What Is RDD in Spark and Why Do We Need It?
Spark has already over taken Hadoop (MapReduce) in general, because of benefits it provides in terms of faster execution in iterative processing algorithms.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeApache Spark has already over taken Hadoop (MapReduce) in general , because of variety of benefits it provides in terms of faster execution in iterative processing algorithms such as Machine learning.
In this post, we will try to understand what makes spark RDDs so useful in batch analytics .
Why RDD?
When it comes to iterative distributed computing, i.e. processing data over multiple jobs in computations such as Logistic Regression, K-means clustering, Page rank algorithms, it is fairly common to reuse or share the data among multiple jobs or you may want to do multiple ad-hoc queries over a shared data set.
There is an underlying problem with data reuse or data sharing in existing distributed computing systems (such as MapReduce) and that is , you need to store data in some intermediate stable distributed store such as HDFS or Amazon S3. This makes the overall computations of jobs slower since it involves multiple IO operations, replications and serializations in the process.
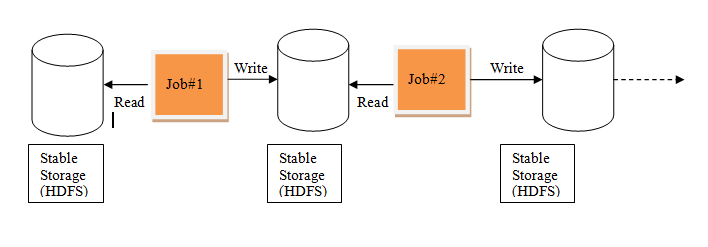
Iterative Processing in MapReduce
RDDs , tries to solve these problems by enabling fault tolerant distributed In-memory computations.
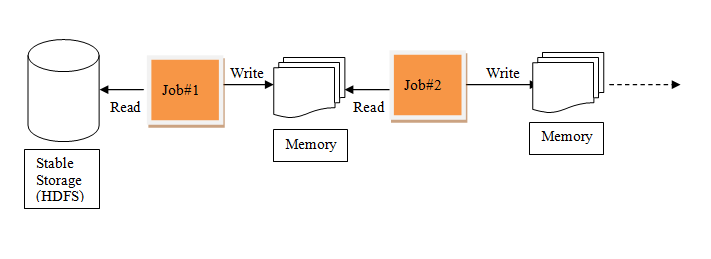
Iterative Processing in Spark
Now, lets understand what exactly RDD is and how it achieves fault tolerance –
RDD – Resilient Distributed Datasets
RDDs are Immutable and partitioned collection of records, which can only be created by coarse grained operations such as map, filter, group by etc. By coarse grained operations , it means that the operations are applied on all elements in a datasets. RDDs can only be created by reading data from a stable storage such as HDFS or by transformations on existing RDDs.
Now, How Is That Helping for Fault Tolerance?
Since RDDs are created over a set of transformations , it logs those transformations, rather than actual data.Graph of transformations to produce one RDD is called as Lineage Graph.
For example –
firstRDD=spark.textFile("hdfs://...")
secondRDD=firstRDD.filter(someFunction);
thirdRDD = secondRDD.map(someFunction);
Spark RDD Lineage Graph
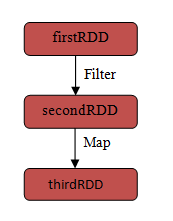
In case of we lose some partition of RDD , we can replay the transformation on that partition in lineage to achieve the same computation, rather than doing data replication across multiple nodes.This characteristic is biggest benefit of RDD , because it saves a lot of efforts in data management and replication and thus achieves faster computations.
Published at DZone with permission of Saurabh Chhajed, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments