Practical Guide to SRE: Incident Severity Levels
Incident severity levels are a measurement of the impact an incident has on the business. Classifying the severity of an issue is critical to decide how quickly and efficiently problems get resolved.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free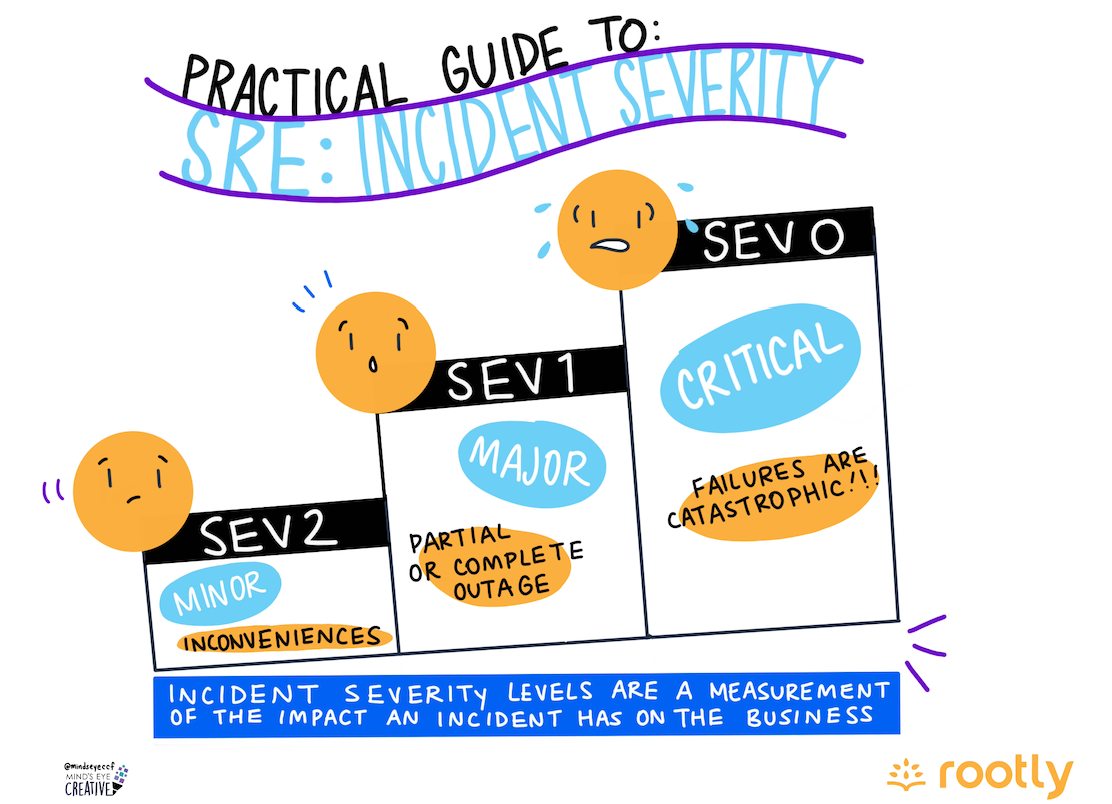
In companies with constant growth and large scale, incidents are inevitable. A robust incident management strategy eventually leads to better management and handling of issues. It is an essential part of reliability engineering, ensuring that a team is prepared to manage incidents. It can prevent the loss of millions of dollars in revenue in times of breaches or downtimes. Good incident management improves customer experience and empowers engineering teams to meet their uptime goals.
In this blog, we will discuss how companies can identify and prioritize incidents for faster resolution. Incidents could vary a lot on the surface level, and hence it is essential to classify them according to specific, well-defined parameters. All incidents are not equal. For instance, a system outage during peak hours is much more stressful than handling when most customers are asleep.
We can categorize incidents into various severity levels. The more well-defined your severity levels are, the more likely it is that your team will be on the same page and able to react quickly and appropriately when incidents happen.
Why Are Severity Levels Useful?
Incident severity levels are a measurement of the impact an incident has on the business. Classifying the severity of an issue is critical to decide how quickly and efficiently problems get resolved. Typically, the lower the severity number, the more impactful the incident.
Allows You to Focus and Prioritize the Task Affecting the Business
Precise severity levels help you to focus on high-priority tasks. For instance, a feature crashing the entire application would be of higher priority than a spelling mistake on a website. Eventually, we focus on resolving the task that could create a business loss.
Leads to a Better Action Plan
Classifying severity levels makes the process of handling bugs smoother. The core value of SEV levels is that they save teams time. It allows creating a proper roadmap for addressing each level and hence enables the team to dive straight into the fix. With well-defined levels, it also reduces and controls the amount of alerting noise. All this leads to a better action plan.
Defining Incident Severity Levels
One of the first steps in classifying severity levels is determining the most critical flows of your applications or services. It helps in determining what constitutes an incident. We can classify incidents by severity using "SEV" definitions. Incidents with a lower SEV number are treated as "major incidents" and warrants a more agile response. When categorizing severity levels, we need to consider various factors other than the impact on business. For instance, the app going down at peak hours will be a huge business loss.
Every organization needs to understand their business, team, and what kind of SEV level definitions work for them. Some organizations classify SEV levels as P0, P1, P2 etc. Broadly, we can categorize it as the following. However, you are free to choose more granular levels than this.
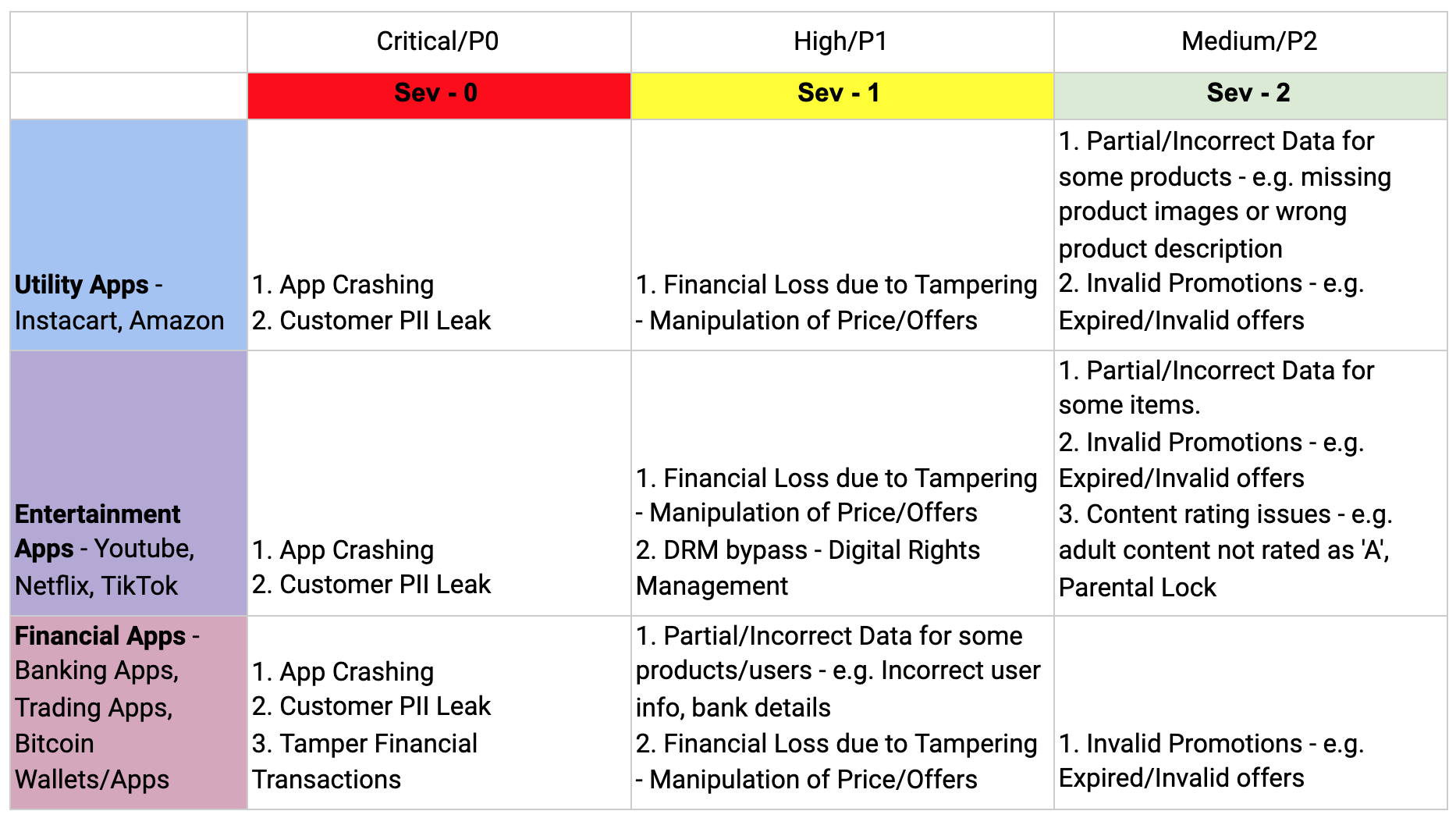
How to Choose These Levels?
SEV 0 or Critical or P0
Failures that are catastrophic in nature such as a security breach or a complete outage that makes your product unavailable for the target audience will come under SEV0. It completely brings the business to standstill and may lead to loss of revenue and/or reputation. A SEV0 incident usually has no quick workaround and requires a coordinated effort across the entire engineering team to fix such an incident.
SEV 1 or Major or P1
SEV1 incidents are issues that cause partial or complete outages on the product, have workarounds or impact a subset of customers. A SEV1 incident, compared to a SEV1, is not a complete outage, but still affects the customer experience. For example, a single feature, such as an outage of the recommendation system in a shopping website is an example of a SEV1 incident. It affects the shopping experience but still allows limited business to go through. Such incidents usually demand immediate attention but are less robust than a SEV1.
SEV 2 or Minor/Moderate or P2
In a SEV2 incident, users are able to complete actions as usual, but experience minor nuisances and inconveniences. Continuing with the example of the shopping website, a few missing descriptions and images could be classified as a SEV2. Such incidents have known quick workarounds and are not difficult to fix.
Conclusion
A well-defined incident severity classification system helps us save time during critical issues by providing guidelines for what needs to be done. Organizations should invest time to define a good incident management process as it leads to fewer disruptions to the business.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments