Throttling Database Using Rate Limits for SQL or REST
Learn how to handle and distribute requests properly and improve the QoS for the ODBC, JDBC, and OData APIs that you generate using Hybrid Data Pipeline servers.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhen you are planning to expose your database to new users or tenants, one of the important areas to consider is resource governance. When in production, there's always a high probability that you will see complex live queries for data visualization or MapReduce jobs impacting your analytical database, which can impact other users. Then, you start to scale, as with any web application, by running a load balancer in front of your servers to distribute requests efficiently. But often, in a production environment, you come across a bad user that affects your quality of service (QoS). To give you an idea on how a bad user can affect your service, here are a couple of abusive scenarios:
- A naïve developer who keeps hogging all the resources due to an inefficiently written client request.
- A low-priority user who keeps hogging the resources, causing service outages for high-priority users.
- A malicious user who keeps attacking your API endpoints to cause DDoS for all other users.
It is not pragmatic to scale your system to accommodate genuine requests whenever there is a drop in QoS due to such abusive behavior. To deal with this, rate limiting is one technique that can be employed. Essentially, rate limiting defines a number of requests or the amount of data that you can request with in an interval of time. This is an effective technique that can mitigate the abusive scenarios discussed above, and you can find rate limits for almost all the SQL and REST APIs that you would want to interact with.
Database-Agnostic Throttling
At Progress, we are really interested in open analytics strategies that leverage Data API Management to expose hosted databases to other users, customers, and tenants for self-service analytics. We engineered DataDirect Cloud (a hosted service) and Hybrid Data Pipeline (a self-hosted service) to provision Data APIs on top of 30+ different data sources, including Oracle, SQL Server, Hadoop Hive, Postgres, MySQL, IBM DB2, Sybase, Greenplum, and more — without having to configure the database itself. In this blog, I will be going through the rate limiting features for SQL or REST APIs generated through Hybrid Data Pipeline to protect your hosted database resources.
Introducing Rate Limits API
With the recent release of Hybrid Data Pipeline, admins can now throttle Data APIs (ODBC, JDBC, or OData) with fine granularity to improve the overall QoS. With the Rate Limits API, you can configure the following parameters:
MaxFetchRows: Maximum number of rows that can be fetched per query.PasswordLockoutInterval: The duration, in seconds, for counting the number of consecutive failed authentication attempts.PasswordLockoutLimit: The number of consecutive failed authentication attempts that are allowed before locking the user account.PasswordLockoutPeriod: The duration, in seconds, for which a user account will not be allowed to authenticate to the system when thePasswordLockoutLimitis reached.CORSBehavior:Configuration parameter for CORS behavior. Setting the value to 0 disables the CORS filter. Setting the value to 1 enables the CORS filter.
You can configure these parameters at three levels wherever they are applicable. Hybrid Data Pipeline offers three levels of granularity to rate limit the OData API. They are:
System level
User level
Data source level
You can set the all the parameters defined above in System Level Limits and only MaxFetchRows parameter for User and Data Source Level settings.
System-Level Rate Limit
System Level limits define the limits for the Hybrid Data pipeline service. For System level limit, you can configure following parameters:
MaxFetchRows(id = 1)PasswordLockoutInterval(id = 2)PasswordLockoutLimit(id = 3)PasswordLockoutPeriod(id = 4)CORSBehavior(id = 5)
Let's look at the Rate Limits API. To fetch all the system level limits all you must do is send a GET request as shown below:
http://<server>:<port>/api/admin/limits/systemResponse:
{
"limits": [
{
"value": 1000,
"id": 1
},
{
"value": 100,
"id": 2
},
{
"value": 10,
"id": 3
},
{
"value": 100,
"id": 4
},
{
"value": 0,
"id": 5
}
]
}To set a limit, you can send a POST request as shown below:
http://<server>:<port>/api/admin/limits/system/<limit-id>Body:
{
"value": 100
}Response
{
"value": 100
}As simple as that, an admin can set limits for all the above parameters at the system level. You can also update and delete the system limits. Visit the documentation here to learn how you can do it.
User-Level Limits
At the user level, you can set limits only for restricting the number of rows that can be fetched for a single query. To fetch all the users and the Max row limits for each of them, execute the GET request as shown below:
http://<server>:<port>/api/admin/limits/usersResponse:
{
"userLimits": [
{
"limits": [
{
"value": 10000000,
"id": 1
}
],
"userId": 1,
"userName": "d2cadmin"
},
{
"limits": [
{
"value": 100,
"id": 1
}
],
"userId": 2,
"userName": "d2cuser"
}
]
}To set a limit for a user, you can send a POST request as shown below:
http://<server>:<port>/api/admin/limits/users/<user-id>/<limit-id>Body:
{
"value": 100
}Response:
{
"value": 100
}You can also update and delete the limits later. To learn how to do that, visit this documentation page.
Data Source-Level Limits
Each user can have multiple data sources defined in his or her account, and you can dictate the limit for each data source individually. To get all the data sources and limits for a user, execute a GET request as shown below.
http://<server>:<port>/api/admin/limits/users/<user-id>/datasourcesResponse:
{
"datasourceLimits": [
{
"limits": [],
"dataSourceId": 1,
"dataSourceName": "SQLServer",
"isGroup": false
}
]
}To set a limit for a datasource under a user, you can send a POST request as shown below:
http://<server>:<port>/api/admin/limits/users/<user-id>/datasources/<datasource-id>/<limit-id>Body:
{
"value": 100
}Response:
{
"value": 100
}As with user-level limits, you can only set set MaxFetchRows limit at the data source level. You can also update and delete the limits later. To learn how to do that, visit this documentation page.
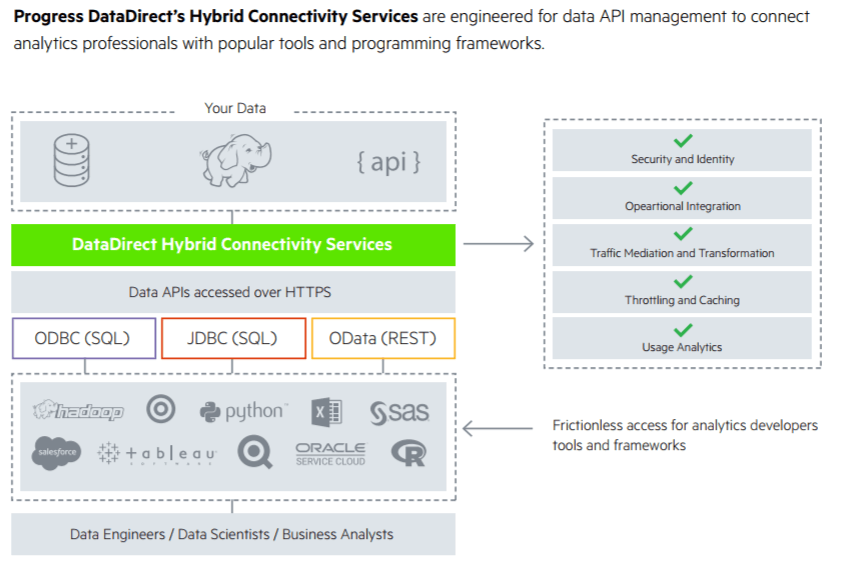
We hope this article gave you a glimpse into how Hybrid Data Pipeline can provide throttling for the Data APIs that you can produce. In addition to this, you can now easily configure a load balancer for clusters of Hybrid Data Pipeline servers, helping you to handle and distribute requests properly and improving the QoS for the ODBC, JDBC, and OData APIs that you are generating using Hybrid Data Pipeline servers.
Published at DZone with permission of Saikrishna Teja Bobba, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments