Everything You Need to Know About System.gc()
Poor code performance is trash.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
In this article, we have attempted to answer the most common questions around System.gc() API call. We hope it may be of help.
You may also like: Java Garbage Collection
What Is System.gc()?
System.gc() is an API provided in Java, Android, C#, and many other popular languages. When invoked, it will make its best effort to clear an accumulated unreferenced object (i.e. garbage) from memory.
Who Invokes System.gc()?
System.gc() calls can be invoked from various parts of your application stack:
- Your own application developers might be explicitly calling
System.gc()method. - Sometimes,
System.gc()can be triggered by your third-party libraries, frameworks, and even your application servers. - It could be triggered by external tools (like VisualVM) through the use of JMX
- If your application is using RMI, then RMI invokes
System.gc()on a periodic interval.
What Are the Downsides of Invoking System.gc()?
When System.gc() or Runtime.getRuntime().gc() API calls are invoked from your application, stop-the-world, full GC events will be triggered. During stop-the-world, full GCs, the entire JVM will freeze (i.e. all the customer transaction that are in motion will be paused). Typically, these full GCs take a long duration to complete. Thus, it has the potential to result in poor user experiences and your SLAs at unnecessary times when GC isn’t required to be run.
JVM has sophisticated algorithm working all the time in the background doing all computations and calculations on when to trigger GC. When you invoke System.gc() call, all those computations will go for toss. What if JVM has triggered GC event just a millisecond back and once again from your application you are going invoking System.gc()? Because from your application you don’t know when GC ran.
Are there any good/valid reasons to invoke System.gc()?
We haven’t encountered that many good reasons to invoke System.gc() from the application. But here is an interesting use case we saw in a major airline’s application. This application uses 1 TB of memory. This application’s Full GC pause time takes around 5 minutes to complete. Yes, don’t get shocked, it’s 5 minutes (but we have seen cases of 23 minutes GC pause time as well). To avoid any customer impact due to this pause time, this airline company has implemented a clever solution. On a nightly basis, they take out one JVM instance at a time from their load balancer pool. Then they explicitly trigger System.gc() call through JMX on that JVM. Once GC event is complete and garbage is evicted from memory, they put back that JVM into load balancer pool. Through this clever solution, they have minimized customer impact caused by this 5 minutes GC pause time.
How to Detect Whether System.gc() Calls Are Made From Your Application
As you may have noticed in the ‘Who invokes System.gc()?’ section, you can see System.gc() calls to be made from multiple sources and not just from your application source code. Thus, searching your application code, the System.gc() string isn’t enough to tell whether your application is making System.gc() calls. This poses a challenge: How do you detect whether System.gc() calls are invoked in your entire application stack?
This is where GC logs come in handy. Enable GC logs in your application. In fact, it’s advisable to keep your GC log enabled all times in all of your production servers, as it helps you to troubleshoot and optimize application performance. Enabling GC logs adds negligible (if at all observable) overhead. Now, upload your GC log to a garbage collection log analyzer tool like GCeasy, HP JMeter, etc. These tools generate rich garbage collection analysis report.
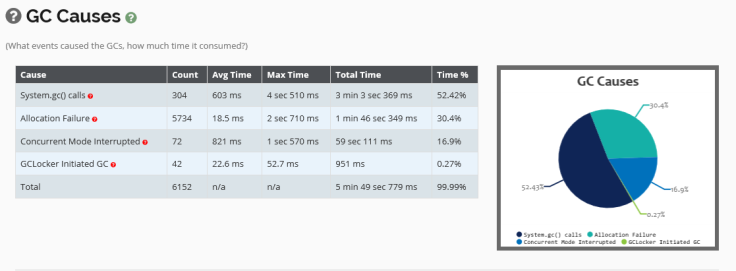
Above figure is an excerpt from the ‘GC Causes’ section of the report generated by GCeasy. You can see that System.gc() call to be invoked 304 times accounting for 52.42 percent of GC pause time.
How to Remove System.gc() Calls
You can remove the explicit System.gc() call through the following solutions:
a. Search & Replace
This might be a moretraditional method :-), but it works. Search in your application code base for System.gc() and Runtime.getRuntime().gc(). If you see a match, then remove it. This solution will work if System.gc() is invoked from your application source code. If System.gc() is going to invoke from your third-party libraries, frameworks, or through external sources, then this solution will not work. In such circumstances, you can consider using the option outlined in item b.
b. -XX:+DisableExplicitGC
You can forcefully disable System.gc() calls by passing the JVM argument -XX:+DisableExplicitGC when you launch the application. This option will silence all System.gc() calls invoked anywhere from your application stack.
c. RMI
If your application is using RMI, then you can control the frequency in which System.gc() calls are made. This frequency can be configured using the following JVM arguments when you launch the application:
-Dsun.rmi.dgc.server.gcInterval=n-Dsun.rmi.dgc.client.gcInterval=nThe default value for these properties in
JDK 1.4.2 and 5.0 is 60000 milliseconds (i.e. 60 seconds)
JDK 6 and later release is 3600000 milliseconds (i.e. 60 minutes)
Lastly, you might want to set these properties to a very high value so that it can minimize the impact.
Further Reading
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments