What the Heck Are WebSockets!?
We take a look at the history of WebSockets, what data transfer models developers used before WebSockets, and why WebSockets have proved so useful.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWe are knee deep into the real-time world by this point with so many applications working with live data. It’s high time there was an explanation of all the events leading up to this point in a technological stance. So, here goes…
These days, applications are moving from utilizing stale data from a database or data that’s created on-the-fly following an event trigger in a live experience that follows real-world events. The first thing we think of when it comes to real-time applications is WebSockets. But, in spite of a lot of people constantly tossing around this term in technological circles, there actually seems to be huge misconceptions associated with its meaning and working.
Let’s bust the jargon and understand what’s happening!
HTTP -> Long Polling -> WebSockets
Back in the day, HTTP’s stateless request-response mechanism worked perfectly well for the use cases of the day, letting any two nodes communicate over the internet. Since it was all stateless, even if the connection dropped, you could easily restore the communication from that very point.
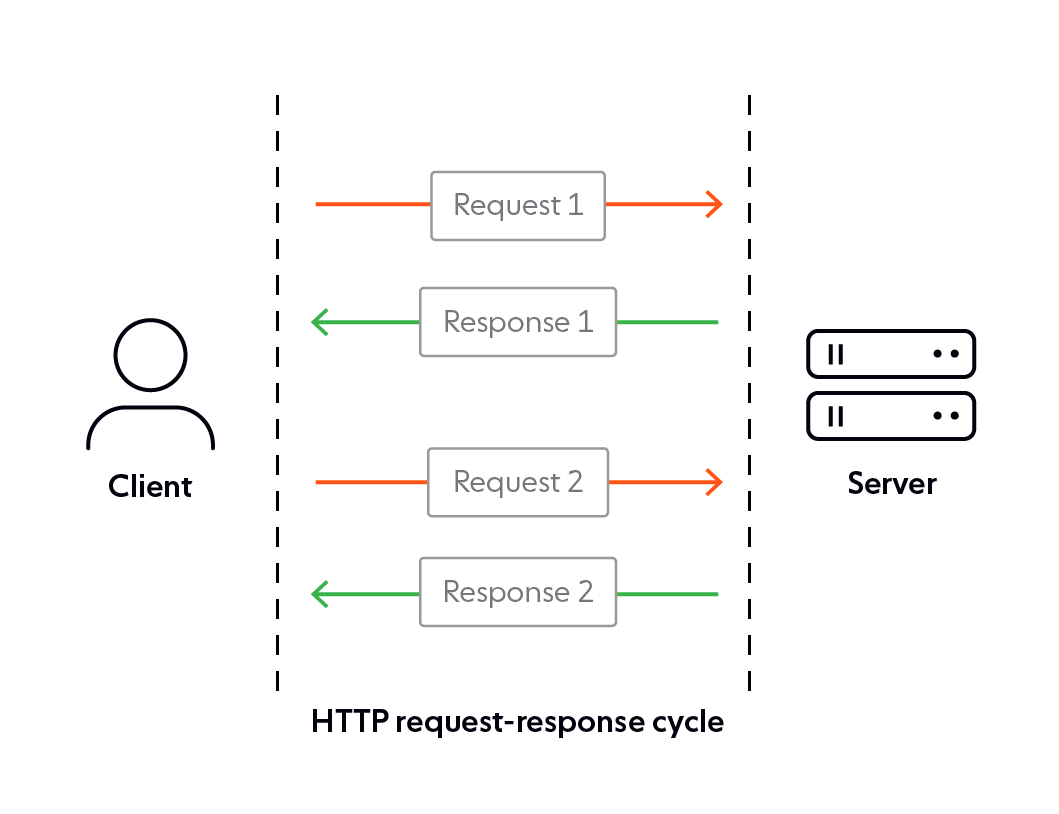
However, with applications moving to real-time implementations, that is, ensuring minimal-latency when sharing data as it is created in the real world, the traditional request-response cycles turned out to be a huge overhead. Why? The high-frequency request-response cycles lead to more latency since each of these cycles required a new connection to be set up every time.
Logically, the next step would be a way to minimize these cycles for the same amount of data flow. Solution? Long-polling!
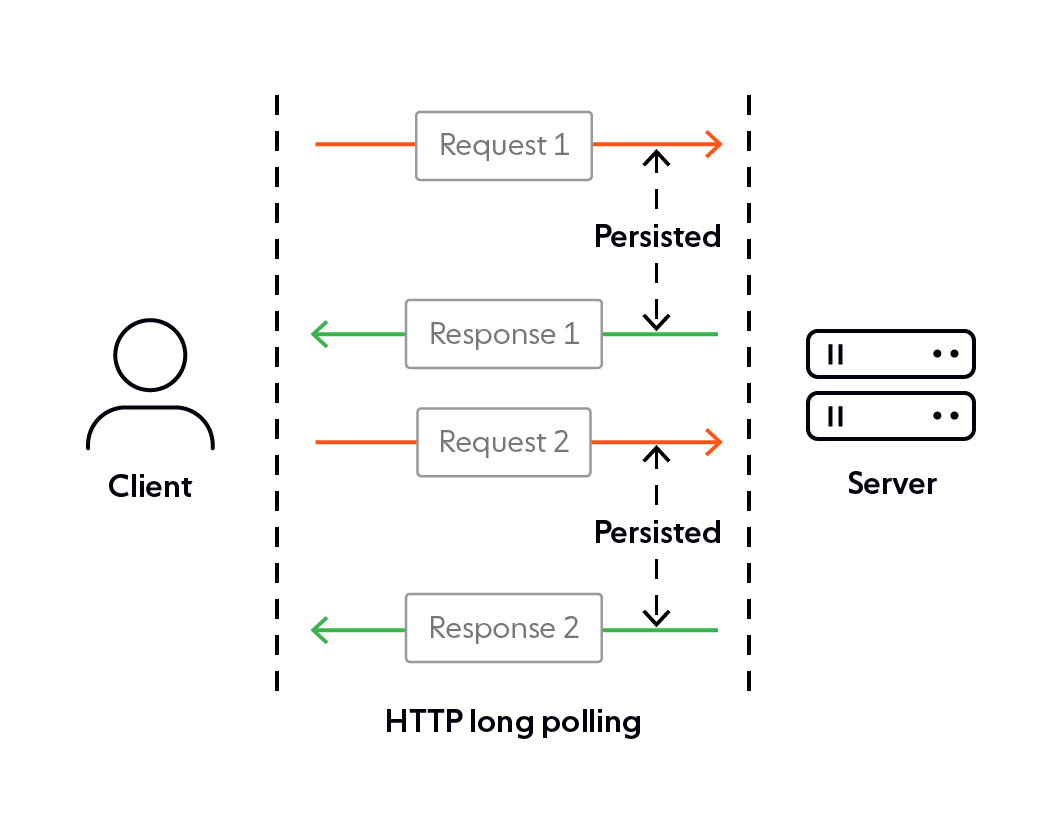
With long polling, the underlying TCP socket connection could be persisted for a little longer, i.e., the connection can be kept open for a little longer than usual. This not only gave the server an opportunity to collate more than one piece of data to send back in a single response rather than doing so in individual responses, but also, it almost completely eliminated the case of empty responses being returned due to lack of data, as now the server could just return a response whenever it has some data to actually give back.
But, even the long polling technique involved connection set up and frequent request-response cycles, similar to the traditional HTTP, which, of course, led to more latency.
For most real-time applications, the speed of data, up to the nearest milliseconds, is absolutely critical, hence neither of the above options proved useful.
What Then?
Since I started off the article by mentioning WebSockets, you obviously would have guessed what I was getting at.
So, WebSockets, unlike HTTP, is a stateful communications protocol that works over TCP.
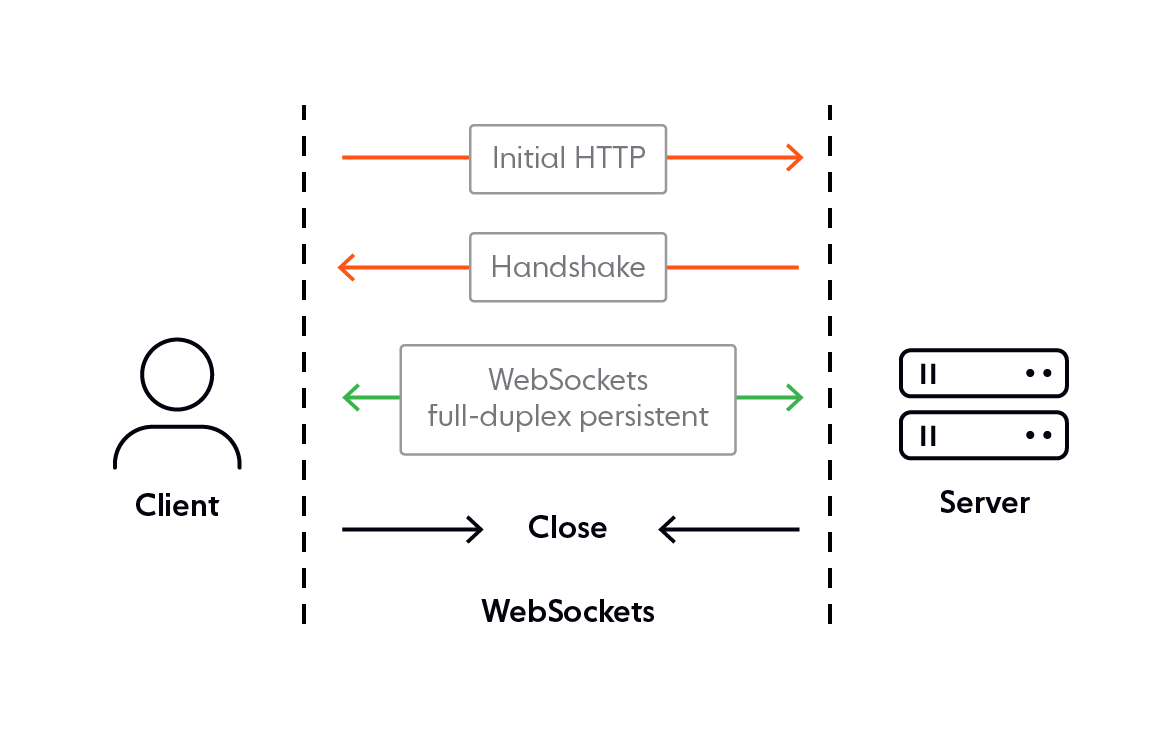
The communication initially starts off as an HTTP handshake but if both of the communicating parties agree to continue over WebSockets, the connection is simply elevated giving rise to a full-duplex, persistent connection. This means the connection remains open for the complete duration that the application's run-time. This gives the server a way to initiate any communication and send off data to pre-subscribed clients, so they don’t have to keep sending in requests inquiring about the availability of new data.

There’s actually a lot more stuff happening under-the-hood of realtime applications, than what I have simply summarized in this article, here are some great resources to learn more about WebSockets:
Published at DZone with permission of Srushtika Neelakantam, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments