Introduction to JIT in PHP 8
The Just-In-Time compiler (JIT) has opened up new avenues for PHP. This article explores how PHP’s recent implementation of JIT improves its performance.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreePHP is the most popular web scripting language and has been available for many years. With the release of the major version of PHP 5, it has been quite stable and is a popular choice among web developers. There are almost 244 million sites built using PHP as a serverside language.
In 2020, PHP 8 was released, introducing many syntactically visible features such as attributes, named argument, and union types. All of these features are not so apparent, and according to many PHP developers, the Just-In-Time compiler (JIT) is the most important milestone. This has opened up new avenues for PHP in comparison to other languages in the market. In this article, we are going to explore how the PHP language is executed and how PHP’s recent implementation of JIT improves its performance.
Why JIT?
As stated earlier, an interpreted language like PHP is a popular choice for developing web apps due to its flexibility and ease of coding. It does not require recompilation every time you change your code, and developers do not need to worry about the nitty-gritty details of memory management.
However, this flexibility comes at the cost of execution speed. Because the interpreter has to analyze, parse and compile the source code on the fly, it adds an extra overhead before every execution, which results in slow code execution. JIT is a solution to this problem. It is a hybrid way of using an interpreter and ahead-of-time compilation at the same time by compiling the portions of code to machine code and then caching it on runtime.
Zend Engine and OPCode
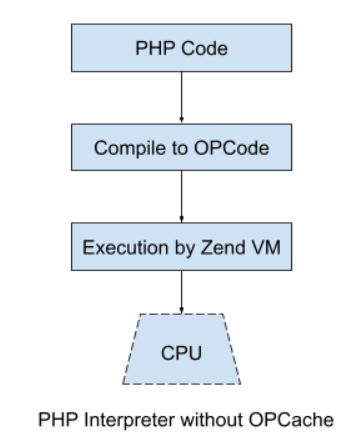
Zend Engine is a set of components that comprises the core of PHP runtime. At the heart of Zend Engine is Zend VM, which is further divided into Zend Compiler and Zend Executor. The role of Zend Compiler is to compile the human-readable PHP script into an intermediary bytecode called OPCode. Every OPCode is a command with operands that the Zend Executor can understand and execute. For each OPCode, there is a C function that runs on the CPU. This is how classic PHP was interpreted.
OPCache Extension and Preloading
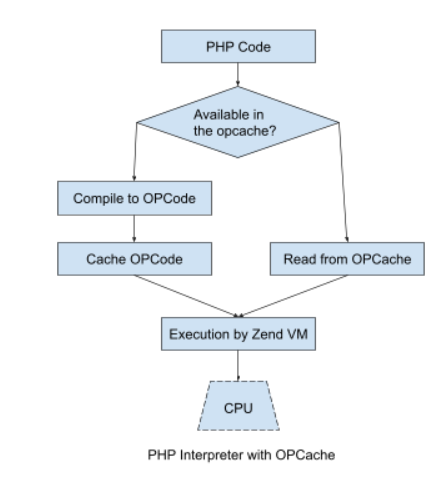
The first performance optimization in the PHP interpretation flow came through the use of the OPCache extension which was introduced in version 5.4. This extension caches the OPCode of PHP script into shared memory. The subsequent calls will not parse and compile the script if its OPCode representation is present in the cache.
In order to eliminate recompiling overhead further, in PHP version 7.4 OPCache preload was added. This requires specifying a preload file with the opcache.preload directive of the php.ini file, which can further add other files using the opcache_compile_file() function.
JIT: The New Frontier
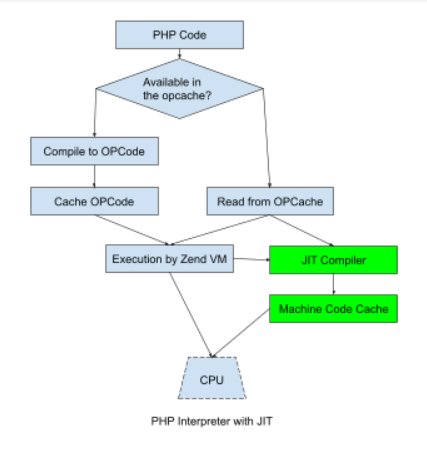
Since PHP 5.x, its maintainers had already applied every possible technique to optimize PHP runtime, including dead code elimination and optimization while generating the OPCode. Therefore, implementing JIT was the next logical step and the team has been working on it since 2011.
PHP’s JIT is part of its OPCache layer. The OPCache analyzes "hot code," or the code that is executed repeatedly. Then it selects the hot OPCode block for JIT compilation. The selected OPCodes are compiled into machine code and cached into OPCaches shared memory for later use. From the next execution of the code block, it uses the cached machine code directly bypassing the Zend VM completely. For CPU-intensive use cases, it has resulted in a significant performance gain.
Configuring JIT
In PHP8, the JIT is enabled out of the box, but it is turned off. To turn it on we need to set some directives in our php.ini file:
opcache.enable=1
opcache.enable_cli=1
opcache.jit_buffer_size=256MThe important directive to keep an eye on here is opcache.jit_buffer_size, which is set to 0 by default, resulting in JIT being turned off.
Final Thoughts
It is important to understand that the JIT feature, as of now, will not significantly increase the performance of different framework-based web applications such as Laravel or WordPress. However, for CPU-intensive calculations-based applications, it has demonstrated an immense performance boost that is on par with compiled languages. This has opened new doors of possibility for newer use cases for PHP. Moreover, it might soon be possible to replace binaries and extensions written with C using PHP code. Therefore, in my opinion, it is indeed an important milestone for PHP.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments