The Bitcoin Protocol: How It Works
Learn the ins and outs of the world's most popular virtual currency, including how Bitcoin and blockchain work together and how Bitcoins are created.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBitcoin is a form of digital cash that allows online payments between the buyer and the seller. It works as a digital ledger that records transactions and balances of accounts.
Bitcoins are exchanged using the Bitcoin Protocol built over the principles of cryptography. The protocol defines the procedure that is followed by a Bitcoin transaction from its creation, through validation and final confirmation.
At the core of protocol is the Bitcoin transaction mechanism. Bitcoins are spent from electronic Bitcoin Wallets and are exchanged using Bitcoin transactions. In order to understand the protocol, let us first try to understand a transaction, the information it contains and how this information is processed.
Bitcoin Transactions
A Bitcoin transaction essentially contains the following information:
- ID: Unique transaction ID which is the SHA256 double-hash of the transaction data.
- Input: The bitcoin addresses that identify the sources of the bitcoins to be transferred. These are usually a previous transaction’s output and are used to verify the sender and check the available balance.
- Amount: The number of bitcoins to be transferred.
- Output: The receiver’s bitcoin address. In cases where there is leftover bitcoin change, the output should also include an entry for the sender’s address to send it back, to be collected as “Transaction Fee" or to be sent to another receiver.
Outputs from one transaction can be used as inputs for another transaction. This creates a chain of ownership as the bitcoin value is moved from address to address.
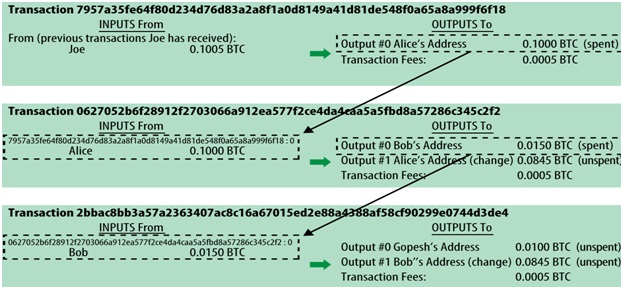 Figure 1: Bitcoin Transaction Chain
Figure 1: Bitcoin Transaction Chain
Transaction Validation
All digital cash transactions also need to be checked and verified for authenticity, duplicity, and cash availability. The validation of the transactions is not centralized and all participating nodes are authorized for it.
A Bitcoin Wallet account that initiates a payment transaction is identified by a Bitcoin address and a pair of public and private keys. To enable verification of the sender identity, transactions are digitally signed using the sender’s private key and validated using his public key that is available to all the nodes.
The Bitcoin system orders the transactions into lists called blocks. These are subsequently linked to form a blockchain, a shared public ledger of all confirmed transactions. Transactions not yet included in the blockchain are unconfirmed and reversible.
The miners confirm and write these transactions into the blockchain. To prevent double-spending, a transaction is not marked confirmed until it has received a certain number of confirmations.
Each bitcoin mining node keeps a personal copy of the BlockChain which is updated whenever a new transaction arrives. This article explained that GPU is also a very efficient tool for the speedy mining of bitcoins. Subsequently, it also tries to validate the current and previous transactions in the block by solving a mathematical puzzle called the Proof of Work. The successful node that solves the puzzle gets a Bitcoin reward and its BlockChain approved and accepted by all nodes.
The Bitcoin Protocol
In terms of the transaction creation and validation process, the Bitcoin Protocol can be stated as below:
- A new transaction is broadcast to all participating nodes in the network.
- Each node collects new transactions into a block.
- Each node tries to validate the new transaction and all previous ones by finding a solution to the Proof of Work for the block.
- The node which finds the solution broadcasts the solved block to the network.
- Nodes validate the transactions in the block and accept the block.
- Nodes start working on the next block. A hash of the last accepted block is created and used as a reference in the next block.
Summary
The Bitcoin protocol is based on collaboratively maintaining the Bitcoin ledger. The digital cash is transferred through transactions which are confirmed only after validation of key criteria and joint consensus by participating nodes through a mathematical puzzle based voting process.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments