RESTful Web Services With Spring Boot, Gradle, HATEOAS, and Swagger
Let's look at RESTful web services with Spring Boot, Gradle, HATEOAS, and Swagger.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWebservices are services that are exposed to the Internet for programmatic access. Those are online APIs that we can call from our code.
Additionally, REST stands for the Representational State Transfer. It's basically an architectural set of guidelines. REST uses already existing HTTP concepts. Because of this, we can use this style of architecture to implement web services. And when we apply REST to our web services, it's called RESTful Web Services.
Even though there are no strict rules, our RESTful web services can be determined by the Richardson Maturity Model. It's a guideline for designing RESTful APIs. As developers, while developing RESTful web services, we should make is as RESTful as possible.
Richardson Maturity Model
Level 0: No HTTP concept is being used, like SOAP, the same URL for many operations. Operations are defined in the message itself.
Level 1: Resource URIs. Individual URI for each resource
Level 2: HTTP methods and status codes are used appropriately
Level 3: Using HATEOAS, ie. responses have links that clients can use
HATEOAS: Hypermedia As The Engine Of Application State
HATEOAS is a component of the REST application architecture that distinguishes it from other network application architectures. With HATEOAS, a client interacts with a network application whose application servers provide information dynamically through hypermedia. A REST client needs little to no prior knowledge about how to interact with an application or server beyond a generic understanding of hypermedia.
Advantages of HATEOAS
- Required APIs could be easily found without any specific documentation
- Make the response navigable with links to common resource URIs
- Get the message URL of the response itself
- If any URL changes from the server-side, there's no need to do any change on the client-side
- If we follow proper HATEOAS, the client actually doesn't need to spend much time understanding API documentation. As an end-user, we don't have to go through documentation every time we visit a new website. We just go to the homepage and go through the links. With HATEOAS, the web service is super helpful to the clients.
HATEOAS is very important in implementing web services. But there's a big problem because different developers can implement HATEOAS in various different ways. I mean, they can structure the JSON response in any format they want, and it can lead to a lot of confusion, and the main objective of HATEOAS wouldn't be achieved. Developers would have to learn how to use various different formats. Some standardization would really simplify the use of web services, particularly open source libraries.
HAL: Hypertext Application Language
HAL is one of the simplest and most widely adopted hypermedia media types adopted when not discussing specific web stacks. It was the first spec-based media type adopted by Spring HATEAOS. In HAL, the _links entry is a JSON object. The property names are link relations, and each value is either a link object or an array of link objects.
HAL is an Internet Draft (a "work in progress") standard convention for defining hypermedia such as links to external resources within JSON or XML code (however, please note that the latest version of HAL Internet-Draft expired on November 12, 2016.). The standard was initially proposed on June 2012, specifically for use with JSON[1] and has since become available in two variations, JSON and XML. The two associated MIME types are media type: application/hal+xml and media type: application/hal+json.
Swagger
Swagger is one of the most popular document format for RESTful webservices. Using Swagger developers can provide very rich API documentation with minimum effort. Also, using Swagger we can test the RESTful APIs, as it comes with inbuild HTTP client.
In this example, we will be using Spring Boot, Gradle, Java (version 8 or above), HATEOAS, and Swagger. Let's understand the APIs we are developing. It's a simple Book application. For simplicity, we won't be using any database, we will create some data in the code itself.
Book can have the following basic properties:
- bookId
- isbn
- title
- author
- priceInINR
Below are the APIs that we are going to implement:
- Retrieve all books: GET /books/all
- Create a book: POST /books
- Retrieve a particular book by ISBN: GET /books/isbn/{isbn}
- Retrieve books by author: GET /books/author/{author}
In the "/books/all" API response for individual books, it would have a link to itself.

Request body for creating a book:
{
"isbn": "1234567891",
"title": "Book Title-2",
"author": "Author-1",
"genre": "Thriller",
"priceInINR": 900
}Response:
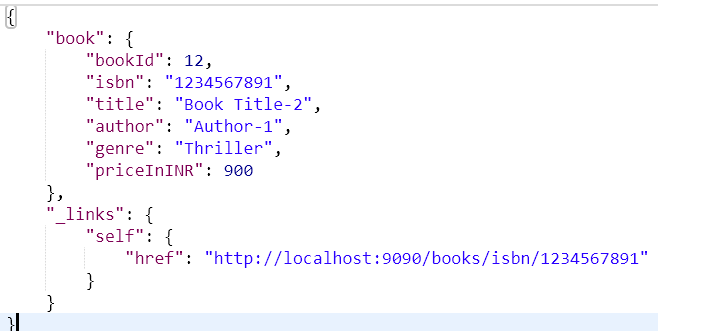
Just check we have a link to the book created in the API response.
Similarly for the API "/books/isbn/{isbn}", in the response, there's a link to retrieve all the books by the same author. Below is a sample response:
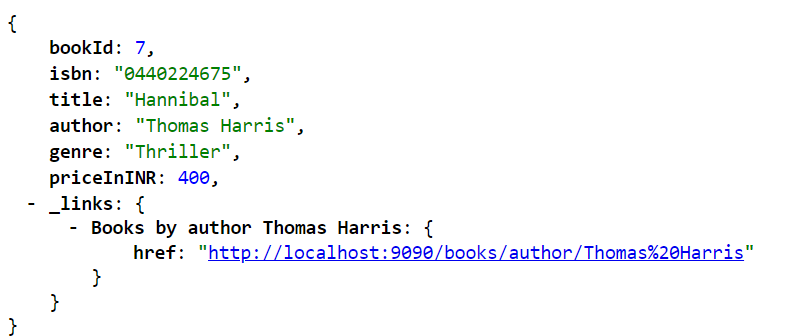
Below is the response for the API "/books/author/{author}":

Finally, let's understand Swagger.
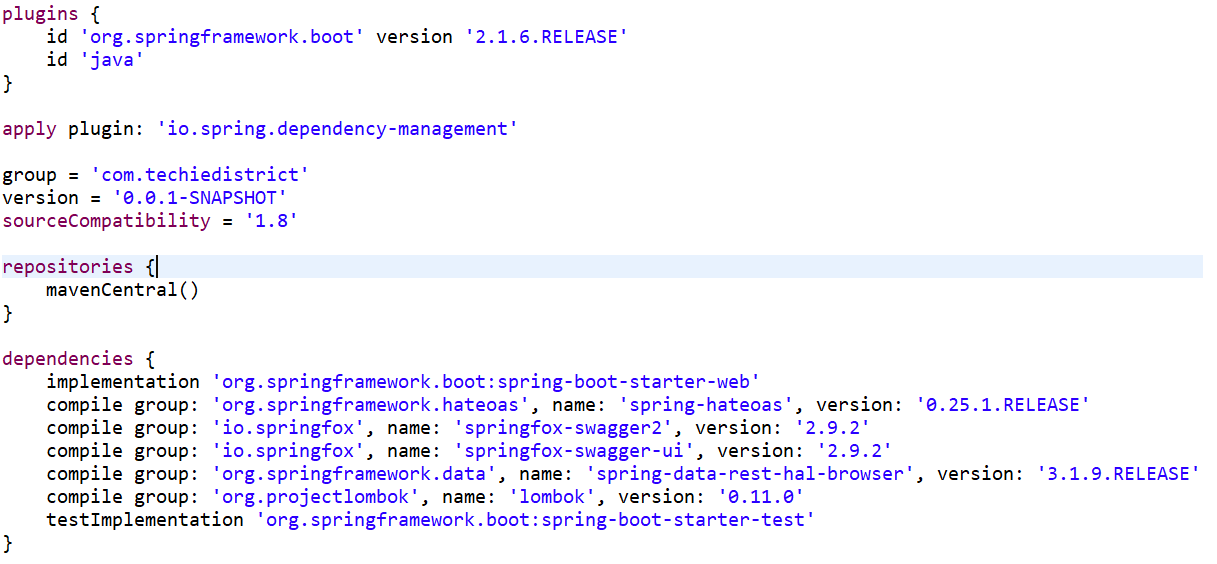
Below are the Gradle dependencies required for the application:
Below are the two Swagger URLs we can use:
http://localhost:9090/v2/api-docs

http://localhost:9090/swagger-ui.html
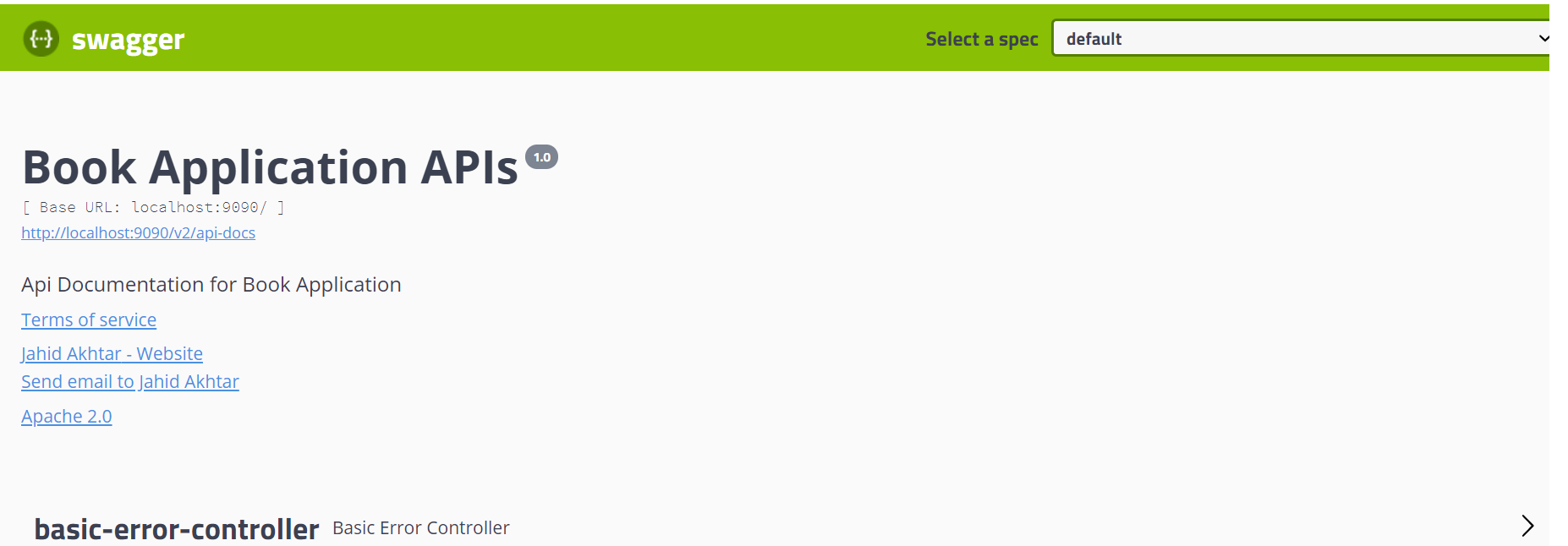
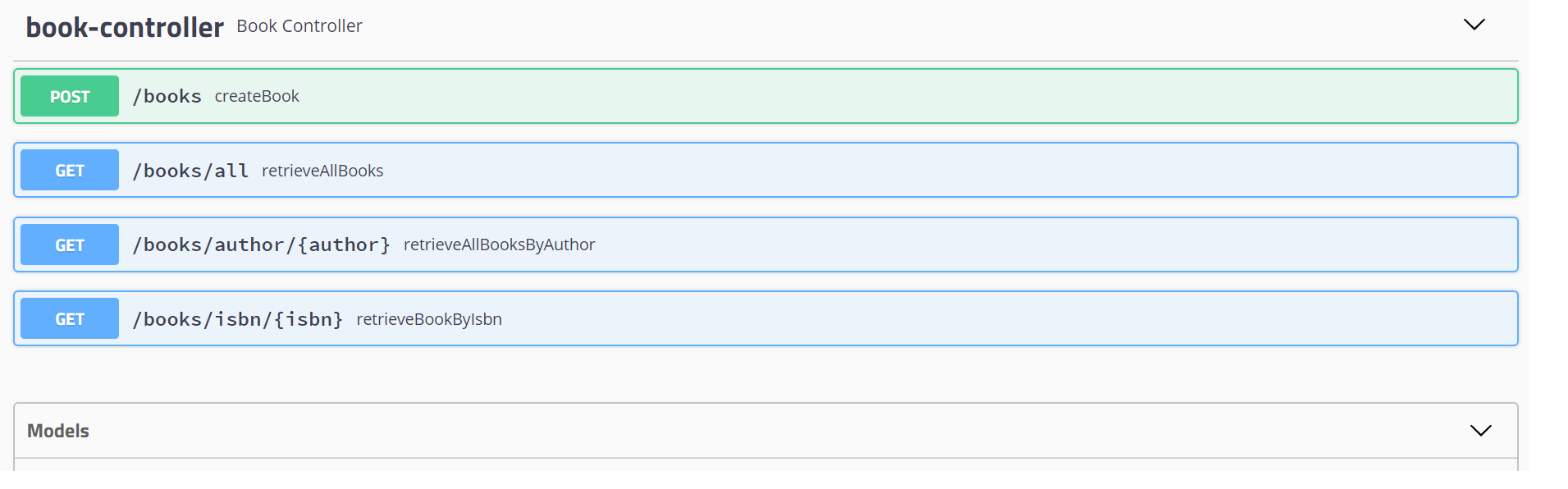
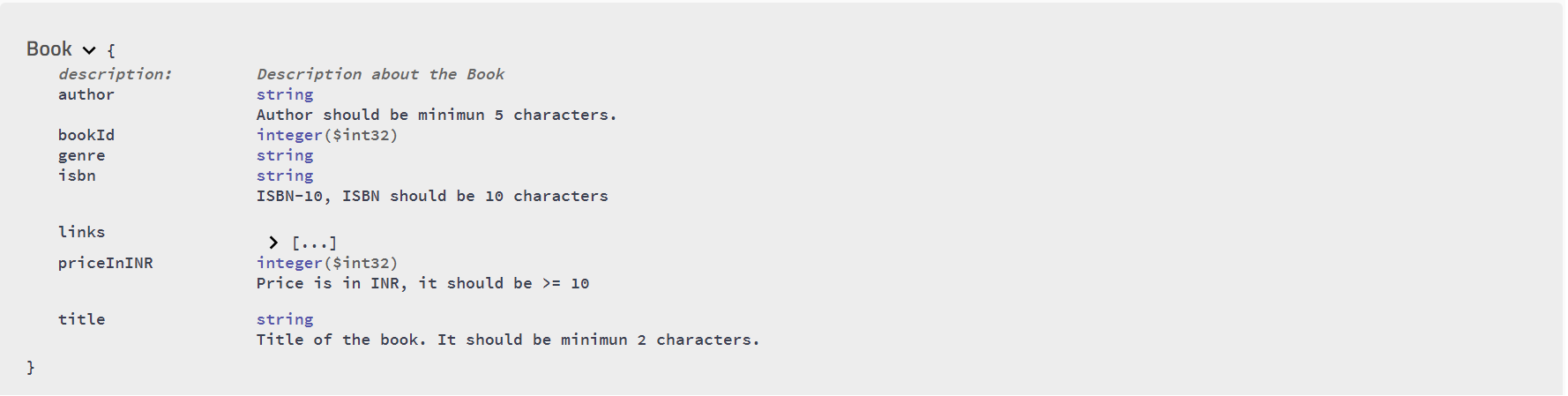
As you can see, Swagger creates quite a rich API documentation. There are a lot of options in Swagger API to enhance the API documentations. I've simply used a few of them. You can download the code from GitHub.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments