All About PL/SQL Compilation Settings
Curious about how best to modify PL/SQL compiler settings? Then you need to check out this post.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeA recent Twitter thread delved into the topic of the best way to enable PL/SQL warnings for program units, including this recommendation from Bryn Llewellyn, Distinguished Product Manager for PL/SQL:
This then led to Bryn volunteering me to delve into the details of PL/SQL compiler settings in an AskTOM PL/SQL Office Hours session.
Which I will do. But I figured I could start right off by writing this post. So let's explore how to set and modify PL/SQL compiler settings.
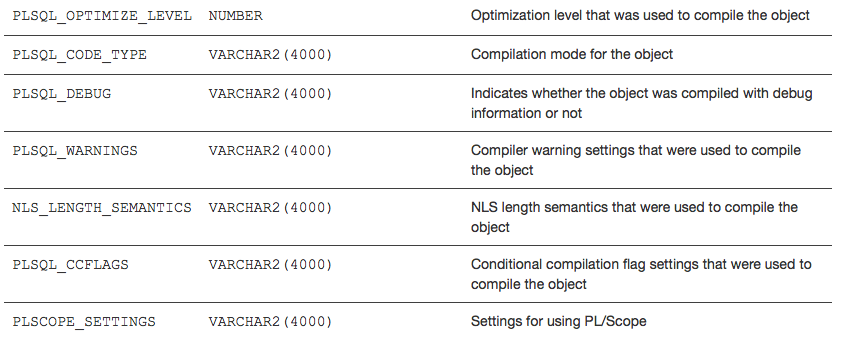
First, you might wonder what those settings are or could be. The best way to check is by examining the USER_PLSQL_OBJECT_SETTINGS view (and of course the ALL* version to examine attributes of code you do not own but can execute):
These values are set each time you compile a program unit (well, except if you specify REUSE SETTINGS — more on that below).
I will explore how to set these attributes at both the session and program unit level below, how to override, and how to preserve them. You can run all of this code yourself on LiveSQL.
When I first connect to a schema, and until I issue any ALTER statements, compilations of code will rely on the system defaults. You can see what they are by connecting, making no changes to session settings, then execute a CREATE OR REPLACE for a program unit and finally query its values from the view, as in:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE check_compile_time_settings
IS
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
SELECT plsql_optimize_level opt,
plsql_code_type ctype,
plsql_debug plsql_warnings warn,
nls_length_semantics len,
plsql_ccflags cc,
plscope_settings plscope
FROM user_plsql_object_settings
WHERE LOWER (name) = 'check_compile_time_settings'
/
OPT CTYPE WARN LEN CC PLSCOPE
------ ----------- ------ -------- ----- ----------------
2 INTERPRETED FALSE BYTE - IDENTIFIERS:NONEHere's the LiveSQL script that performs these two steps.
Note: I hope to update this post soon with a query that does not require you to create a database object first.
Now let's take a look at how you can change the compilation settings for a program unit, at the session level and also for specifics.
There are three ways you can compile an individual program unit:
- CREATE OR REPLACE DDL statement
- ALTER-COMPILE statement
- DBMS_DDL.ALTER_COMPILE
The third option is really just an API to the ALTER-COMPILE statement.
When you compile your code via CREATE OR REPLACE that program unit will inherit all the current settings in your session.
With both ALTER-COMPILE and DBMS_DDL.ALTER_COMPILE, you can either inherit those settings or reuse (re-apply) the settings that are currently associated with the program unit.
All right, then, let's get going. I connect to my schema and immediately change the setting for PL/SQL compile-time warnings. I then compile my procedure and confirm that it used the session setting.
ALTER SESSION SET plsql_warnings = 'ENABLE:ALL'
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE aftercompile
AUTHID DEFINER
IS
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
SELECT plsql_warnings "From Session"
FROM user_plsql_object_settings
WHERE name = 'AFTERCOMPILE'
/
From Session
------------
ENABLE:ALLNow I am going to recompile that procedure with an ALTER statement and specify a value different from the sessions for PL/SQL warnings. As you can see in the query, the procedure now has PL/SQL warnings set to treat any warning as a compile error.
ALTER PROCEDURE aftercompile COMPILE plsql_warnings = 'ERROR:ALL'
/
SELECT plsql_warnings "From Procedure Override"
FROM user_plsql_object_settings
WHERE name = 'AFTERCOMPILE'
/
From Procedure Override
-------------------------
ERROR:ALLNow I CREATE OR REPLACE to demonstrate that the session setting is now applied to the procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE aftercompile
AUTHID DEFINER
IS
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
SELECT plsql_warnings "Compile From Source"
FROM user_plsql_object_settings
WHERE name = 'AFTERCOMPILE'
/
Compile From Source
-------------------
ENABLE:ALLBut what if you want to recompile your program unit and you do not want to pick up the current session settings? You want to keep all settings intact. We offer you the REUSE SETTINGS clause.
From the last sequence of statements, we can see that the session setting for PL/SQL warnings is "ENABLE:ALL". Below, I recompile my procedure, specifying "ERROR:ALL". Then I recompile again, but this time I do not specify a value for PL/SQL warnings. Instead, I ask to reuse settings for the procedure.
ALTER PROCEDURE aftercompile COMPILE plsql_warnings = 'ERROR:ALL'
/
SELECT plsql_warnings "Back to Procedure Override"
FROM user_plsql_object_settings
WHERE name = 'AFTERCOMPILE'
/
Back to Procedure Override
--------------------------
ERROR:ALL
ALTER SESSION SET plsql_warnings = 'ENABLE:ALL'
/
ALTER PROCEDURE aftercompile COMPILE REUSE SETTINGS
/
SELECT plsql_warnings "Session Change No Impact with REUSE SETTINGS"
FROM user_plsql_object_settings
WHERE name = 'AFTERCOMPILE'
/
Session Change No Impact with REUSE SETTINGS
--------------------------------------------
ERROR:ALL
As you can see, the setting for my procedure did not change.
Okay, I think that covers this territory pretty well (until my readers point out what I missed!).
Here are some links you might find helpful.
Published at DZone with permission of Steven Feuerstein, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments