5 Types of Software Testing Models
One of the critical aspects of the software development life cycle is software testing. Let's look at various software testing models, their advantages and disadvantages.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOriginally published October 17, 2021
One of the critical aspects of the software development life cycle is software testing. Today, there are a plethora of different software development models to choose from, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. As a result, depending on the project's requirements and difficulties, you must choose just the right model. Let's look at various software testing models, their advantages and disadvantages.
Types of Software Testing Models
Different types of software testing models are as follow:
- Waterfall Model
- V Model
- Agile Model
- Spiral Model
- Iterative Model
Let's look into each one of them in detail!
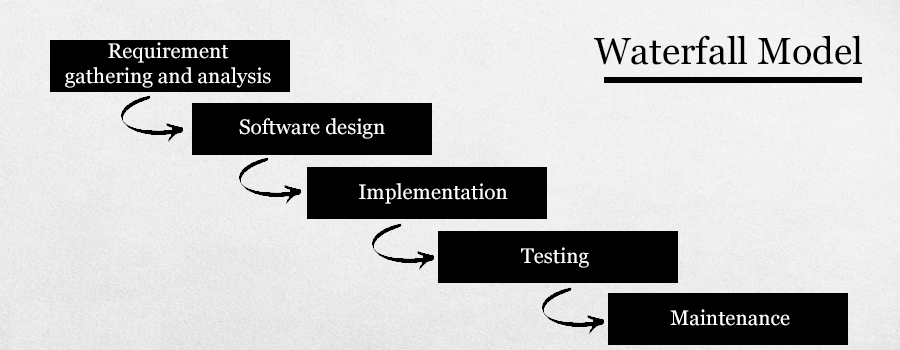
Waterfall Model
The entire software development process is divided into discrete parts in the "Waterfall Model" approach. In this model, the output of one phase serves as the input for the following step in the sequence. There are four steps in the waterfall model: requirement collection and analysis, software design, programmed implementation and testing, and maintenance.
The first phase of this model is requirement collection and analysis, which involves observing and determining all conceivable system needs for designing a certain piece of software. This, in turn, is dependent on the software requirement specification, which includes particular details about the end-user preferences. It is also where the Requirement Specification is created.
The document is prepared to be used as an input for the next phase, i.e., software design. One thing to keep in mind here is that once you move on to the next phase, you won't be able to change the prerequisites. As a result, the end-user requirements must be very clear and precise.
Advantages
- Easy to implement and maintain.
- The initial phase of requirement gathering and analysis helps to save time in the development phase.
- The resources requirement is minimum and after completion of each phase, testing is done.
Disadvantages
- You cannot change or update user requirements.
- You cannot make changes to the previous phase when once you are into the next phase.
- You cannot start the next phase until the previous phase is completed.
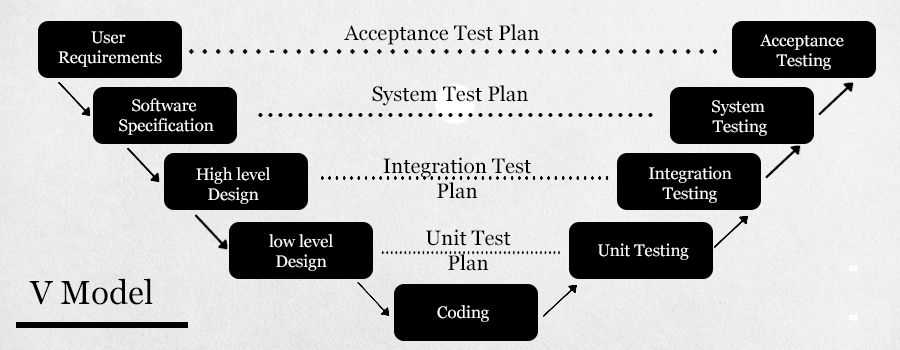
V Model
In comparison to the waterfall model, the V Model is much more preferred due to its flexibility. In this model, the development and testing operations are carried out in downhill and uphill patterns. Additionally, it allows the development and testing phases to be carried out at the same time. The testing in this model starts at the unit level and progresses towards the integration of the entire system.
Advantages
- It is simple to use because testing activities like planning and test designing are already done before coding.
- This model enhances the success rate and saves a lot of time.
- The majority of bugs are discovered early on which prevents the downward bug flow..
Disadvantages
- It is a strict model.
- Initial prototypes of the product are not available because the software is being built throughout the implementation phase.
- You'll need to update the test document if there are any changes in the middle.
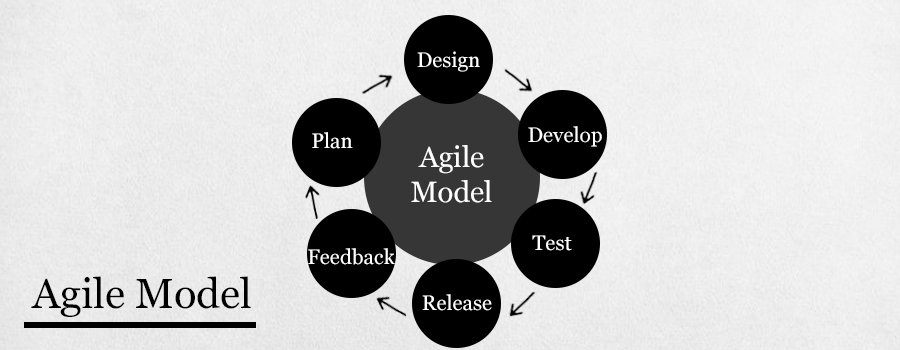
Agile Model
In the Agile model, requirements and solutions are developed by the collaboration between various cross-functional teams. The agile model is also known as an iterative and incremental model. The agile software testing model focus on process flexibility and customer satisfaction by rapid delivery of working software product and by breaking the product into little incremental builds.
Advantages
- Rapid and continual development of deliverables ensures client satisfaction.
- It is a flexible model because of the constant contact between consumers, developers, and testers.
- You'll be able to quickly design working software and adjust to changing requirements.
Disadvantages
- For large and intricate software development situations, estimating the work necessary at the start of the cycle can be difficult.
- If the customer is unclear about the aim, the project may veer off course due to constant discussion with the customer.
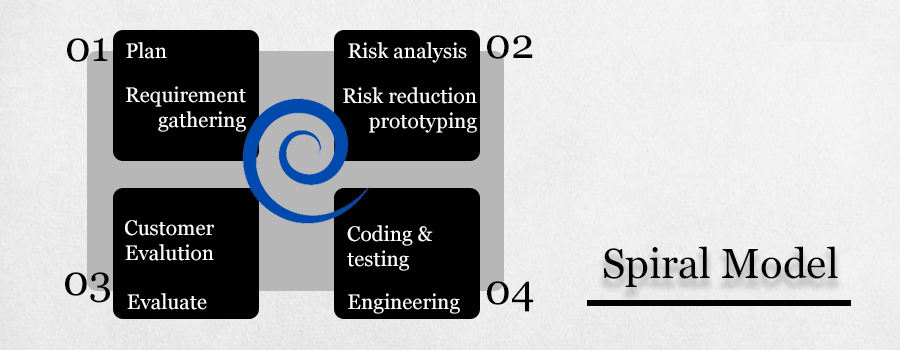
Spiral Model
This software testing model is almost similar to the Agile model, except it places a greater emphasis on risk analysis. The different phases of the spiral model include planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation. In this model, you need to collect the requirements and perform the risk assessment at the base level with each subsequent spiral building on top of that.
Advantages
- It is appropriate for complex and massive systems.
- You can add real-time functionalities depending on the changed circumstances.
- Software is generated early in the cycle.
Disadvantages
- It's an expensive model requiring a high level of risk analysis skills.
- It is unsuitable for small and easy projects.
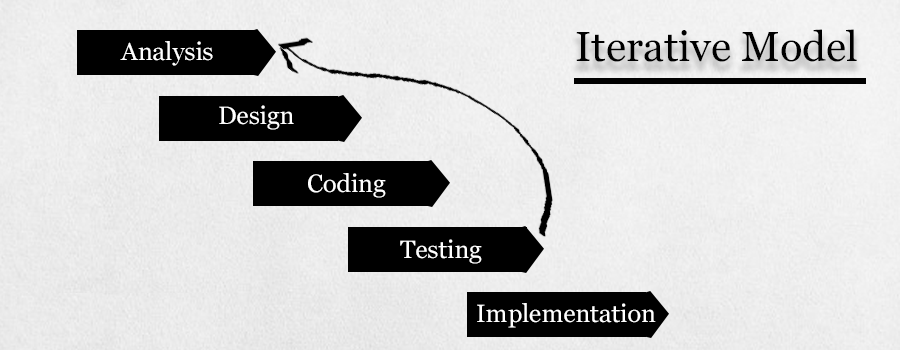
Iterative Model
The Iterative model does not need a whole list of requirements before starting the project. The development process in this model begins with the functional part's requirements that can be extended later. For every cycle, the process is repeated, resulting in new product versions. Every iteration includes the development of a divided system component that is added to the previously developed functioning.
Advantages
- It is simple to control the risks as high-risk tasks are completed first.
- The progress is plainly observable.
- Problems and dangers identified in one iteration can be avoided in subsequent sprints.
Disadvantages
- When compared to the waterfall model, the iterative model requires more resources.
- The process is tough to manage.
- Even at the end of the project, the risks may not be completely determined.
Published at DZone with permission of Twisa Mistry. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments