Amazon Simple Queue Service With Spring Boot: How To Send and Receive Messages
Learn how to send your Spring Boot messages with confidence.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat is AWS SQS?
Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) is a distributed message queuing service introduced by Amazon.com in late 2004. It supports programmatic sending of messages via web service applications as a way to communicate over the Internet. SQS is intended to provide a highly-scalable hosted message queue that resolves issues arising from the common producer-consumer problemor [BS1] connectivity between producer and consumer.
Amazon SQS automatically deletes messages that have been in a queue for more than maximum message retention period. The default message retention period is 4 days. However, you can set the message retention period to a value from 60 seconds to 1,209,600 seconds (14 days) using the SetQueueAttributes action.
Message Lifecycle
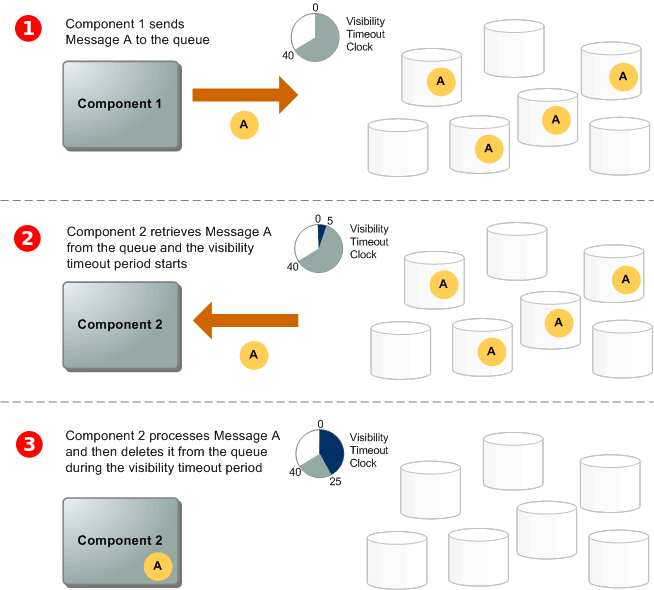
(Image reference from aws.amazon.com)
A producer (component 1) sends message A to a queue, and the message is distributed across the Amazon SQS servers redundantly.
When a consumer (component 2) is ready to process messages, it consumes messages from the queue, and message A is returned. While message A is being processed, it remains in the queue and isn't returned to subsequent receive requests for the duration of the visibility timeout.
The consumer (component 2) deletes message A from the queue to prevent the message from being received and processed again when the visibility timeout expires.
SQS Types
- Standard Queue: Amazon SQS offers standard as the default queue type. Standard queues support a nearly unlimited number of transactions per second (TPS) per action. Standard queues support at-least-once message delivery.
- FIFO Queue: FIFO queues are available in the US East (N. Virginia), US East (Ohio), US West (Oregon), EU (Ireland), Asia Pacific (Sydney), and Asia Pacific (Tokyo) regions. FIFO queues have all the capabilities of the standard queue.
FIFO (First-In-First-Out) queues are designed to enhance messaging between applications when the order of operations and events is critical, or where duplicates can't be tolerated, for example:
Ensure that user-entered commands are executed in the right order.
Display the correct product price by sending price modifications in the right order.
Prevent a student from enrolling in a course before registering for an account.
Creating an Amazon SQS Queue
- Sign in to the Amazon SQS console.
- Choose Create New Queue.
- On the Create New Queue page, ensure that you're in the correct region and then type the Queue Name. The name of a FIFO queue must end with the .fifo suffix.
- Standard is selected by default.
- Create your queue
Integration AWS SQS with Spring Boot
To send a message to SQS from Spring Boot, we require below dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-aws-messaging</artifactId> <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Define the SQS url in application.properties:
sqs.url:https://[EC2-Instance OR region or zone ].amazonaws.com/[20XXXXXXXXXX]/sqs-queue-name
Sending Message to SQS:
final AmazonSQS sqs = AmazonSQSClientBuilder.defaultClient(); //to create AmazonSQS
object.sqs.sendMessage(new SendMessageRequest(sqsURL, “This is my first message to SQS”));sqsURL is the url that you can get from the application.properties. To inject the value from application properties or Environment value, please use the @Value annotation:
@Value("${sqs.url}")
private String sqsURL;By using the above code snippets, you can easily send the message to SQS.
Reading Message from SQS (Asynchronous)
@Value("${sqs.url}")
private String sqsURL;
final AmazonSQS sqs = AmazonSQSClientBuilder.defaultClient();
while(true) {
log.info("Receiving messages from MyQueue.\n");
final ReceiveMessageRequest receiveMessageRequest =
new ReceiveMessageRequest(sqsURL)
.withMaxNumberOfMessages(1)
.withWaitTimeSeconds(3);
final List<com.amazonaws.services.sqs.model.Message> messages =
sqs.receiveMessage(receiveMessageRequest).getMessages();
By default, it will read a single message from the queue. It won’t read all the message and respond. To get the multiple messages, you need define the number in withMaxNumberOfMessages(1).
Conclusion
So, here we saw that it is very easy to send and receive message to Amazon SQS with Spring Boot. We can build and consume SQS by using the AWS provided libraries and function for our application as per the requirement.
Please have a look at the code implementation.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments