Custom Rate Limiting for Microservices
Enforcing rate limits on microservices is a common requirement in the API economy. In this article, we are going to build a custom rate limiting solution.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAPI providers use rate limit design patterns to enforce API usage limits on their clients. It allows API providers to offer reliable service to the clients. This also allows a client to control its API consumption. Rate limiting, being a cross-cutting concern, is often implemented at the API Gateway fronting the microservices.
There are a number of API Gateway solutions that offer rate-limiting features. In many cases, the custom requirements expected of the API Gateway necessitate developers to build their own API Gateway. The Spring Cloud Gateway project provides a library for developers to build an API Gateway to meet any specific needs. In this article, we will demonstrate how to build an API Gateway using the Spring Cloud Gateway library and develop custom rate limiting solutions.
Scenario
A SaaS provider offers APIs to verify the credentials of a person through different factors. Any organization that utilizes the services may invoke APIs to verify credentials obtained from national ID cards, face images, thumbprints, etc. The service provider may have a number of enterprise customers that have been offered a rate limit - requests per minute, and a quota - requests per day, depending on their contracts. The following table shows an example configuration that the service provider needs to enforce. The rate limit is measured in requests per minute (RPM) and quota is the number of requests allowed per day, for example.
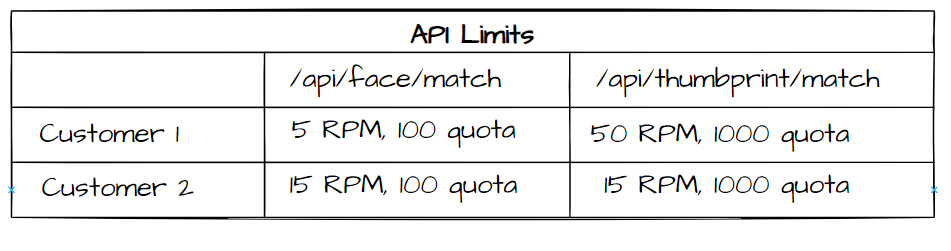
The customer authentication may be passed in the API by different means, e.g., custom headers or a claim in the OAuth2 token. In addition to the limits placed on customers, the service provider also needs to enforce a global rate limit to protect the APIs and ensure reliable service. The RequestRateLimiter filter that comes out of the box with Spring Cloud Gateway does not provide enough features to implement this scenario.
Custom Filters
Spring Cloud Gateway allows us to define custom RateLimiter and invoke them in custom GatewayFilter.
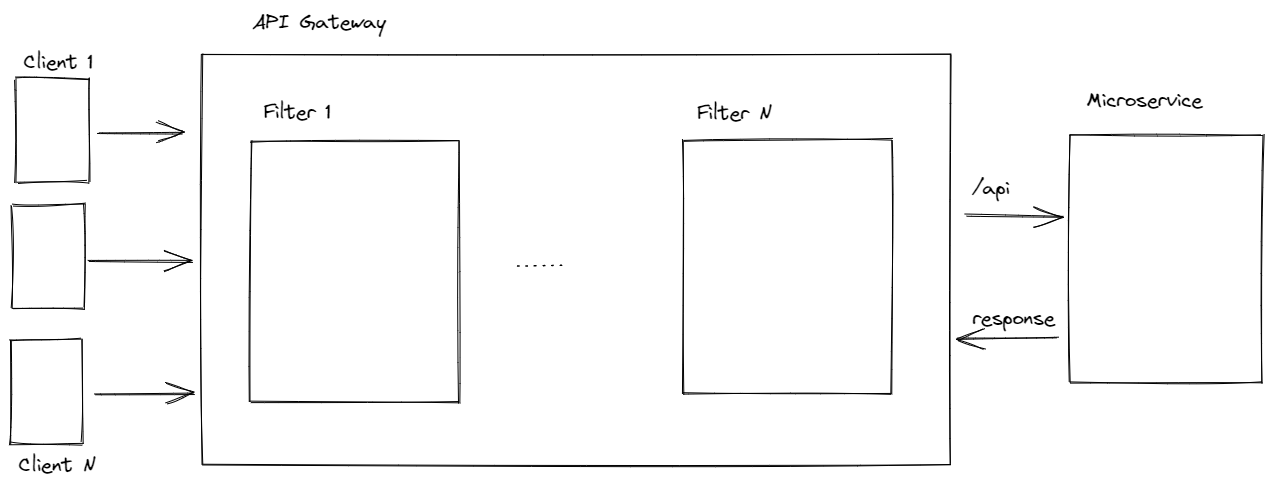
We need to develop two custom Gateway filters:
- CustomerRateLimitFilter: This filter uses a customer rate limiter that reads rate limit configuration from a database or over an API. The custom key resolver fetches customer details and returns a custom key which is a combination of API name and customer identity. It then decides whether to allow or not the request based on the key.
- CustomerQuotaFilter: This filter uses a customer rate limiter that reads quota configuration from a database or over an API. It allows the request if the quota for the customer and the API name is not exhausted for the day.
CustomerRateLimitFilter
To develop this custom gateway filter, we need to provide - CustomerKeyResolver, which will provide a custom key, and CustomerRateLimiter, which will use the custom key to make a rate-limiting decision.
CustomerKeyResolver
Let us say, we want to implement a KeyResolver that will first look for customer identity in a custom header in HTTP Request, and if not found, will look for a claim in OAuth2 token.
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ratelimit.KeyResolver;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWT;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.JWTDecodeException;
import com.auth0.jwt.interfaces.Claim;
import com.auth0.jwt.interfaces.DecodedJWT;
import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
public class CustomerKeyResolver implements KeyResolver {
private static final Logger log = LogManager.getLogger(CustomerKeyResolver.class);
@Override
public Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
String apiName = exchange.getRequest().getPath().toString();
List<String> customerIds = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().get("X-Customer-Id");
if (customerIds != null && ! customerIds.isEmpty() && ! StringUtil.isNullOrEmpty(customerIds.get(0))) {
return Mono.just(customerIds.get(0) + StringUtil.COMMA + apiName);
}
List<String> authHeaders = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().get("Authorization");
if (authHeaders != null && ! authHeaders.isEmpty() && ! StringUtil.isNullOrEmpty(authHeaders.get(0))) {
String jwtString = (authHeaders.get(0).split("\\s+")[1]).trim();
try {
DecodedJWT jwt = JWT.decode(jwtString);
Map<String, Claim> claims = jwt.getClaims();
Claim customerIdClaim = claims.get("customerId");
if (customerIdClaim != null) {
return Mono.just(customerIdClaim.asString() + StringUtil.COMMA + apiName);
}
} catch (JWTDecodeException exception){
log.error("Error while decoding JWT: {}", exception.toString());
}
}
return Mono.just(StringUtil.EMPTY_STRING);
}
}CustomerRateLimiter
A custom RateLimiter implements RateLimiter interface. We can use a rate-limiting library, e.g., Bucket4j which is based on the token-bucket algorithm to implement rate-limiting in our custom rate limiter. To configure the bucket with rate limit configuration, get the customer details from the request and fetch the rate limits configured for the customer. The bucket is then placed in a cache of choice and remains in the cache for the duration. Once the duration is completed, the bucket is removed from the cache.
public class CustomerRateLimiter extends AbstractRateLimiter<CustomerRateLimiter.Config> {
//Initialize Bucket4j
public CustomerRateLimiter(CacheManager cacheManager) {
super(Config.class, CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_NAME, null);
this.multiBucket = Bucket4j.extension(JCache.class)
.proxyManagerForCache(cache);
}
@Override
public Mono<Response> isAllowed(String routeId, String key) {
if (multiBucket == null) {
log.error("Proxy manager multi bucket not initialized");
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Proxy manager multi bucket not initialized");
}
Bucket requestBucket = null;
try {
requestBucket = this.multiBucket.getProxy(key, createBucket(routeId, key));
ConsumptionProbe probe = requestBucket.tryConsumeAndReturnRemaining(NUMBER_OF_TOKEN);
if (probe.isConsumed()) {
Response response = new Response(true, new HashMap<>());
return Mono.just(response);
}
return Mono.just(new Response(false, getHeaders(probe)));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Rate limiting failed: {} ", e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
return Mono.just(new Response(true, new HashMap<>()));
}
private Supplier<BucketConfiguration> createBucket(String routeId, String key) {
// 1. Load configuration from DB or API
// 2. Return a bucket with rate limit configured
}
public static class Config {
}
}Now we can use the custom key resolver and custom rate limiter to implement the custom rate-limiting filter.
public class CustomerRateLimitFilter extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<CustomerRateLimitFilter.Config> {
private final RateLimiter<?> rateLimiter;
private final KeyResolver keyResolver;
public PartnerRateLimitFilter(final RateLimiter rateLimiter, final KeyResolver keyResolver) {
super(Config.class);
this.rateLimiter = rateLimiter;
this.keyResolver = keyResolver;
}
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) {
return new OrderedGatewayFilter((exchange, chain) -> {
Route route = exchange.getAttribute(ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
return keyResolver.resolve(exchange).flatMap(key -> {
if (StringUtil.isNullOrEmpty(key)) {
return handleErrorResponse(exchange, HttpStatus.UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY);
}
Mono<RateLimiter.Response> result = rateLimiter.isAllowed(route.getId(), key);
return result.flatMap(response -> {
response.getHeaders().forEach((k, v) -> exchange.getResponse().getHeaders().add(k, v));
if (response.isAllowed()) {
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
return handleErrorResponse(exchange, HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS);
});
});
}, RATELIMIT_ORDER);
}
public static class Config {
}
}CustomerQuotaFilter
In the same manner, as CustomerRateLimitFilter developed above, we can define a key resolver and a rate limiter to develop a custom filter that enforces quota limits for each customer.
Configure the Custom Filters
We have developed custom filters that will implement custom logic to enforce rate limits and quotas for customers. Let us configure the filters in our API Gateway as shown below in the route configuration. Here, we are applying CustomerRateLimitFilter first, and then CustomerQuotaFilter. This route is applied on API matching the path pattern. It first checks if the requester is adhering to the rate limits and then it checks if the quota is not exhausted. Only then, it routes the API request to the configured URI.
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: face-match-api-route
uri: http://localhost:8800
predicates:
- Path=/face/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- name: CustomerRateLimitFilter
- name: CustomerQuotaFilterIf the filter does not allow the call because it exceeds the limits, we may choose to return HTTP 429 Too Many Requests. Alternatively, we may queue the requests until the remaining time period has elapsed or allow the request immediately but charge extra for this request.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments