Which Flow Is Best for Your Data Needs: Time Series vs. Streaming Databases
While both are used to handle time-related data, their underlying technologies and main purpose are built to serve different purposes.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeData is being generated from various sources, including electronic devices, machines, and social media, across all industries. However, unless it is processed and stored effectively, it holds little value.
A significant evolution is taking place in the way data is organized for further analysis. Some databases prioritize organizing data based on its time of generation, while others focus on different functionalities.
Although time series and streaming databases perform different functions, they complement each other well in data management and analytics. While both are used to handle time-related data, their underlying technologies and main purpose are built to serve different purposes.
Time Series Database
A time series database (TSDB) is designed to store, manage, and analyze data points indexed by time. Each data point typically consists of a timestamp and associated values often collected from sensors, logs, or financial markets. However, a streaming database is designed to manage and analyze constant streams of data in real time. It focuses on consuming, processing, and querying data on arrival instead of waiting for data to be stored.
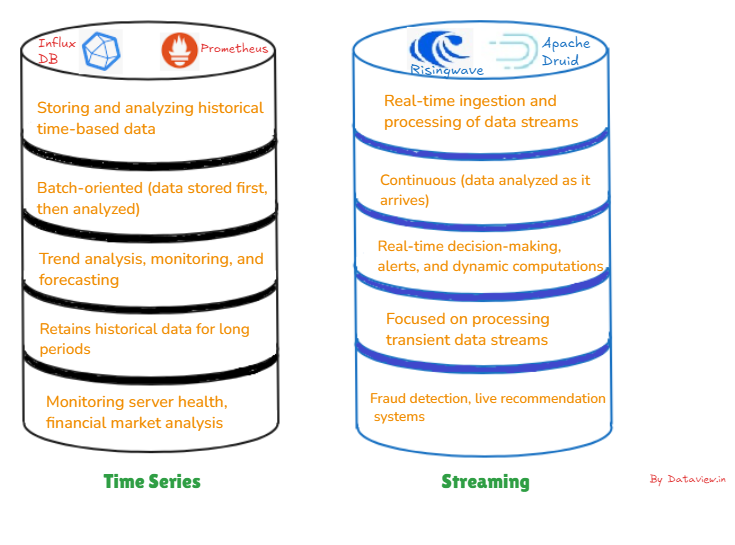
TSDB follows a time-centric architecture where the data is primarily organized around timestamps and supports managing data lifecycles, automatically archiving or deleting older data. Besides, it is designed to handle high-frequency inserts, often from IoT devices or real-time monitoring systems. Also proficient at performing aggregations like averages, minimum, maximum, and trends over time periods.
Streaming Databases
Streaming databases are primarily focused on real-time processing that allows querying and analysis on the fly as data streams in. They are suited for event-driven architecture where computations or alerts based on specific conditions can be triggered by connecting with event-driven systems. They are also majorly connected or integrated with data streaming platforms like Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis.
Finding the Perfect Match
A TSDB can be used if you want to store everything from continuous monitoring and metrics collection, such as server uptime, CPU usage, memory utilization, network bandwidth, etc. It is well-suited for handling large volumes of high-frequency writes and query metrics over defined time ranges, allowing for real-time monitoring and long-term trend analysis.
For IoT applications, the TSDB is the best fit as IoT devices generate data like smart thermostats, industry-based equipment devices, or wearables, and the data will have associated timestamps. For financial market analysis, TSDBs are perfect, as financial data is often time-sensitive and needs to be indexed correctly and TSDB can be leveraged to store the historical data and access it quickly for analytics, forecasting, and modeling at scale.
Streaming databases are the right choice in event-driven architectures where timely decision-making is critical, such as tracking user behavior on websites, processing financial transactions, or managing supply chain logistics. When you need to process and evaluate data as it enters your system in real time, a streaming database is perfect. Applications like fraud detection, live dashboards, recommendation engines, and IoT device anomaly monitoring that require instant insights are best served by streaming databases.
Conclusion
Because both time series and streaming databases are time-centric, they may appear to be comparable, although they serve essentially different needs. Streaming databases are excellent for real-time data processing and analytics, whereas time series databases are best for storing and analyzing historical data. The key to choosing the best technology for your application is knowing your unique use case.
Published at DZone with permission of Gautam Goswami, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments