Scaling a Node JS Application
Learn more about scaling a Node JS application.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhenever we build an awesome product we first build it standalone but sooner or later it attracts more users and then our minds start thinking about how to accommodate more users and there comes the need of scaling the application. Generally scaling means providing more elasticity to the application so that it can sustain the high influx of users and run smoothly without any glitches.
Software scalability is an attribute of a tool or a system to increase its capacity and functionalities based on its users’ demands. Scalable software can remain stable while adapting to changes, upgrades, overhauls, and resource reduction
So we need the right software protocols and hardware aligned to meet a high number of requests per minute (RPM). Software applications can be written in a way where it just works. On the other hand, it can be written in a way with software scalability, maintenance, and resilience in mind.
Scalability can happen in two ways either horizontal or vertical scaling.
Vertical scaling means adding more power to your server like more ram, increasing CPU strength and many more so that it handles more no of concurrent requests but the problem with the vertical scaling is that at a certain point it has some limits like some time you will get into resource deficient state. The second option we have is horizontal scaling was run the service on multiple servers and whenever requests come it gets load balanced between these servers and the responses are provided. For more details please refer to this video.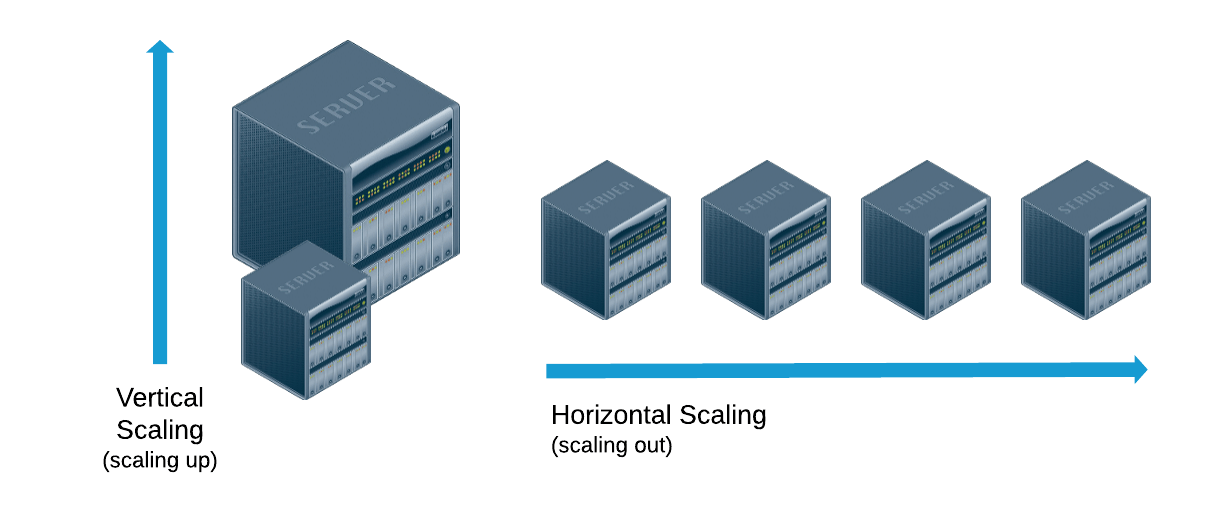
In this blog, we will mainly focus on horizontal scaling and we will build up a small Node JS application, and then we will scale it horizontally.
Prerequisites:
- Node version: v14.19.0
- Npm version: v6.14.16
- Docker Installed on your machine: Docker version 20.10.12. and docker-compose installed on your machine.
I have created a node JS application and below is the code written in the index.js file.
const http = require(‘http’);
const port = process.env.PORT || 5000;
const os = require(‘os’);
const handler = (request, response)=> {
if(request.method === ‘GET’ && request.url === ‘/’) {
return response.end(`Hello world! My hostname/container ID is: ${os.hostname} and no of core s : ${os.cpus.length}`);
}};
const server = http.createServer(handler);
server.listen(port, ()=> {
console.log(`Application listening on port ${port}`);
});In the above index.js, I have created a naive node js application running on port 5000, and in order to start the node js service just run the below command
node index.jsand the node service can be reached over localhost:5000.
We did create a simple node JS service but the problem here is that it has a limitation on the number of requests it can handle and if suppose the node service crashes down then our service will be in a not reachable state which we never went want to happen. So in order to tackle this issue, I came up with a plan to handle this, here I will containerize the application so that in a single server we can run multiple instances of node JS service, and on top of the instances I will add a load balancer so the on receiving the requests, the load balancer will route to any of the available instances based on the load balance algorithm. So to containerize the node service we need to create an image and start a container based on the created image. I have created a Dockerfile from which a docker image will be created.
FROM node:17-alpine3.14
USER root
RUN mkdir /home/appWORKDIR /home/app
COPY — chown=node:node package.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY — chown=node:node . .
CMD [“node”, “src/index.js”]Below steps are required to run the container out of it.
1. Run docker build --tag="node-app-1" .
2. Run docker run --publish 5000:5000 node-app-1 .
Now the node service is running inside a container and the service can be reached over localhost:5000.
Now we need to create multiple instances and add a load balancer to them. For creating multiple instances we will take the help of docker-compose which will help us to efficiently start the containers and stop their containers. And for load balancing I will NGINX. Now we need to create a docker-compose.yaml file.
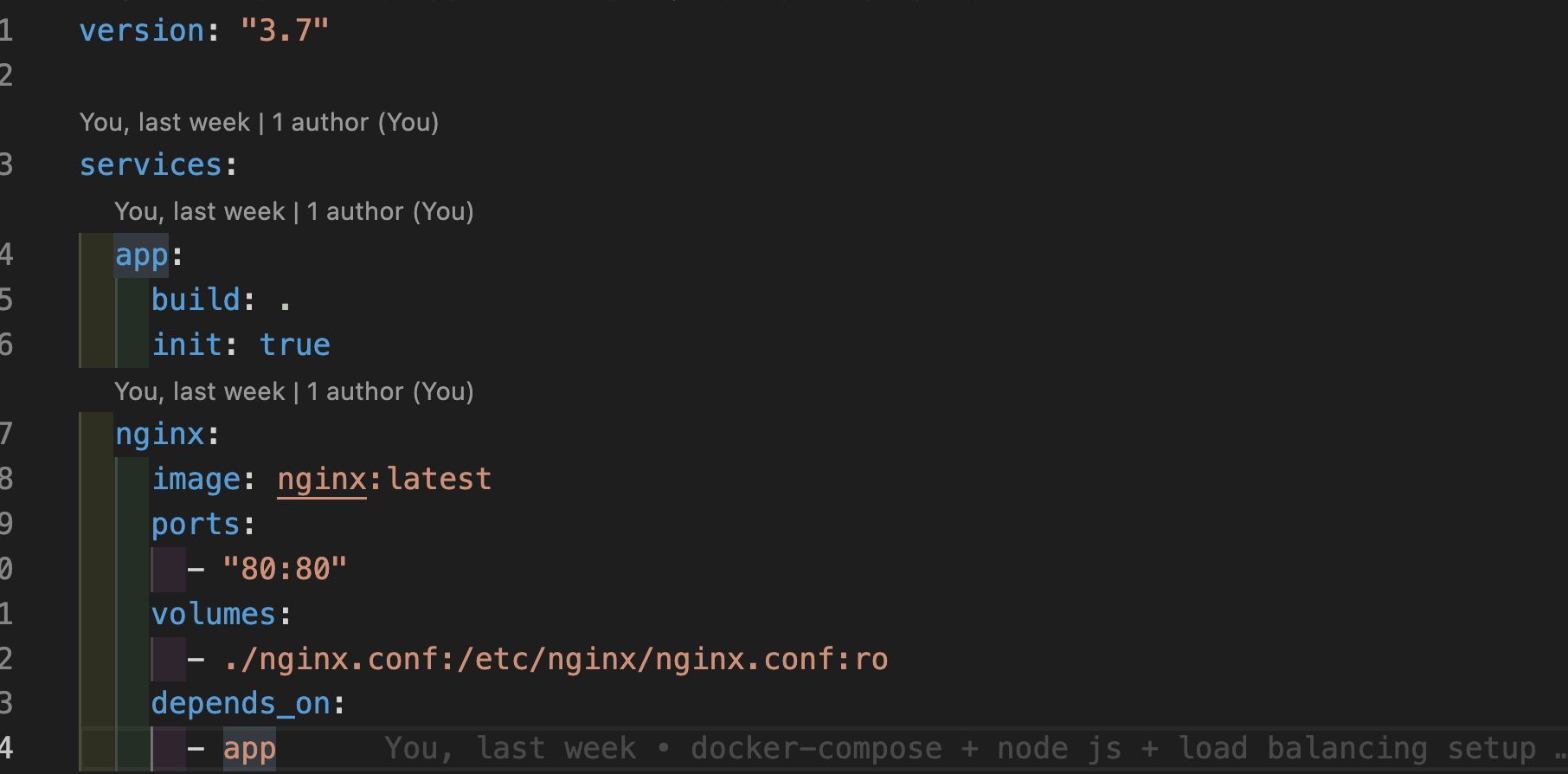
For more information on docker-compose please visit the official website.
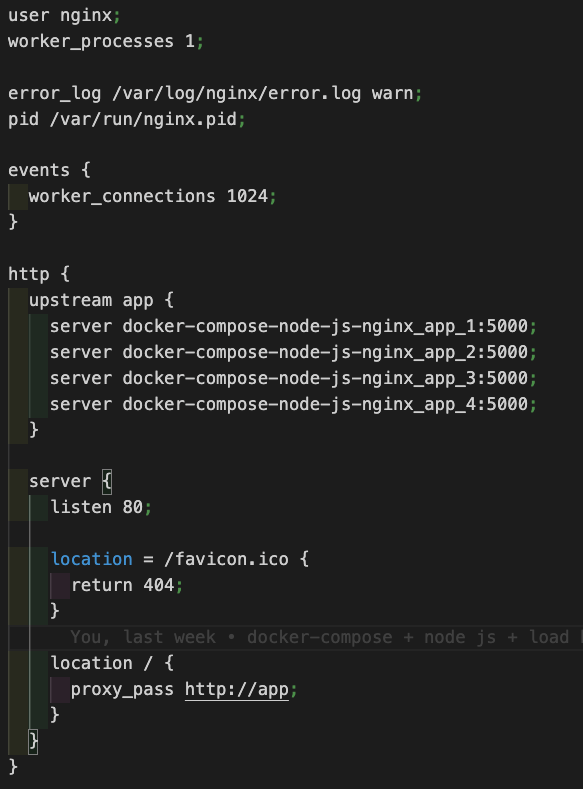
Here we have created an Nginx container out of Nginx:latest image refers to this and created an Nginx.conf file where we have set the rules for load balancing and as Nginx listens on HTTP port 80, our node application will also listen on port 80 but internally it will get load balanced to the available node JS service instances.
nginx. conf details
Here we have set up the upstream part where we have mentioned 4 server instances and it load balances the requests whenever the server is hit on http://localhost:80.
We have almost reached the setup part now just we need to start the services. Now we need to run the application using the below commands
docker-compose up -d — scale app=4
The above command will create 4 instances of the Node App and Nginx container which will load and balance the request.

Wow !!! Now we have successfully scaled our Node App and the request is getting served by any of the available Node instances based on the load balancer principle.
The entire code is available on the Github Repository.
Thanks for reading this blog. Keep Learning.
Published at DZone with permission of Piyush BISWAL. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments