Service Mesh and Management Practices in Microservices
In this blog, we will understand service mesh in microservices architecture, components of service mesh, and best practices for managing service mesh.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the dynamic world of microservices architecture, efficient service communication is the linchpin that keeps the system running smoothly. To maintain the reliability, security, and performance of your microservices, you need a well-structured service mesh. This dedicated infrastructure layer is designed to cater to service-to-service communication, offering essential features like load balancing, security, monitoring, and resilience. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of service meshes and explore best practices for their effective management within a microservices environment.
Understanding Service Mesh
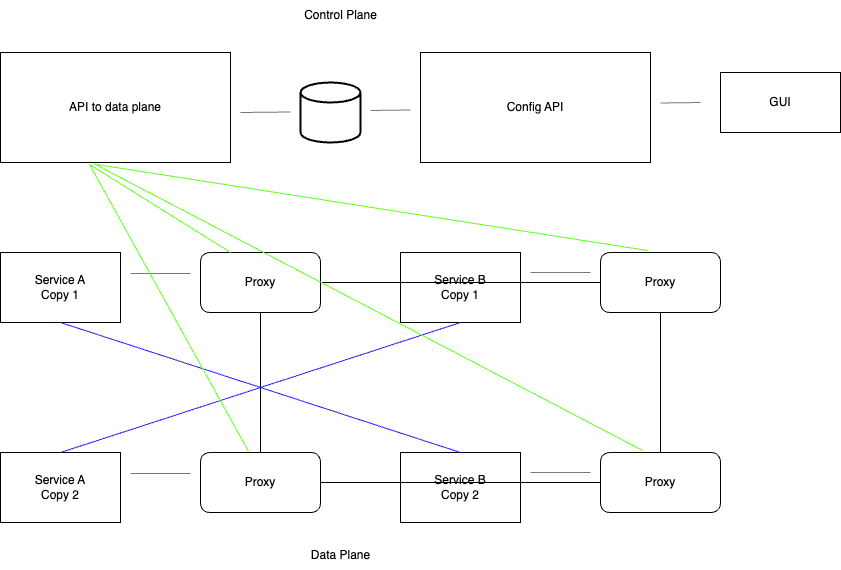
A service mesh is essentially the invisible backbone of a network, connecting and empowering the various components of a microservices ecosystem. It comprises a suite of capabilities, such as managing traffic, enabling service discovery, enhancing security, ensuring observability, and fortifying resilience. To execute these tasks, service meshes employ a set of proxy instances seamlessly integrated alongside application code. These proxies act as vigilant guardians, adept at intercepting and directing incoming and outgoing traffic between services. A service mesh typically consists of two primary components:
1. Data Plane
The data plane, also known as the sidecar proxy, is responsible for handling the actual network traffic between microservices. Each microservice in your architecture is paired with a sidecar proxy. These sidecar proxies intercept, route, and manage the network traffic to and from the microservices they are associated with. Some popular sidecar proxies used in service meshes are Envoy, Linkerd’s proxy, and Nginx.
2. Control Plane
The control plane is the central management and configuration component of the service mesh. It’s where you define and enforce the policies that govern traffic management, security, observability, and other aspects of service-to-service communication. The control plane also provides tools for monitoring, managing, and analyzing the performance and behavior of the service mesh.
Why Service Mesh Matters in Microservices
In the intricate realm of microservices, service-to-service communication poses multifaceted challenges. Services must interact seamlessly, but issues like load balancing, authentication, encryption, and service discovery can become formidable hurdles. Here’s why a service mesh stands out as a centralized solution:
Traffic Management
Example: Imagine a scenario where you’re implementing a blue-green deployment strategy to roll out a new version of a service. A service mesh can be configured to intelligently route a fraction of incoming traffic to the new version, ensuring a smooth transition and minimizing potential downtime and risks.
Service Discovery
Example: As your microservices dynamically scale in and out, they need to locate and communicate with one another in real time. Service meshes provide the magic of automatic service discovery, making the chore of services finding their peers as effortless as pie, regardless of their ever-changing locations.
Security
Example: In the security-conscious landscape of microservices, safeguarding communications between services is paramount. Service meshes come equipped with robust security features, including mutual TLS (mTLS) encryption. This ensures that every interaction is not only encrypted but also authenticated, enhancing the overall security posture.
Observability
Example: Clear insights into how requests flow through your microservices are crucial for diagnosing issues and optimizing performance. Service meshes often include tools for collecting metrics and distributed tracing data. You can visualize this data in real time using tools like Grafana and Prometheus or delve deep into the intricacies of distributed tracing analysis with tools like Jaeger.
Resilience
Example: Failures are inevitable in any system. However, service meshes offer a lifeline by implementing resilience patterns like circuit breakers and retries. In the face of a service failure, a service mesh can skillfully reroute traffic to healthy instances or provide informative error messages, saving the day with finesse.
Best Practices for Managing Your Service Mesh
To master the art of managing your service mesh in a microservices environment, consider these tried-and-tested best practices:
Choose the Right Service Mesh Technology
Example: Service mesh technologies like Istio, Linkerd, and Consul are your allies. Evaluate their features and community support to align your choice with your specific project needs. For large-scale deployments, Istio shines with its comprehensive feature set and widespread community backing.
Define and Enforce Service Mesh Policies
Example: The success of your service mesh largely depends on the policies you define. From traffic management to security and observability, these policies need to be crystal clear. Use the built-in tools provided by the service mesh technology to enforce these policies effectively. For instance, configure mutual TLS (mTLS) to ensure encrypted and authenticated communications within your service mesh.
Monitor and Analyze Mesh Performance
Example: Utilize the monitoring and tracing capabilities woven into the service mesh. Keep your finger on the pulse of your system’s performance with real-time visualizations through Grafana and Prometheus. Dive deeper into the mysteries of distributed tracing analysis with the likes of Jaeger.
Implement Fine-Grained Access Control
Example: Keep control at your fingertips by implementing role-based access control (RBAC) within your service mesh. Define who can communicate with whom. For instance, restrict the payment service from directly accessing the customer database and mandate it to go through the customer service for a finer level of control.
Regularly Update and Patch Service Mesh Components
Example: Stay ahead of the curve by keeping your service mesh components up-to-date. Regularly update the control plane components to benefit from bug fixes, new features, and enhanced security. For instance, keeping your Istio control plane up-to-date ensures that your service mesh stays secure and efficient.
Conclusion
In the world of microservices, the adept management of service communication is non-negotiable. A well-tamed service mesh streamlines these interactions, guaranteeing secure, observable, and resilient microservices. By adhering to these best practices, you can unlock the true potential of your service mesh, facilitating the efficient operation and maintenance of your microservices ecosystem while laying a solid foundation for future growth and innovation.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments