A Look at React Native and React.js
We look at React Native and React.js, and where they architecture, use, and coding styles overlap and differ. Read on to get started!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBacked by Facebook, Instagram, and a reputed community of developers, React is one of the most used JavaScript libraries at present. According to Libscore, at present React is being utilized on a number of reputed sites, such as Netflix, Airbnb, Walmart, HelloSign, and Imgur, to name a few.
React.js development is not in any way similar to React native mobile app development and both of them serve a different purpose. The blog will explain all of the main differences between these two PLs and will provide you with an approach to choose the one for your particular project.
The Difference Between React.js and React Native
React.js is a JavaScript Library While React Native Is a Mobile App Development Framework
React.js is a JavaScript library that helps businesses in creating beautiful User Interfaces. One of the main features of React.js is that it can perform on the client-side and, in addition, can be rendered on the server-side, and they can function together interoperable. It is broadly utilized for building high-performing web applications and UIs.
However, React Native is a mobile app development framework that builds mobile apps using React.js. It lets you build a rich mobile User Interface from declarative components. React Native mobile app development offers functions like Hot Reloading to develop the apps faster and with fewer efforts. React Native libraries were released by Facebook in 2015 giving the React architecture to native Android, iOS, and Windows apps.
Both Improve Developers' Efficiency but in Different Ways
React.js specializes in its ability to provide great performance along with an entirely managed rendering cycle for its components which enhances developer efficiency. By setting up the distribution, creation, and utilization of reusable parts in a simpler way, it empowers developers to have more opportunity to utilize and make basic abstractions. It proves to be useful for lower level parts like clickable buttons and also for higher level parts like dropdowns.
React Native provides the same benefits but with a different approach. Building blocks in React Native are reusable native components that compile directly to native. Using React, components you would use in Android or iOS have counterparts right in React, so you will get the same look and feel. This component-based structure enables you to make applications with a faster. The application will have the look, speed, and functionality of a native mobile app and that makes React Native different from other mobile app development frameworks.
React.js Utilizes Virtual DOM While React Native Uses Native APIs
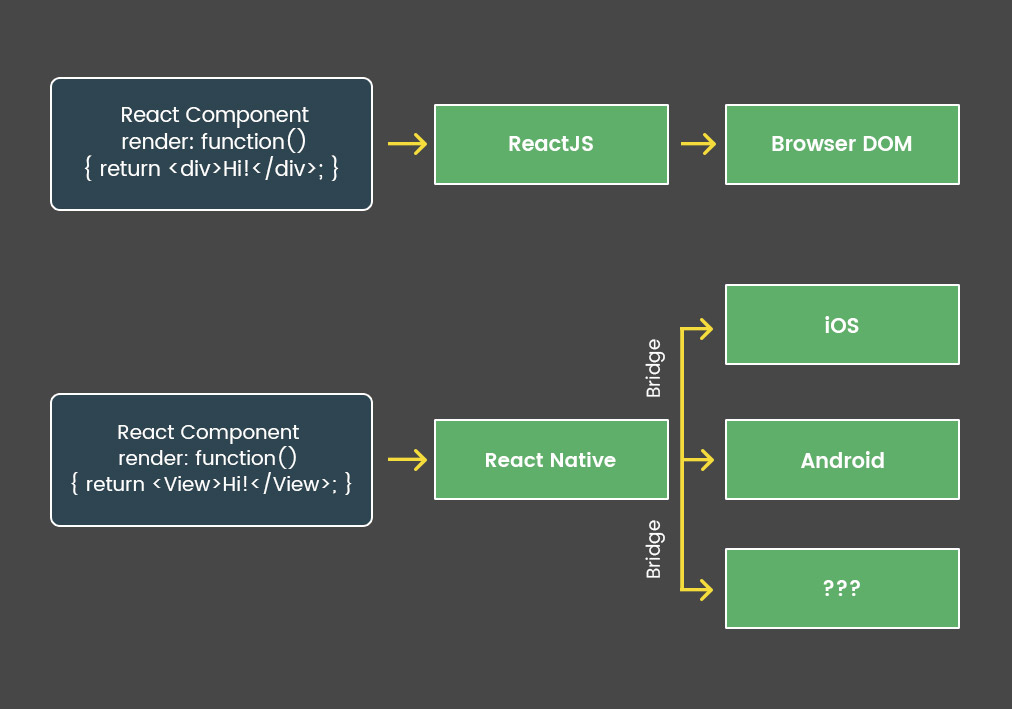
React.js utilizes the virtual DOM to create better UX. The DOM construct takes time as DOM trees are large today. But, React.js manages to execute this procedure quicker by utilizing a virtual DOM. So React.js utilizes an abstract copy of the Document Object Model and rolls out changes to one component without influencing the rest of the UI. This is the thing that makes React.js so awesome at making updates rapidly and creating dynamic UIs.
React Native took this a step further. It utilizes native APIs to render UI parts that can be reused over both iOS and Android platforms. So what it truly does is that it utilizes Java APIs to render Android components and Objective-C APIs to write iOS components. It then utilizes JavaScript to compose whatever remains of the code, individualizing the application for every platform. This gives React Native mobile applications maximum components reusability and code shareability.
React.js Improves SEO of Your Web App While React Native is All About UI
React.js was designed keeping Search Engine Optimization in mind. It utilizes Node to render on the server of the user. Similar tools do give this server viewpoint to rendering, but, they require a ton of unstable hacks and an extensive amount of developer support to maintain.
On the other hand, as React Native is not used for websites it has nothing to do with SEO. It is centered exclusively on building a mobile UI. Compared with other mobile application development frameworks, React Native is fully UI-centered, making it more like a JavaScript library rather than a framework. The resultant UI is exceedingly responsive. This implies the application will have speedier load times than a normal hybrid application, and a smoother feel.
React.js Combines Technologies While React Native's Code Can Be Combined With Any Existing App
React uses HTML and JS following the rule that they come together all the time. This idea is stretched out more to include CSS, which expels a bunch of issues identified with CSS development, for example, worldwide namespace, and variable/scope isolation.
On the other hand, React Native provides opportunities for businesses that want to add more to an existing app but do not prefer to change the code of the whole app. You can add React Native components into your existing app’s code. Or, if your current hybrid application was made with Ionic and Cordova, reuse that Cordova-based code effectively with a plugin.
Also, React.js uses HTML and CSS while React Native does not. React.js uses <p> and <div> while React Native uses <text> and <view> respectively. Here is an example to show the same:
For React.js:
function tick() {
const element = (
<div>
<p>Hello, world!</p>
</div>
);
ReactDOM.render(element, document.getElementById('root'));
}
setInterval(tick, 1000);For React Native:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Text, View } from 'react-native';
export default class HelloWorldApp extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View>
<Text>Hello world!</Text>
</View>
);
}
}Navigation: A Different Approach for React.js and React Native
This is an angle where both of them adopt a different approach, but the outcomes are fairly neck-and-neck. Web apps made in React.js utilize React-router for navigation while React Native has a totally unique library-Navigator for the purpose.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments