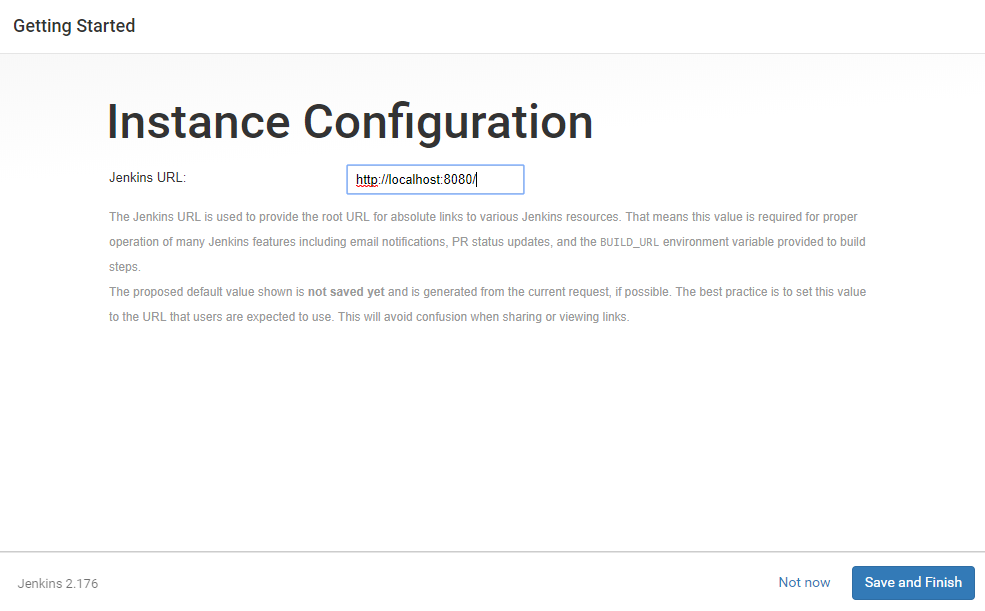
16. Once all configurations are done, you can see the Jenkins is ready screen.
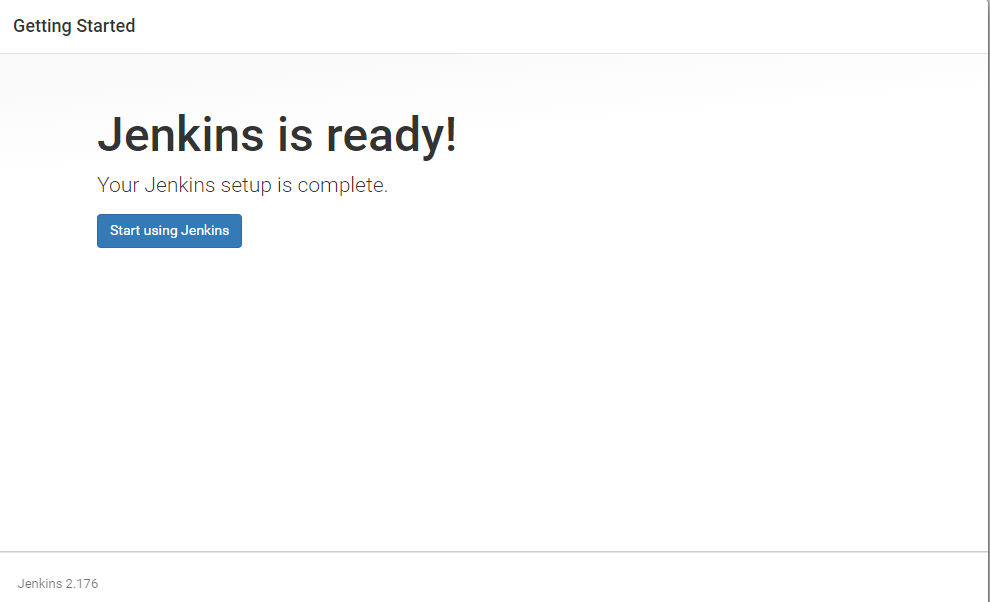
17. Click Start using Jenkins and you will redirected to the Jenkins dashboard.
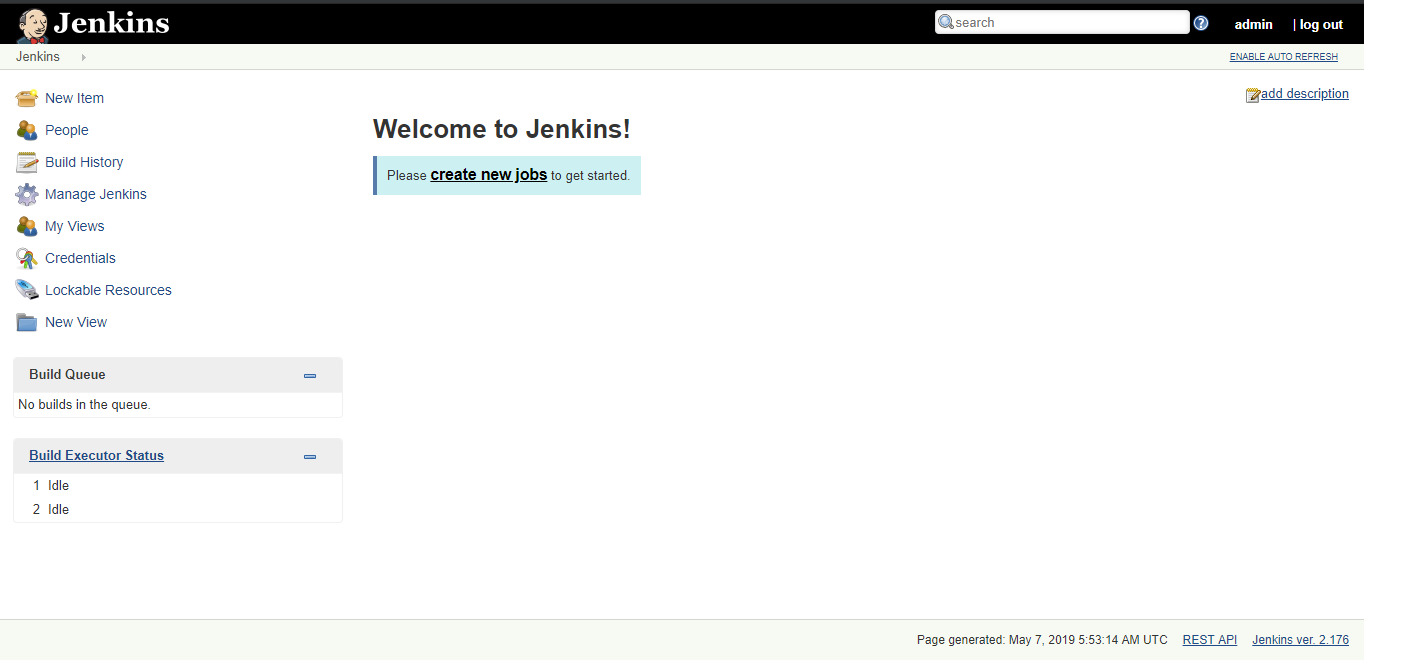
Create a Freestyle Project
Jenkins can be used to perform the builds on servers that work like regular builds and run tests and repetitive tasks.
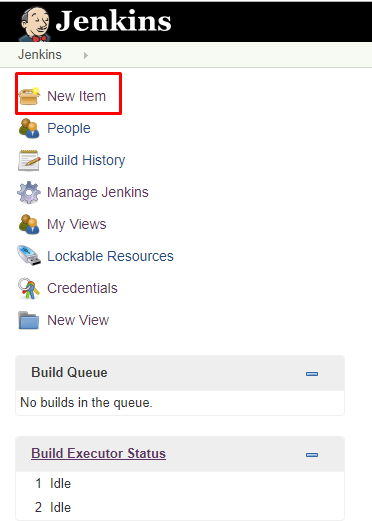
1. Select New Item in the top left-hand corner on the dashboard.
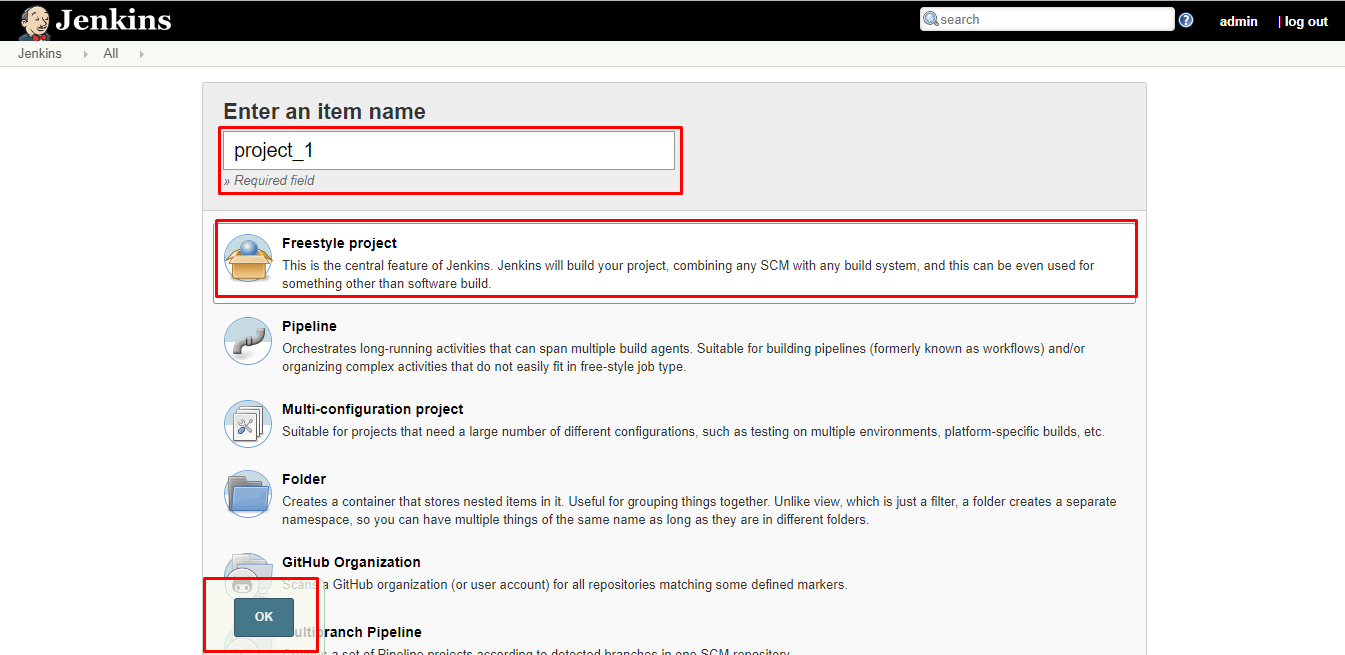
2. Enter the name of your project in the Enter an item name field, and select Freestyle Project, and click OK button.
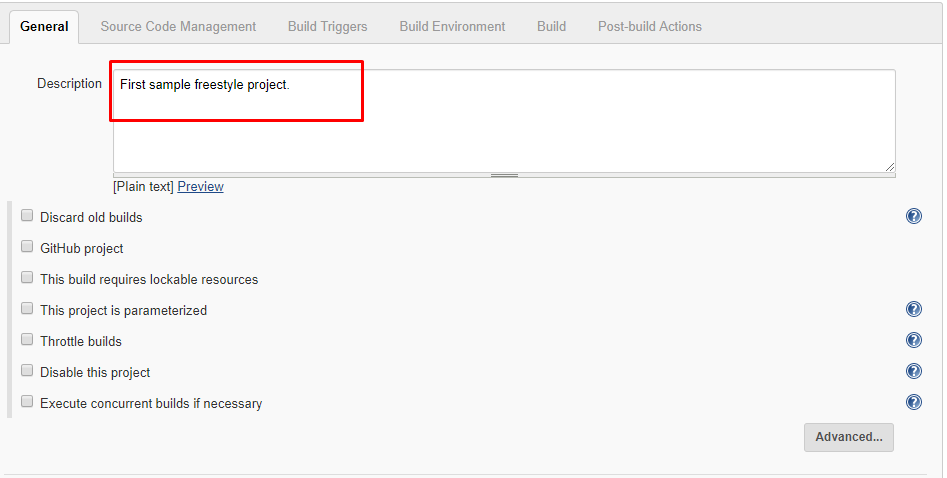
3. Enter Description (optional).
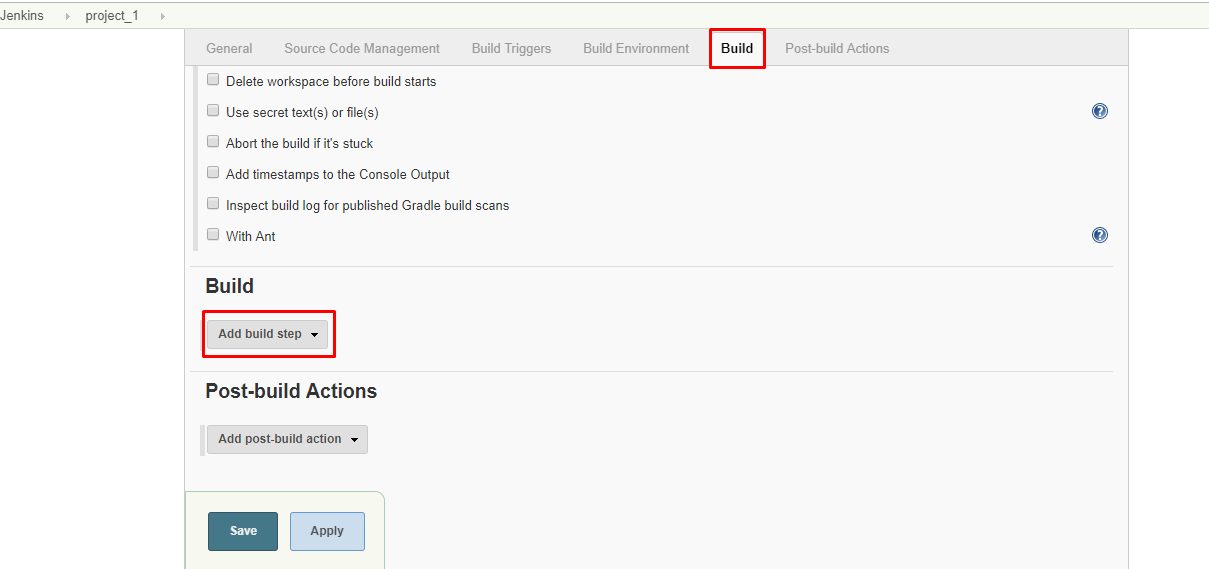
4. Go to the Build section and click on the Add build step.
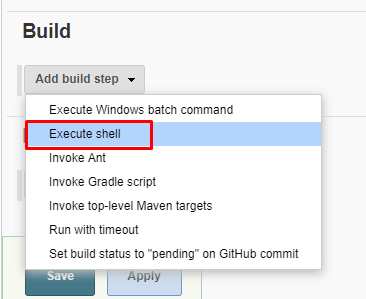
5. Select Execute Shell as a build step.
6. Copy and paste the following command into a command field.
date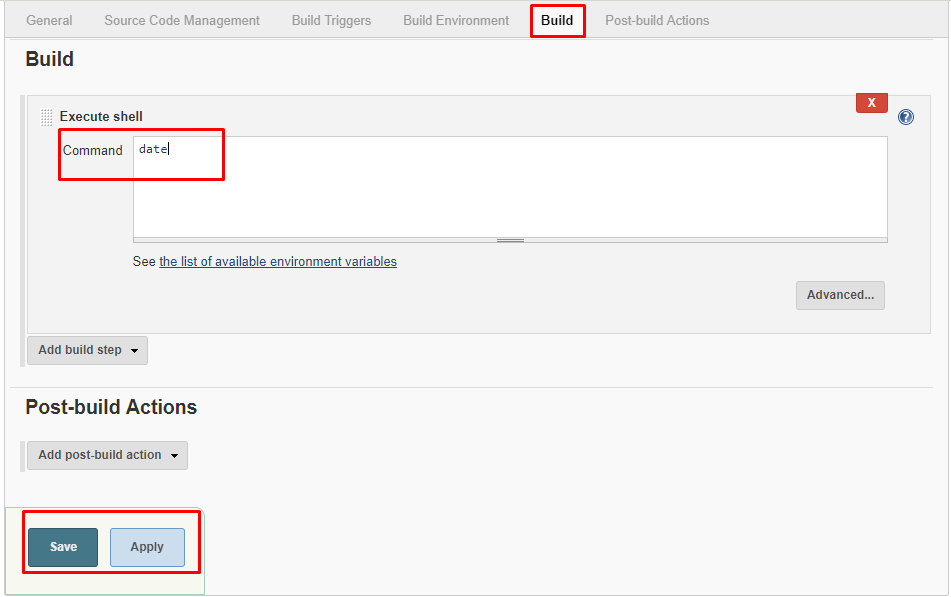
7. Click on Save, and it will redirect to the job's view page.
8. On the left pane, click the Build Now button to execute your job.
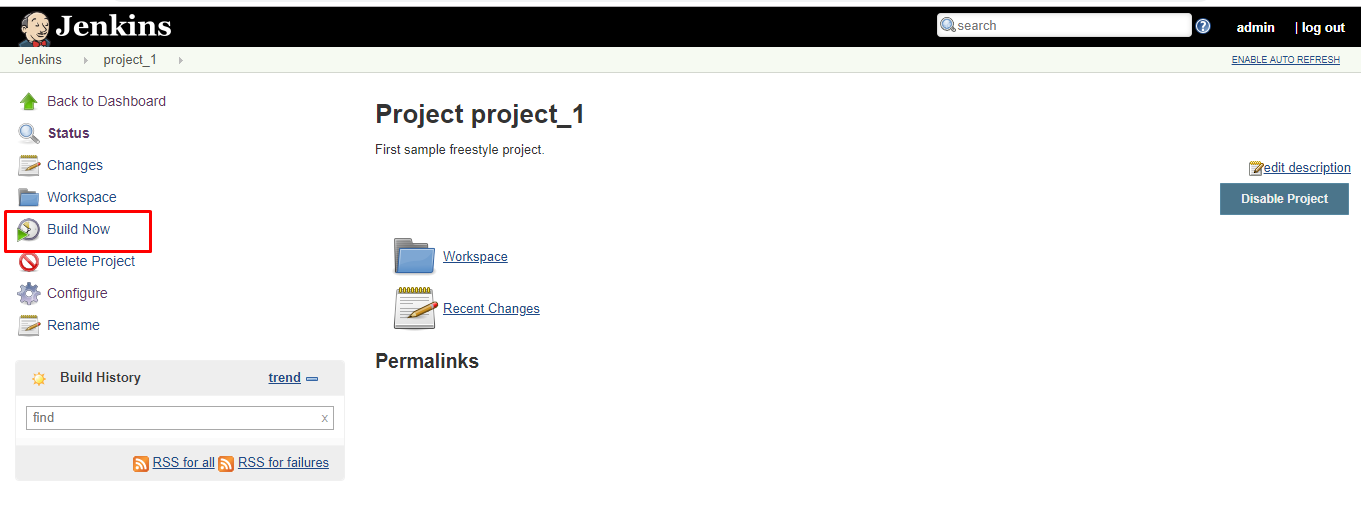
9. We can verify the history of executed build under the Build History by clicking the build number.
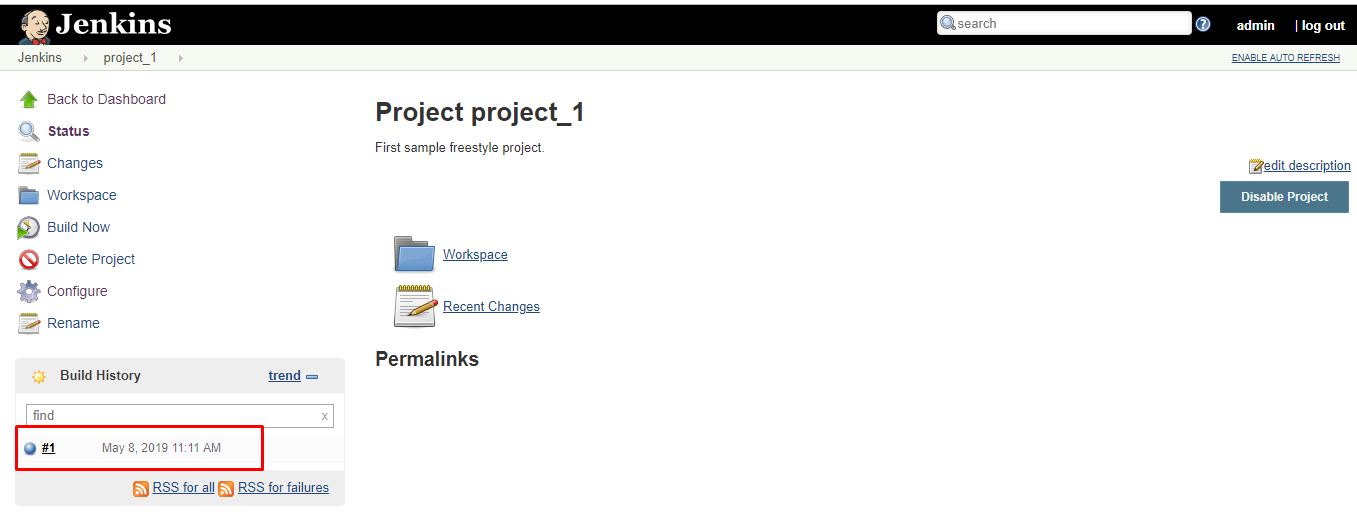
10. Click on build number and select Console Output. Here you can see the outputs of executed commands.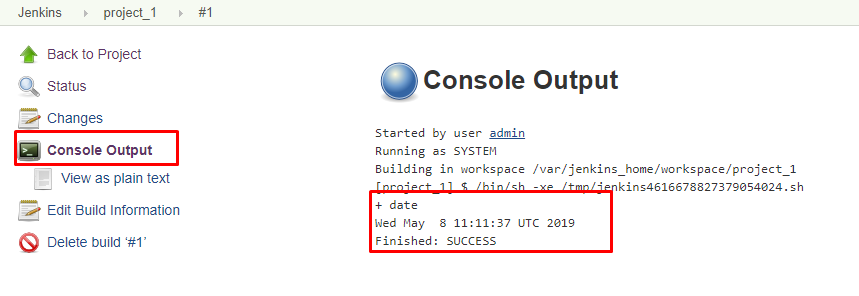
Further Reading
Set Up Jenkins CI in 30 Minutes
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments