Redis Clustering Best Practices With Keys
See Redis clustering best practices.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat is a key anyway in Redis? The original intention of Redis (or any key-value store) was to have a particular key, or identifier, for each individual piece of data. Redis quickly stretched this concept with data types, where a single key could refer to multiple (even millions of) pieces of data. As modules came to the ecosystem, the idea of a key was stretched even further because a single piece of data could now span multiple keys (for a RediSearch index, as an example). So, when asked if Redis is a key-value store, I usually respond with "it descends from the key-value line of databases" but note that, at this point, it's hard to justify Redis as a key-value store alone.

One place, however, where keys in Redis are still vitally important is clustering. In Redis, data resides in one place in a cluster, and each node or shard has a portion of the . Of course, when running with high availability, your data may reside in a replica, but at no point is a single key split among multiple nodes.
A cluster is divided up among 16,384 slots - the maximum number of nodes or shards in a Redis cluster (if you have that many, get in touch with us!). Since most clusters consist of a much smaller number of nodes, these hash slots are logical divisions of the keys. In an oversimplified example of a 4-node cluster, we'd have the following layout:

Note: In Redis Enterprise, there is a further division into shards on each node. It is done the same way, but instead of nodes it's divided into shards.
As an example, if you have a key that you know is in slot 2,000, then you know the data resides on Node #0. If the key is in slot 9,000, then it's on Node #2. In reality, it's much more complex than this (with slots moving and rebalancing all the time), but for the purposes of understanding transactions and keys, this simplified conceptual understanding of clustering will do.
So how are keys related to slots? These slots are actually hash slots, in which each key is put through a hashing function to mathematically derive a single number from a string of characters of any length. Hashing enters public conversations most often when it comes to password hashing, which is a related but much more complex calculation. In the same way, your password is not directly stored, but rather a mathematical representation of that password, the key you request actually boils down to its mathematical representation (in this case with the CRC16 hashing function). CRC16 will return a 14-bit number we can then modulo by 16384. Interesting coincidence that this is the number of hash slots available, no?
How Does This All Relate to Transactions in Redis?
Transactions in Redis only occur within the same hash slot, which ensures the highest throughput. Since there is no inter-node/shard communication is needed, many failures scenarios are eliminated. Given this, you have to be sure that when you go out to do a transaction, all the keys involved are on the same slot. So, how do you if your key is on the same slot (and the same node/shard) as another key in a transaction?
While it is possible for many keys to be in the same hash slot, this is unpredictable from a key naming standpoint and it's not sane to constantly check the slot (with CLUSTER KEYSLOT in open source or Enterprise in Cluster API mode) when naming keys. The best way to approach this is with some advanced planning and a feature called hash tags. In open source Redis, curly braces ({ and }) are signifiers of a hash tag and the string between these two characters is put through the CRC16 hashing function. Let's take a look at a few examples:
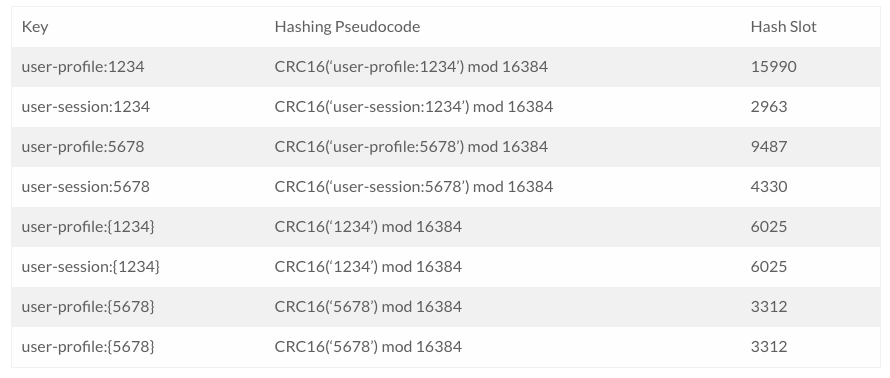
Given these examples, you can see that Redis would not allow a transaction over keys user-session:1234 and user-profile:1234, but would allow one with user-profile:{1234} and user-session:{1234}.
Note: You might think, "Great, put everything under one hash slot and I won't have to worry about clustered transactions!" You wouldn't be alone, as I've heard this ill-guided plot more than once. Redis won't stop you from doing this or similar things, but you'll end up with an unbalanced cluster, or worse, one full node and many empty nodes. Use hashtags only when needed and, even then, sparingly.
Redis Enterprise can use this strategy but it also adds another feature to make sharding more transparent. Instead of using curly braces, you can use regular expressions to define a particular part of the key to be put through the hashing function. With the regular expression /user\-.*\:(?<tag>.+)/ let's revisit some of our examples from above:
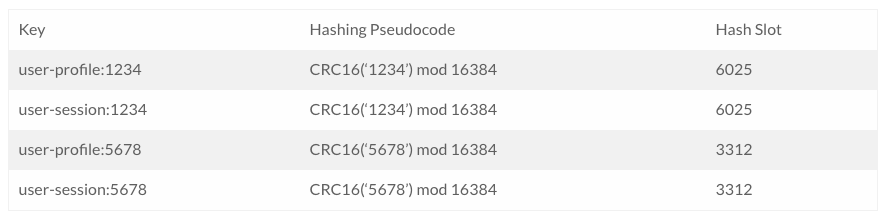
This regular expression would be flexible enough to also handle other keys that start with "user-", so we could have keys like "user-image" or "user-pagecount". In this scheme, each user's information would be kept on a single hash slot, enabling all sorts of transactions to occur within the scope of a single user.
Let's extend this example a bit further. Say a user changes some information on their profile and we want to update both the profile and session information, and also extend their session so it doesn't expire. Here is a typical (if simplified) version of a transaction:
> MULTI
OK
> HSET user-profile:1234 username "king foo"
QUEUED
> HSET user-session:1234 username "king foo"
QUEUED
> EXPIRE user-session:1234 7200
QUEUED
> EXEC
1) (integer) 1
2) (integer) 1
3) (integer) 1This would work just fine in Redis Enterprise with the regular expression setup because the hashed portion of both the keys are the same. If you were to run this on open source Redis, you’d need to make sure your keys have curly braces, otherwise, you’d encounter a CROSSSLOT error. The nice thing about this type of error is that Redis will immediately notify you of the invalid transaction/slot crossing violation:
> MULTI
OK
> HSET user-profile:1234 username "king foo"
QUEUED
> HSET user-session:1234 username "king foo"
(error) ERR CROSSSLOT Keys in request don't hash to the same slot (command='HSET', key='user-session:1234') within 'MULTI'
> EXPIRE user-session:1234 7200
(error) ERR CROSSSLOT Keys in request don't hash to the same slot (command='EXPIRE', key='user-session:1234') within 'MULTI'
> EXEC
(error) EXECABORT Transaction discarded because of previous errors.Keep in mind that some hash slots and key issues are not quite transactions, but are somewhat similar in behavior — single commands that operate over multiple keys. Take this example:
> LPUSH my-list 1 2 3
(integer) 3
> RPOPLPUSH my-list my-new-list
(error) ERR CROSSSLOT Keys in request don't hash to the same slot (command='RPOPLPUSH', key='my-new-list')RPOPLPUSH is an atomic operation that takes an element off one list and pushes it onto another. The operative word is atomic. If these two lists reside on two different hash slots (much like in a transaction), you'll get the CROSSSLOT error. Open source Redis is quite strict about this and any command that manipulates multiple hash slots is forbidden. Redis Enterprise has a few workarounds for simple commands, notably MGET and MSET.
Getting the Most out of Your Cluster
If you've been a power user of a single instance of Redis, moving to a cluster can feel a bit odd. Some of the commands and/or transactions you've relied on will no longer work on specific keys, and if you're really unlucky, the way you designed your keyspace could be problematic. Here are a few tips for designing your application to work best on a cluster:
- Think about the keyspace. Is there a common feature of the key that divides your workload in a smart way (by users, by operation, by time, etc.)? Use hashtags or regular expressions to smartly divvy up the keys into hash slots.
- Avoid global state under a single key that needs to be transactionally manipulated, otherwise you're likely to run into CROSSSLOTS errors.
- Evaluate your MULTI/EXEC transactions. See if you truly need a transaction or if a pipeline will do. Don't forget to think about multikey commands and whether they can be replaced by multiple commands.
Published at DZone with permission of Kyle Davis, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments