Redis Replication vs Sharding
Replication and sharding can both be helpful in providing for these needs. Whether your database is in need of one, the other, or both, it is helpful to know what each of these does.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat Is Database Replication?
Replication, also often called mirroring, is simply copying all of the data to another location. This allows data to be pulled from two or more locations, which ensures high availability. It can also be quite helpful should the main data location go down for some reason, as the data can still be read from one of the replicas.
In Redis, you can set up replication once you have at least one slave installation (Redis uses a master/slave(s) setup for replication). In the slave configuration file, you use the slaveof command, as in the following example.

If you set a master password, you will also need to set it in the masterauth setting. Once this is done, you can start (or restart) the Redis service on the slave to enable replication.
What is Database Sharding?
Sharding, also often called partitioning, involves splitting data up based on keys. This increases performance because it reduces the hit on each of the individual resources, allowing them to share the burden rather than having it all in one place.
For example, you can use a hash function on your Redis keys to turn them into numbers. Then, if you want two shards, you can send all the even-numbered keys to one instance while placing all of the odd-numbered keys to the second instance. This could be done using other algorithms for different numbers of shards.
Redis sharding can be implemented in several ways:
Client side partitioning: Clients select the proper Redis instance to read or write a particular key.
Proxy-assisted partitioning: A proxy is used to handle requests and send the requests to the proper Redis instance.
Query routing: The query is sent to a random instance, which then takes on the responsibility of redirecting the client to the proper Redis instance.
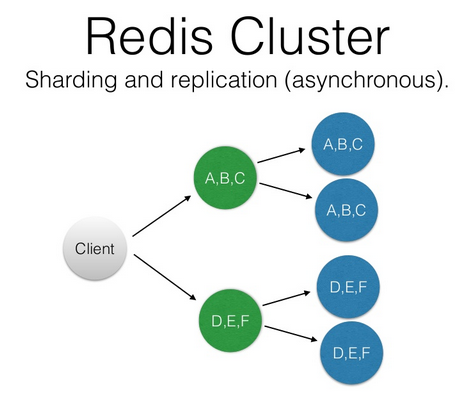
Using Replication and Sharding Together
If you want both high availability and improved performance, both replication and sharding can be used together to provide this. With sharding, you will have two or more instances with particular data based on keys. You can then replicate each of these instances to produce a database that is both replicated and sharded, which will provide for reliability and speed at the same time!
Whether you're using Redis or focusing on Sharding, Morpheus can help make your job easier. Check it out here.
Published at DZone with permission of Darren Perucci, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments