A Scalable Java Thread Pool Executor
The Java Thread Pool Executor is biased towards queuing rather than spawning new threads. On the bright side, we've got couple of workarounds.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIdeally, from any thread pool executor, the expectation would be the following:
- An initial set of threads (core threads pool size) created up front, to handle the load.
- If the load increases, then more threads should be created to handle the load up to max threads (Max pool size).
- If the number of threads increases beyond Max Pool Size, then queue up the tasks.
- If Bounded Queue is used, and the queue is full, then bring in some rejection policy.
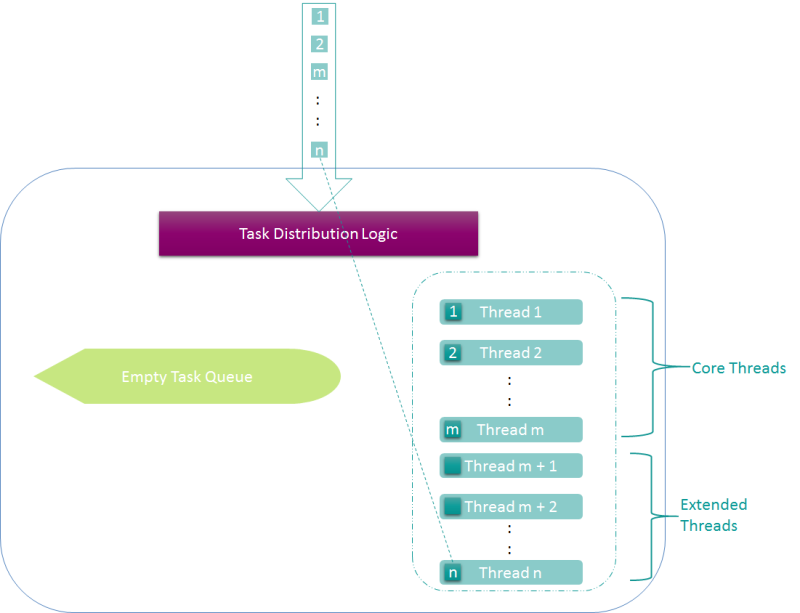
The following diagram depicts the process; only initial threads are created to handle tasks (when load is very low).
As more tasks come in, more threads are created to handle the load (task queue is still empty), assuming the total number threads created is less than max pool size.
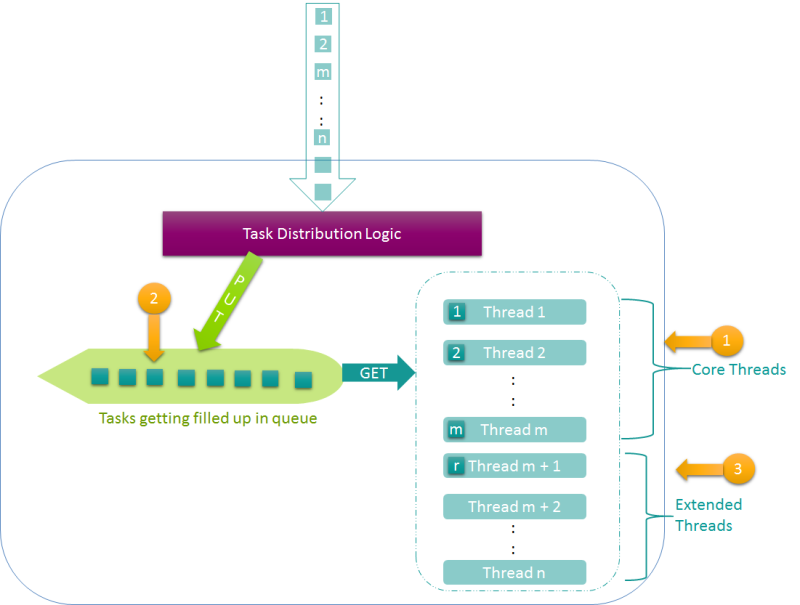
The Task Queue starts to fill if the total number of tasks is more than total number of threads (initial + extended):
Unfortunately, Java Thread Pool Executor (TPE) is biased toward queuing rather than spawning new threads, i.e., after the initial core threads get occupied, tasks gets added to queue, and after the queue reaches its limit (which would happen only for bounded queues), extra threads would be spawned. If the queue is unbounded, then extended threads won’t get spawned at all, as depicted in the following image.
Initial core threads were created to handle the load.
Once there are more tasks than the number of core threads, the queue starts filling up to store the tasks.
Once the queue is filled, extended threads are created.
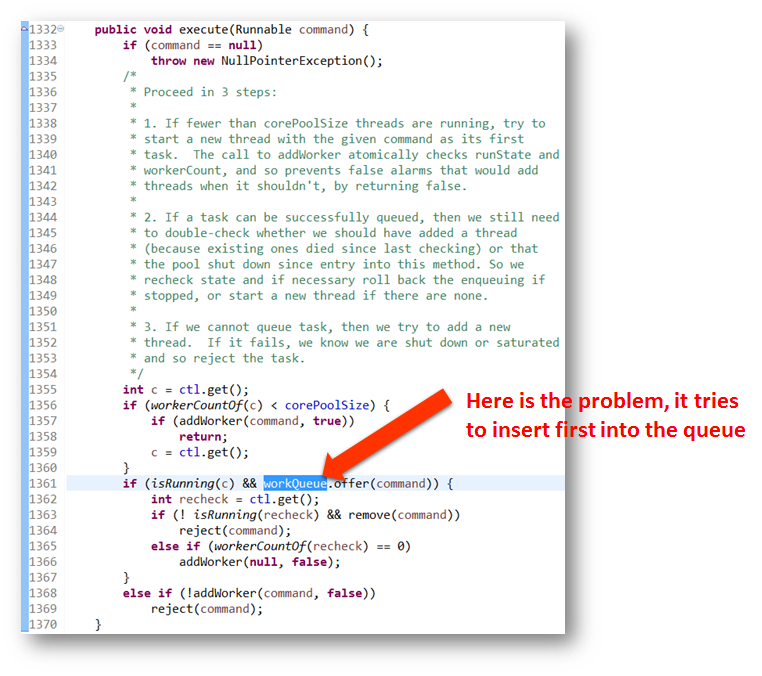
Here is the code in TPE, which has problem
We have got a couple of workarounds:
Workaround #1: Tweaking the Pool Sizes
Set the corePoolSize and maximumPoolSize to the same value and set allowCoreThreadTimeOut to true.
Pros
- No coding hack required.
Cons
- There is no real caching of threads, as threads are getting created and terminated quite often.
- There is no proper scalability.
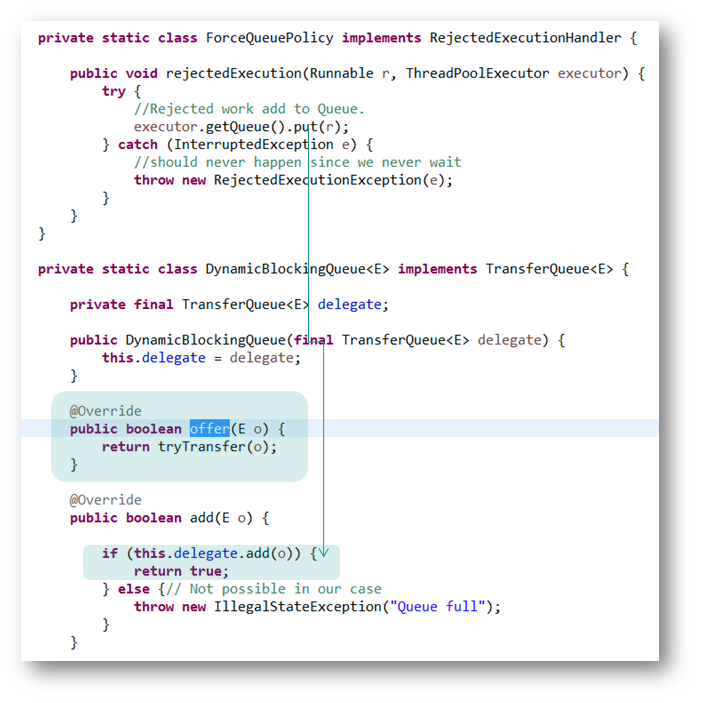
Workaround #2: Override the Offer Method
- Override the offer method of delegator TransferQueue and try to provide the task to one of the free worker threads. Return false if there are no waiting threads.
- Implement a custom RejectedExecutionHandler to always add to the queue.
Refer to this implementation for more detail.
Pros
- TransferQueue ensures that threads are not unnecessarily created, and transfers the work directly to waiting queue.
Cons
- Customized rejection handler cannot be used, since it is used to insert the the tasks to queue.
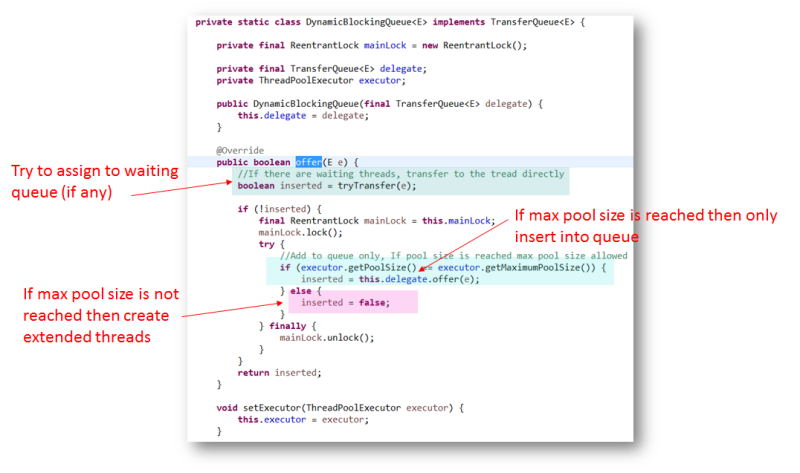
Workaround #3: Use a Custom Queue
Use a custom queue (TransferQueue) and override the offer method to do the following:
- Try to transfer the task directly to a waiting queue (if any).
- If the above fails, and max pool size is not reached, then create an extended thread by returning false from the offer method.
- Otherwise, insert it into the queue.
Refer to this implementation for more detail.
Pros
- TransferQueue ensures that threads are not unnecessarily created and transfers the work directly to a waiting queue.
- A custom rejection handler can be used.
Cons
- There is a cyclic dependency between Queue and Executor.
Workaround #4: Use a Custom Thread Pool Executor
Use a Custom Thread pool executor specially dedicated for this purpose. It uses LIFO scheduling as described in Systems @ Facebook scale.
Published at DZone with permission of Mohammad Nadeem, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.



Comments