Software Bill of Materials (SBOM): Enhancing Software Transparency and Security
Explore key concepts of SBOMs and how they are an essential tool in modern software development and cybersecurity frameworks.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAbstract
This article explores the concept of a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) as an essential tool in modern software development and cybersecurity frameworks. The SBOM acts as a detailed inventory of all software components, dependencies, and associated metadata within an application. By providing transparency, facilitating risk mitigation, and supporting regulatory compliance—particularly for software products intended for U.S. federal agencies—the SBOM strengthens software security. Through a detailed examination of SBOM implementation, benefits, and associated technologies—such as composition analysis and binary detonation—this article highlights the SBOM's role in fostering a secure development environment.
Introduction
The Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) is a comprehensive list detailing every software component, dependency, and metadata associated with an application. By cataloging software parts, it enables organizations to manage software more effectively and enhances visibility into potential security risks. The significance of SBOMs lies in their ability to offer transparency, build trustworthy software, and address cybersecurity challenges—especially relevant in compliance-heavy environments. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of SBOMs, their roles in cybersecurity and compliance, and how they integrate into modern software frameworks.
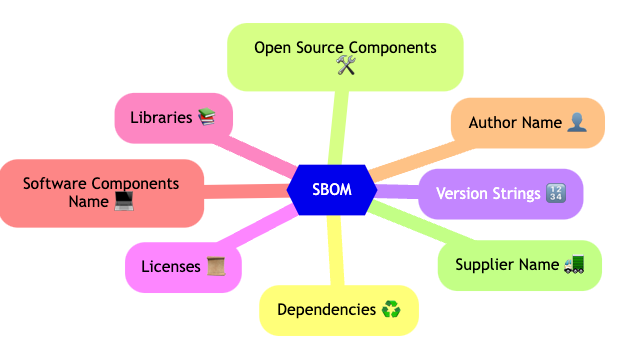
Understanding SBOMs and Their Importance
Definition and Structure of an SBOM
An SBOM comprises a detailed record of software libraries, dependencies, and metadata for each component. It serves as an inventory for developers, enabling them to understand what’s inside their software products and make informed security decisions.
Key Benefits of an SBOM
- Transparency: SBOMs enhance the visibility of a software product's components, providing a clearer view of what’s running under the hood.
- Risk mitigation: They support proactive vulnerability identification and allow for timely remediation.
- Compliance requirements: SBOMs are critical for products sold to U.S. federal agencies, aligning with Executive Order 14028, which emphasizes improved cybersecurity in critical software infrastructure (The White House, 2021).
- Software security: By identifying components susceptible to supply chain attacks or vulnerabilities in third-party libraries, SBOMs contribute significantly to a secure software environment (CrowdStrike, n.d.).
Technologies and Methods Used in SBOMs
Composition Analysis
Composition analysis identifies and assesses each software component within an SBOM. This method enables organizations to evaluate dependencies and potential risks tied to each component, helping them manage risk effectively and improve transparency (NTIA, 2021).
Variability Management
In the SBOM context, variability management maintains consistency across software versions and configurations, helping organizations ensure compatibility and minimize security risks in software variations. This process is essential for managing software that may be customized or modified for different environments (Synopsys, 2022).
Binary Detonation
Binary detonation is an advanced cybersecurity technique used to analyze software binaries for potential threats. By isolating and detonating these binaries in a controlled environment, organizations can detect malicious behaviors, enhancing SBOM's ability to manage security risks in executable files (Jin & Austin, 2020).
Open-Source Approaches
With the extensive use of open-source components in modern software, SBOMs play a pivotal role in addressing associated security risks. By integrating open-source SBOM tools, organizations can automate the tracking of open-source components and manage vulnerabilities more effectively (OpenSSF, 2022).
Approach Architecture
SBOMs integrate with CI/CD pipelines, facilitating automation in creating, updating, and managing SBOMs throughout the software lifecycle. This approach allows for continuous monitoring and ensures that SBOMs remain up-to-date as software evolves (CycloneDX, 2023).
Implementation of SBOMs in Organizations
Steps for SBOM Implementation
Implementing SBOMs involves identifying components, performing composition analysis, and ensuring continuous monitoring. Automated SBOM generation tools can streamline this process, reducing the complexity of manual updates and integration into workflows (Garfinkel & Cox, 2022).
Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges include managing SBOM complexity, resource allocation, and maintaining current data. Solutions involve automating SBOM generation and leveraging SBOM-integrated tools in development workflows, simplifying compliance and security efforts (Synopsys, 2023).
Case Studies
Successful SBOM implementations are seen in high-security industries, such as finance and defense, where SBOMs help protect software from supply chain vulnerabilities and regulatory risks.
Benefits and Impact of SBOMs on Cybersecurity
Enhanced Vulnerability Detection
SBOMs improve vulnerability management by providing a clear view of all components in use, allowing organizations to pinpoint potential threats and address them proactively (Black Duck by Synopsys, 2023).
Facilitating Incident Response
In the event of a security incident, SBOMs enable rapid response by identifying specific affected components, making it easier to resolve issues efficiently.
Compliance and Legal Benefits
SBOMs offer substantial compliance benefits, especially regarding regulatory requirements. By clearly documenting components, they aid organizations in meeting legal standards and cybersecurity mandates (CISA, 2022).
Improving Software Supply Chain Security
SBOMs enhance supply chain security by identifying and mitigating risks associated with dependencies. By providing transparency into third-party components, they help secure software ecosystems against potential attacks (NIST, 2022).
Future Directions and Trends in SBOMs
Advances in SBOM Standards
Emerging SBOM standards, such as SPDX and CycloneDX, aim to unify SBOM formats and facilitate widespread adoption. These standards will enable greater interoperability between tools and systems, making SBOMs more versatile (SPDX, 2020; CycloneDX, 2023).
SBOM Automation and AI Integration
AI-driven tools offer promising potential for enhancing SBOM generation, vulnerability scanning, and threat detection. As AI tools mature, they may automate many SBOM functions, simplifying software transparency and security processes (Gartner, 2022).
Regulatory Landscape
With regulatory mandates evolving, particularly in the U.S., organizations across various industries may be required to adopt SBOM practices. This trend is anticipated to expand as cybersecurity becomes a national and international priority (The White House, 2021).
Conclusion
SBOMs are crucial for building secure, transparent, and compliant software systems. As software environments become increasingly complex, SBOMs stand to play a foundational role in modern cybersecurity practices and secure the software supply chain. Future research should focus on AI-enhanced SBOM management and advancements in SBOM standards, which can promote more robust security measures across industries.
References
- The White House. (2021). Executive Order 14028: Improving the Nation's Cybersecurity. Retrieved from https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/05/12/executive-order-on-improving-the-nations-cybersecurity/
- National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA). (2021). The Minimum Elements For a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM). Retrieved from https://www.ntia.gov/report/2021/minimum-elements-software-bill-materials-sbom
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). (2022). Software Bill of Materials (SBOM). Retrieved from https://www.cisa.gov/sbom
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). (2022). Secure Software Development Framework (SSDF) Version 1.1. NIST Special Publication 800-218. Available at: https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.800-218
- SPDX. (2020). SPDX Specification Version 2.3. The Linux Foundation. Retrieved from https://spdx.github.io/spdx-spec/
- CycloneDX. (2023). CycloneDX SBOM Standard Specification Version 1.4. OWASP Foundation. Retrieved from https://cyclonedx.org/specification/
- CrowdStrike. (n.d.). What is a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM)? Retrieved from https://www.crowdstrike.com/platform/cloud-security/
- Synopsys. (2022). Understanding the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM). Synopsys Blog. Retrieved from https://www.synopsys.com/blogs/software-security/understanding-sbom/
- Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF). (2022). Supply Chain Security Best Practices. Retrieved from https://openssf.org/blog/2022/09/01/npm-best-practices-for-the-supply-chain/
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments