10 Things to Know When Using SHACL With GraphDB
Using SHACL with GraphDB was not as easy as I thought. Here is what I needed to learn.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeToday I have one of those moments where I am absolutely sure if I do not write this down, I will forget how to do this next time. For one of the projects I am working on, we need to do SHACL validation of RDF data that will be stored in Ontotext GraphDB. Here are the 10 things I needed to learn in doing this. Some of these are rather obvious, but some were less than obvious to me.
Number 1: To be able to do SHACL validation, your repository needs to be configured for SHACL when you create your repository. This cannot be done after the fact.
Number 2: It seems to be better to import your ontology (or ontologies) and data into different graphs. This is useful when you want to re-import your ontology (or ontologies) or your data, because then you can replace a specific named graph completely. This was very useful for me while prototyping. Screenshot below:

Number 3: SHACL shapes are imported into this named graph:
http://rdf4j.org/schema/rdf4j#SHACLShapeGraph
...by default. At configuration time, you can provide a different named graph or graphs for your SHACL shapes.
Number 4: To find the named graphs in your repository, you can do the following SPARQL query:
select distinct ?g
where {
graph ?g {?s ?p ?o }
}You can then query a specific named graph as follows:
select *
from <myNamedGraph>
where {
?s ?p ?o .
}Number 5: However, getting the named graphs does not return the SHACL named graph. On StackOverflow someone suggested SHACL shapes can be retrieved using:
http://address:7200/repositories/myRepo/rdf-graphs/service?graph=http://rdf4j.org/schema/rdf4j#SHACLShapeGraphHowever, this did not work for me. Instead, the following code worked reliably:
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.model.Model;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.model.impl.LinkedHashModel;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.model.vocabulary.RDF4J;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.repository.RepositoryConnection;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.repository.http.HTTPRepository;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.rio.RDFFormat;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.rio.Rio;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.rio.WriterConfig;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.rio.helpers.BasicWriterSettings;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class RetrieveShaclShapes {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String address = args[0]; /* i.e. http://localhost/ */
String repositoryName = args[1]; /* i.e. myRepo */
HTTPRepository repository = new HTTPRepository(address, repositoryName);
try (RepositoryConnection connection = repository.getConnection()) {
Model statementsCollector = new LinkedHashModel(
connection.getStatements(null, null,null, RDF4J.SHACL_SHAPE_GRAPH)
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
Rio.write(statementsCollector, System.out, RDFFormat.TURTLE, new WriterConfig().set(
BasicWriterSettings.INLINE_BLANK_NODES, true));
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
}...using the following dependencies in the pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.rdf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>rdf4j-client</artifactId>
<version>4.2.3</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>Number 6: Getting the above code to run was not obvious since I opted to using a fat jar. I encountered an "org.eclipse.rdf4j.rio.UnsupportedRDFormatException: Did not recognise RDF format object" error. RFD4J uses the Java Service Provider Interface (SPI) which uses a file in the META-INF/services of the jar to register parser implementations. The maven-assembly-plugin I used, to generate the fat jar, causes different jars to overwrite META-INF/services thereby loosing registration information. The solution is to use the maven-shade-plugin which merge META-INF/services rather overwrite it. In your pom you need to add the following to your plugins configuration:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<transformers>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ServicesResourceTransformer"/>
</transformers>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>You can avoid this problem by using the separate jars rather than a single fat jar.
Number 7: Importing a new shape into the SHACL shape graph will cause new shape information to be appended. It will not replace the existing graph even when you have both the
- "Enable replacement of existing data" and
- "I understand that data in the replaced graphs will be cleared before importing new data."
options enabled, as seen in the next screenshot:
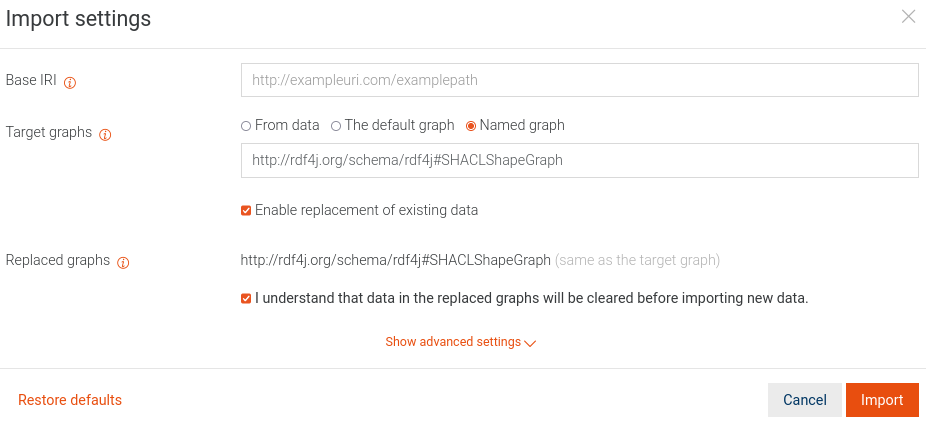
To replace the SHACL named graph, you need to clear it explicitly by running the following SPARQL command:
clear graph <http://rdf4j.org/schema/rdf4j#SHACLShapeGraph>
For myself, I found it easier to update the SHACL shapes programmatically. Note that I made use of the default SHACL named graph:
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.model.vocabulary.RDF4J;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.repository.RepositoryConnection;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.repository.http.HTTPRepository;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.rio.RDFFormat;
import java.io.File;
public class UpdateShacl {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String address = args[0]; /* i.e. http://localhost/ */
String repositoryName = args[1]; /* i.e. myRepo */
String shacl = args[2];
File shaclFile = new File(shacl);
HTTPRepository repository = new HTTPRepository(address, repositoryName);
try (RepositoryConnection connection = repository.getConnection()) {
connection.begin();
connection.clear(RDF4J.SHACL_SHAPE_GRAPH);
connection.add(shaclFile, RDFFormat.TURTLE, RDF4J.SHACL_SHAPE_GRAPH);
connection.commit();
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Number 8: Programmatically you can delete a named graph using this code and the same Maven dependency as we used above:
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.model.IRI;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.model.ValueFactory;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.model.impl.SimpleValueFactory;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.repository.RepositoryConnection;
import org.eclipse.rdf4j.repository.http.HTTPRepository;
public class ClearGraph {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String address = args[0]; /* i.e. http://localhost/ */
String repositoryName = args[1]; /* i.e. myRepo */
String graph = args[2]; /* i.e. http://rdf4j.org/schema/rdf4j#SHACLShapeGraph */
ValueFactory valueFactory = SimpleValueFactory.getInstance();
IRI graphIRI = valueFactory.createIRI(graph);
HTTPRepository repository = new HTTPRepository(address, repositoryName);
try (RepositoryConnection connection = repository.getConnection()) {
connection.begin();
connection.clear(graphIRI);
connection.commit();
}
}
}
Number 9: If you update the shape graph with constraints that are violated by your existing data, you will need to first fix your data before you can upload your new shape definition.
Number 10: When uploading SHACL shapes, unsupported features fails silently. I had this idea to add human readable information to the shape definition to make it easier for users to understand validation errors. Unfortunately "sh:name" and "sh:description" are not supported by GraphDB version 10.0.2. and 10.2.0. Moreover, it fails silently. In the Workbench, it will show that it loaded successfully as seen in the next screenshot:
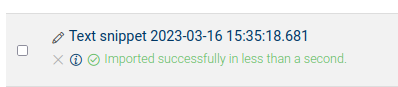
However, in the logs I have noticed the following warnings:

As these are logged as warnings, I was expecting my shape to have loaded fine, except that triples pertaining to "sh:name" and "sh:description" are skipped. However, my shape did not load at all.
You find the list of supported SHACL features here.
Conclusion
This post may come across as being critical of GraphDB. However, this is not the intention. I think it is rather a case of growing pains that are still experienced around SHACL (and Shex, I suspect) adoption.
Resources that have been helpful for me in resolving issues are:
- GraphDB documentation, and
- RDF4J on which GraphDB is built.
Published at DZone with permission of Henriette Harmse, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments