Alexa Skill With Python
In this article, let's see how to create a custom skill for Alexa using Python, npm, and AWS Lambda Functions.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAlexa skills can be developed using Alexa Lambda functions or a REST API endpoint. Lambda function is Amazon's implementation of serverless functions available in AWS. Amazon recommends using Lambda functions despite they are not easy to debug. While you can log to a CloudWatch log, you can't hit a breakpoint and step into the code.
This makes live debugging of Alexa requests a very hard task. In this post, we will implement a custom skill for Amazon Alexa by using Python, npm, and AWS Lambda Functions. This skill is basically a Hello World example. With this post, you will be able to create a custom skill for Amazon Alexa, implement functionality by using Python and start your custom skill both from your local computer and from AWS. This post contains materials from different resources that can be seen in the Resources section.
Prerequisites
Here you have the technologies used in this project
- Amazon Developer Account — How to get it
- AWS Account — Sign up here for free
- ASK CLI — Install and configure ASK CLI
- Python 3.x
- Visual Studio Code
- pip Package Manager
- Alexa ASK for Python (Version >1.10.2)
- ngrok
The Alexa Skills Kit Command Line Interface (ASK CLI) is a tool for you to manage your Alexa skills and related resources, such as AWS Lambda functions. With ASK CLI, you have access to the Skill Management API, which allows you to manage Alexa skills programmatically from the command line. We will use this powerful tool to create, build, deploy and manage our Hello World Skill. Let's start!
Creating the Skill With ASK CLI
For creating the Alexa Skill, we will use de ASK CLI previously configured. First of all, we have to execute this command:
ask new
This command will run and interactive step-by-step creation process:
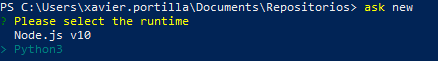
- The first thing the ASK CLI is going to ask us is the runtime of our Skill. In our case,
Python3:
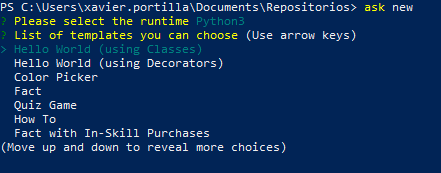
- The second step is the template of the Skill that our Skill is going to base on. In our case, we will select
Hello World (Using Classes)template:
- Finally, the ASK CLI is going to ask about the name of the Skill. We will set up the name
alexa-python-lambda-helloworld
Project Files
These are the main files of the project:
x
├───.ask
│ config
│
├───.vscode
│ launch.json
│ tasks.json
├───hooks
├───lambda
│ └───py
│ ├───errors
│ ├───intents
│ ├───interceptors
│ ├───locales
│ ├─── hello_world.py
│ └─── requirements.txt
├───models
│ es-ES.json
├───skill.json
└───local_debugger.py
- .ask: a folder that contains the ASK CLI's config file. This config files will remain empty until we execute the command
ask deploy .vscode/launch.json: Launch preferences to run locally your Skill for local testing and executes all the tasks in.vscode/tasks.json. This setting launcheslocal_debugger.py. This script runs a server on http://localhost:3001 for debugging the Skill.- hooks: A folder that contains the hook scripts. Amazon provides two hooks: post_new_hook and pre_deploy_hook.
post_new_hook: executed after the Skill creation. In Python, creates a Virtual Environment located at.venv/skill_env.pre_deploy_hook: executed before the Skill deployment. In python, creates the folderlambda/py/lambda_uploadwhere will be stored all the necessary to upload the lambda to AWS..
- lambda/py: A folder that contains the source code for the skill's AWS Lambda function:
hello_world.py: the lambda main entry point.locales: i18n dictionaries used by the librarypython-i18n, which allows us to run the same Skill in different configuration languages.requirementes.txt: this file stores the Python dependencies of our project and is a basic part of understanding and working with Python and pip.errors: folder that contains all Error handlers.intents: folder that contains all Intent handlers.interceptors: here you can find all interceptors.
- models – A folder that contains interaction models for the skill. Each interaction model is defined in a JSON file named according to the locale. For example, es-ES.json.
skill.json– The skill manifest. One of the most important files in our project.local_debugger.py: used for debugging our skill locally.
Lambda Function in Python
The ASK SDK for Python makes it easier for you to build highly engaging skills by allowing you to spend more time implementing features and less time writing boilerplate code.
You can find documentation, samples and helpful links in their official GitHub repository.
The main Python file in our lambda project is hello_world.py located in lambda/py folder. This file contains all handlers, interceptors, and exports the Skill handler in handler object.
The handler object is executed every time AWS Lambda is initiated for this particular function. In theory, an AWS Lambda function is just a single function. This means that we need to define dispatching logic so a single function request can route to appropriate code, hence the handlers.
x
from ask_sdk_core.skill_builder import SkillBuilder
from ask_sdk_model import Response
from intents import LaunchRequestHandler as launch
from intents import HelloWorldIntentHandler as hello
from intents import HelpIntentHandler as help
from intents import CancelOrStopIntentHandler as cancel
from intents import SessionEndedRequestHandler as session
from intents import IntentReflectorHandler as reflector
from errors import CatchAllExceptionHandler as errors
from interceptors import LocalizationInterceptor as locale
# The SkillBuilder object acts as the entry point for your skill, routing all request and response
# payloads to the handlers above. Make sure any new handlers or interceptors you've
# defined are included below. The order matters - they're processed top to bottom.
sb = SkillBuilder()
sb.add_request_handler(launch.LaunchRequestHandler())
sb.add_request_handler(hello.HelloWorldIntentHandler())
sb.add_request_handler(help.HelpIntentHandler())
sb.add_request_handler(cancel.CancelOrStopIntentHandler())
sb.add_request_handler(session.SessionEndedRequestHandler())
# make sure IntentReflectorHandler is last so it doesn't override your custom intent handlers
sb.add_request_handler(reflector.IntentReflectorHandler())
sb.add_global_request_interceptor(locale.LocalizationInterceptor())
sb.add_exception_handler(errors.CatchAllExceptionHandler())
handler = sb.lambda_handler()
It is important to take a look into the LaunchRequestHandler as an example of Alexa Skill handler written in Python:
x
class LaunchRequestHandler(AbstractRequestHandler):
"""Handler for Skill Launch."""
def can_handle(self, handler_input):
# type: (HandlerInput) -> bool
return ask_utils.is_request_type("LaunchRequest")(handler_input)
def handle(self, handler_input):
# type: (HandlerInput) -> Response
speak_output = i18n.t("strings.WELCOME_MESSAGE")
return (
handler_input.response_builder
.speak(speak_output)
.ask(speak_output)
.response
)
Building the Skill With Visual Studio Code
The build of the skill is fully automated with the launch.json and tasks.json in the .vscode folder. The first file is used for running the skill locally but before that moment we will execute some tasks defined in the second file which are:
create_env: this task will execute thehooks\post_new_hook. This script will do these tasks:- Will install if it is not installed the
virtualenvlibrary usingpip. - After install it, it will create a new Python Virtual Environment if it is not created at
.venv/skill_env
- Will install if it is not installed the
install_dependencies: This task will install all dependencies located inlambda/py/requirements.txtusing the Python Virtual Environment created above.build: Finally, it will copy all the source code fromlambda\pyto the Python Virtual environmentsite-packagesfolder.
Here, you have the tasks.json where you can find the tasks explained above and the commands separated per operative system:
x
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "create_env",
"type": "shell",
"osx": {
"command": "${workspaceRoot}/hooks/post_new_hook.sh ."
},
"windows": {
"command": "${workspaceRoot}/hooks/post_new_hook.ps1 ."
},
"linux": {
"command": "${workspaceRoot}/hooks/post_new_hook.sh ."
}
},{
"label": "install_dependencies",
"type": "shell",
"osx": {
"command": ".venv/skill_env/bin/pip -q install -r ${workspaceRoot}/lambda/py/requirements.txt",
},
"windows": {
"command": ".venv/skill_env/Scripts/pip -q install -r ${workspaceRoot}/lambda/py/requirements.txt",
},
"linux": {
"command": ".venv/skill_env/bin/pip -q install -r ${workspaceRoot}/lambda/py/requirements.txt",
},
"dependsOn": [
"create_env"
]
},{
"label": "build",
"type": "shell",
"osx": {
"command": "cp -r ${workspaceRoot}/lambda/py/ ${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/lib/python3.8/site-packages/",
},
"windows": {
"command": "xcopy \"${workspaceRoot}\\lambda\\py\" \"${workspaceRoot}\\.venv\\skill_env\\Lib\\site-packages\" /s /e /h /y",
},
"linux": {
"command": "cp -r ${workspaceRoot}/lambda/py/ ${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/lib/python3.8/site-packages/",
},
"dependsOn": [
"install_dependencies"
]
}
]
}
After that, the skill is ready to be launched locally!
So for building your skill, the only thing you have to do is run it locally in Visual Studio Code:
NOTE: pay attention with folder ${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/lib/python3.8/site-packages/ in Linux and OSX in the task build. You have to replace python3.8 if you are using another version of Python.
Running the Skill With Visual Studio Code
The launch.json file in the .vscode folder has the configuration for Visual Studio Code, which allows us to run our lambda locally:
x
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Launch Skill",
"justMyCode": false,
// Specify path to the downloaded local adapter(for python) file
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/local_debugger.py",
"osx": {
"preLaunchTask": "build",
"pythonPath": "${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/bin/python",
"args": [
// port number on your local host where the alexa requests will be routed to
"--portNumber", "3001",
// name of your python main skill file
"--skillEntryFile", "${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/lib/python3.8/site-packages/hello_world.py",
// name of your lambda handler
"--lambdaHandler", "handler"
],
},
"windows": {
"preLaunchTask": "build",
"pythonPath": "${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/Scripts/python.exe",
"args": [
// port number on your local host where the alexa requests will be routed to
"--portNumber", "3001",
// name of your python main skill file
"--skillEntryFile", "${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/Lib/site-packages/hello_world.py",
// name of your lambda handler
"--lambdaHandler", "handler"
],
},
"linux": {
"preLaunchTask": "build",
"pythonPath": "${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/bin/python",
"args": [
// port number on your local host where the alexa requests will be routed to
"--portNumber", "3001",
// name of your python main skill file
"--skillEntryFile", "${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/lib/python3.8/site-packages/hello_world.py",
// name of your lambda handler
"--lambdaHandler", "handler"
],
},
}
]
}
This configuration file will execute the steps explained in the previous section and the will run the following command:
xxxxxxxxxx
.venv/skill_env/scripts/python local_debugger.py --portNumber 3001 --skillEntryFile .venv/skill_env/Lib/site-packages/hello_world.py --lambdaHandler handler
This configuration uses the local_debugger.py file, which runs a TCP server listening on http://localhost:3001
For a new incoming skill request, a new socket connection is established. From the data received on the socket the request body is extracted, parsed into JSON and passed to the skill invoker's lambda handler. The response from the lambda handler is parsed as a HTTP 200 message format as specified here. The response is written onto the socket connection and returned.
After configuring our launch.json file and understanding how the local debugger works, it is time to click on the play button:
After executing it, you can send Alexa POST requests to http://localhost:3001.
NOTE: pay attention with folder ${workspaceRoot}/.venv/skill_env/lib/python3.8/site-packages/hello_world.py in Linux and OSX in the task build. You have to replace python3.8 if you are using another version of Python.
Debugging the Skill With Visual Studio Code
Following the steps before, now you can set up breakpoints wherever you want inside all Python files in the site-package folder of the Python Virtual Environment in order to debug your skill:
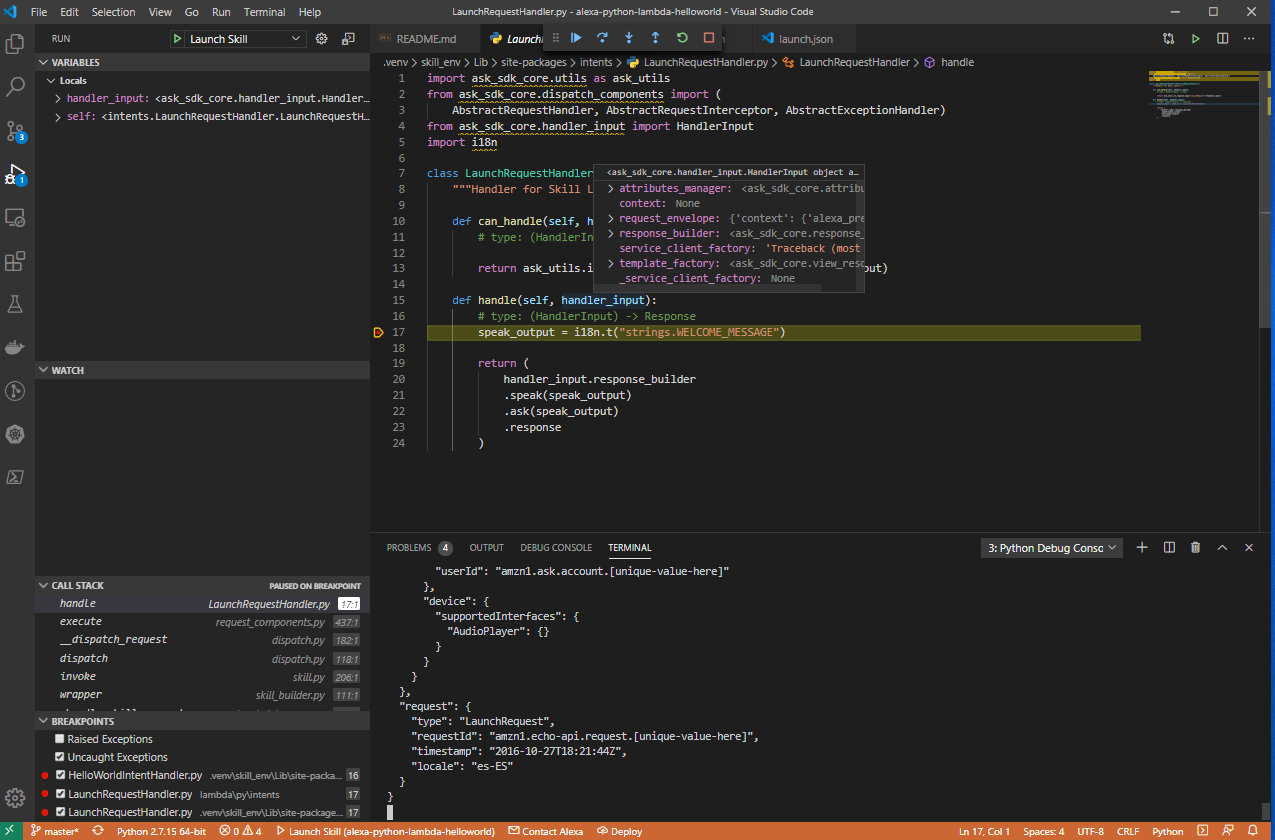
Testing Requests Locally
I'm sure you already know the famous tool call Postman. REST APIs have become the new standard in providing a public and secure interface for your service. Though REST has become ubiquitous, it's not always easy to test. Postman, makes it easier to test and manage HTTP REST APIs. Postman gives us multiple features to import, test and share APIs, which will help you and your team be more productive in the long run.
After running your application, you will have an endpoint available at http://localhost:3001. With Postman, you can emulate any Alexa Request.
For example, you can test a LaunchRequest:
x
{
"version": "1.0",
"session": {
"new": true,
"sessionId": "amzn1.echo-api.session.[unique-value-here]",
"application": {
"applicationId": "amzn1.ask.skill.[unique-value-here]"
},
"user": {
"userId": "amzn1.ask.account.[unique-value-here]"
},
"attributes": {}
},
"context": {
"AudioPlayer": {
"playerActivity": "IDLE"
},
"System": {
"application": {
"applicationId": "amzn1.ask.skill.[unique-value-here]"
},
"user": {
"userId": "amzn1.ask.account.[unique-value-here]"
},
"device": {
"supportedInterfaces": {
"AudioPlayer": {}
}
}
}
},
"request": {
"type": "LaunchRequest",
"requestId": "amzn1.echo-api.request.[unique-value-here]",
"timestamp": "2020-03-22T17:24:44Z",
"locale": "en-US"
}
}
Deploying Your Alexa Skill
With the code ready to go, we need to deploy it on AWS Lambda so it can be connected to Alexa.
Before deploying the Alexa Skill, we can show that the config file in the .ask folder is empty:
x
{
"deploy_settings": {
"default": {
"skill_id": "",
"was_cloned": false,
"merge": {}
}
}
}
Deploy Alexa Skill with ASK CLI:
ask deploy
As the official documentation says:
When the local skill project has never been deployed, ASK CLI creates a new skill in the development stage for your account, then deploys the skill project. If applicable, ASK CLI creates one or more new AWS Lambda functions in your AWS account and uploads the Lambda function code. Specifically, ASK CLI does the following:
- Look in your skill project's config file (in the .ask folder, which is in the skill project folder) for an existing skill ID. If the config file does not contain a skill ID, ASK CLI creates a new skill using the skill manifest in the skill project's skill.json file, then adds the skill ID to the skill project's config file.
- Look in your skill project's manifest (skill.json file) for the skill's published locales. These are listed in the manifest.publishingInformation.locales object. For each locale, ASK CLI looks in the skill project's models folder for a corresponding model file (for example, es-ES.json), then uploads the model to your skill. ASK CLI waits for the uploaded models to build, then adds each model's eTag to the skill project's config file.
- Look in your skill project's manifest (skill.json file) for AWS Lambda endpoints. These are listed in the manifest.apis..endpoint or manifest.apis..regions..endpoint objects (for example, manifest.apis.custom.endpoint or manifest.apis.smartHome.regions.NA.endpoint). Each endpoint object contains a sourceDir value, and optionally a URI value. ASK CLI upload the contents of the sourceDir folder to the corresponding AWS Lambda function and names the Lambda function the same as the URI value. For more details about how ASK CLI performs uploads to Lambda, see AWS Lambda deployment details.
- Look in your skill project folder for in-skill products, and if it finds any, uploads them to your skill. For more information about in-skill products, see the In-Skill Purchasing Overview.
In Python, there are some more steps. Before deploying your Alexa Skill, the script pre_deploy_hook in the hooks folder will be executed. This script will be run the following tasks:
- It will copy all the files of your
site-packagesof your Python Virtual Environment in a new folder calledlambda_uploadlocated inlambda/pyfolder. - Then will copy the source code of your skill written in Python located in
lambda/pyinlambda/py/lambda_puload. - Finally, this new folder as a
.zipwill be deployed to AWS.
After the execution of the above command, we will have the config file properly filled:
x
{
"deploy_settings": {
"default": {
"skill_id": "amzn1.ask.skill.53ad2510-5758-48db-9c43-e4263a2055db",
"resources": {
"lambda": [
{
"alexaUsage": [
"custom/default"
],
"arn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:141568529918:function:ask-custom-alexa-python-lambda-helloworld-default",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"codeUri": "lambda/py/lambda_upload",
"functionName": "ask-custom-alexa-python-lambda-helloworld-default",
"handler": "hello_world.handler",
"revisionId": "b95879d0-d039-4fa2-b7e5-96746f36689f",
"runtime": "python3.6"
}
],
"manifest": {
"eTag": "3809be2d04cfb7f90dd0fa023920e0bd"
},
"interactionModel": {
"es-ES": {
"eTag": "235f49ae9fa329de1b7e2489ec7e4622"
}
}
},
"was_cloned": false,
"merge": {}
}
}
}
Test Requests Directly From Alexa
ngrok is a very cool, lightweight tool that creates a secure tunnel on your local machine along with a public URL you can use for browsing your local site or APIs.
When ngrok is running, it listens on the same port that you’re local web server is running on and proxies external requests to your local machine
From there, it’s a simple step to get it to listen to your web server. Say you’re running your local web server on port 3001. In terminal, you’d type in: ngrok http 3001. This starts ngrok listening on port 3001 and creates the secure tunnel:
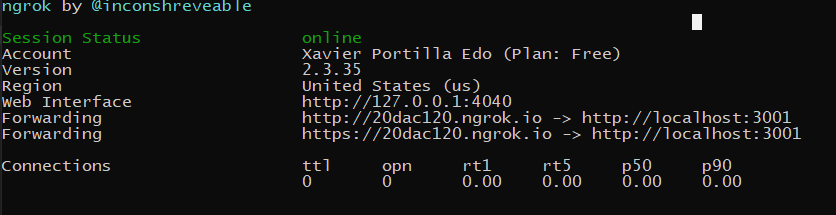
So now you have to go to Alexa Developer console, go to your skill > endpoints > https, add the https url generated above . Eg: https://20dac120.ngrok.io.
Select the My development endpoint is a sub-domain.... option from the dropdown and click save endpoint at the top of the page.
Go to Test tab in the Alexa Developer Console and launch your skill.
The Alexa Developer Console will send a HTTPS request to the ngrok endpoint (https://20dac120.ngrok.io) which will route it to your skill running on Web API server at http://localhost:3001.
Resources
- Official Alexa Skills Kit Python SDK
- Official Alexa Skills Kit Python SDK Docs
- Official Alexa Skills Kit Docs
Conclusion
This was a basic tutorial to learn Alexa Skills using Python. As you have seen in this example, the Alexa Skill Kit for Python and the Alexa Tools like ASK CLI can help us a lot and give us the possibility to create skills in an easy way.
That’s all, folks! You can find all the code in my GitHub.
I hope it will be useful! If you have any doubts or questions, do not hesitate to contact me or put a comment below.
Happy coding!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments