Understanding Mule Events in Mule 4
In this article, let's find out more about the structure and basic functionality of each segment or part of Mule Events in Mule 4.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn MuleSoft integration, events play a crucial role in ensuring communication between two or more flows. Within MuleSoft's Anypoint Studio, each flow that is triggered operates with its event and can make it possible to transfer data and control from one flow to another. Before delving deep into today's topic, let us discover why Mule events are essential to understand for MuleSoft developers. It is because it enables efficient data flow management, and helps in debugging and troubleshooting errors, which ultimately boosts developer productivity.
Let's find out more about the structure and basic functionality of each segment or part of Mule Events in Mule 4.
What Is a Mule Event?
A Mule Event contains all the core information processed by the Mule runtime. A Mule event is triggered by a message source, such as a Listener or an HTTP request. These Mule Events are critical for the smooth execution of flows in an API creation. As we discussed earlier, each flow has its event, and thus events are immutable, which means a small change to an instance of a Mule event will create a whole new instance. When an event is triggered, all the core information like attributes, payload, and variables are passed to the next processor.
It is important to note that for a flow to execute, the event processor plays a more crucial role than the event source.
A Mule event consists of two main components: the Mule Message and Variables.
Mule 4 contains a simplified Mule message model in which each Mule event has a message and associated variables.
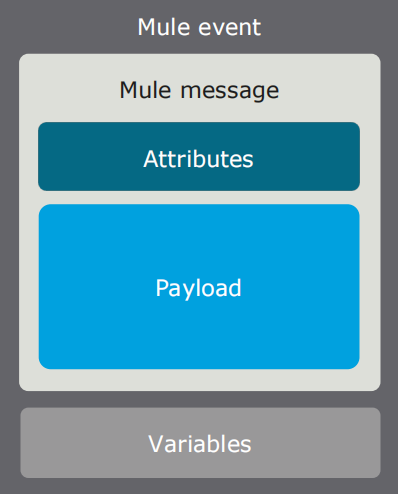
Mule Message
The Mule Message contains two different parts, namely the attributes and the payload. It serves as a container for message content and metadata, from external sources, as it is processed within flows of a Mule 4 application.
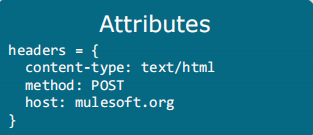
Attributes contain metadata such as headers and properties, including the method type used, host, and port. When an HTTP request is sent, attributes such as method type, host, and port are included. These attributes are stored in the attributes section under the Mule Message. These attributes will be passed to the rest of the flow until the attributes are updated.
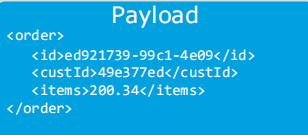
The payload contains the core data being processed throughout the flow. It stores the data that is processed by the application. 'Set payload' is usually used to set the payload, and is carried till the end of the flow in the payload section of the Mule message. Whatever JSON or XML code you write will be stored in the payload section. It is also considered as the main body of a Mule message. The payload is replaced when a new 'set payload' is triggered every time in the Mule runtime flow.
Have you thought about why variables are separated from the Mule message? Because they are the temporary values in an event flow that will be replaced each time a new variable is set.
Variables
Variables are used to store per-event values for use within a flow of a Mule app. Variables in a Mule event are created using the Set Variable component. They are used to store temporary values specific to an event within a flow. Variables can hold any supported data type, such as objects, numbers, or strings. They are accessible only within the scope of the flow where they were created.
Summary
Hope you understand how a Mule Event works in Mule 4. Please do like and comment on your views on today's topic. Happy learning!!
Do check my previous blogs on system integration using Mulesoft:
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments