Jenkins Pipeline
Pipeline adds a powerful set of automation tools to Jenkins. It supports software delivery from simple continuous integration tasks to comprehensive continuous delivery pipelines. The steps to build, test, and deliver each application become part of the application itself, stored in a Jenkinsfile.
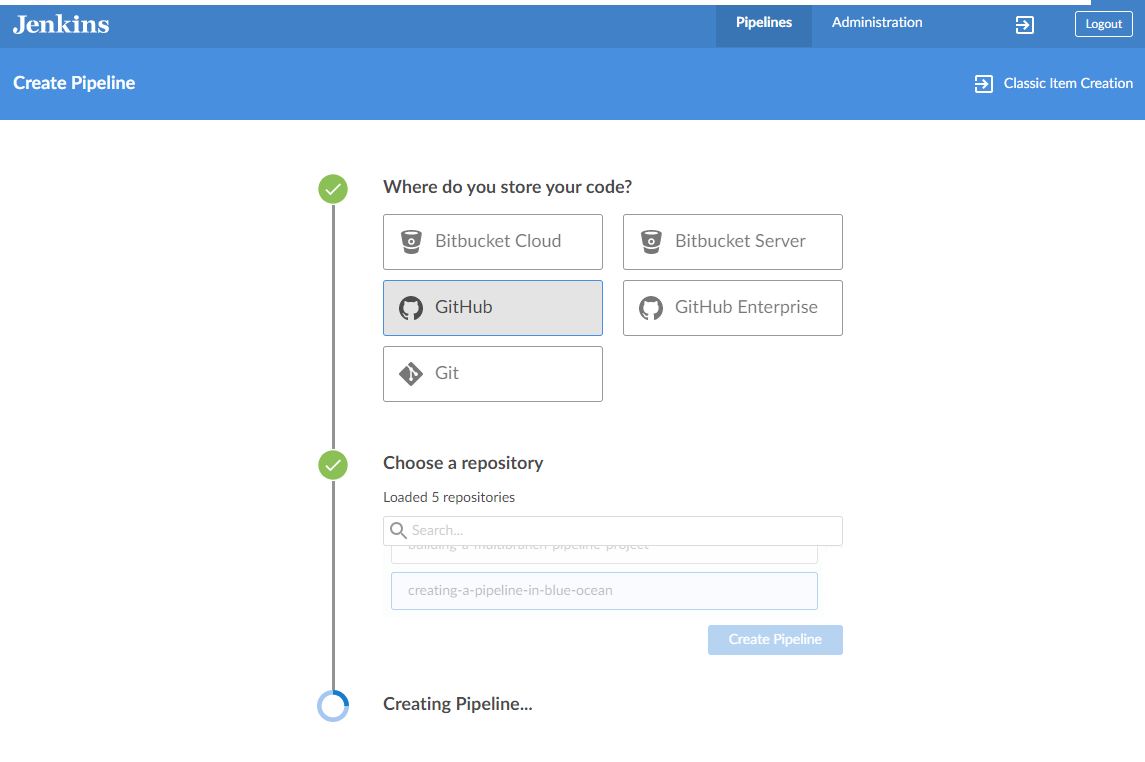
The Jenkins Pipeline provides a domain-specific language to create, edit, view, and run software delivery pipelines. Users of all experience levels can quickly create Jenkins Pipelines using interactive tools included with Jenkins.
This is a preview of the Continuous Delivery With Jenkins Pipeline Refcard. To read the entire Refcard, please download the PDF from the link above.