Apache Ignite: Partitioned Cache
Get started with Apache Ignite.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Background
Many enterprise applications are distributed and deployed on multiple servers and accessed by many interfacing applications. In this series, we will go through various scenarios of usage of Apache Ignite in large applications.
We will implement the following scenario in this article:
- “Partitioned” Caching:
- In-Memory Caching Grid with three caching nodes and a single client. The server will be responsible for storing the objects, and the client will be responsible for accessing objects. This client will put and get data from the server.
- Use a command line monitoring tool to view statistics of the cache.
In subsequent articles, we will enhance this scenario with additional complexities like:
- Additional Cache: Partitioned cache with custom objects for products and additional cache and compute.
- Grid caching with an underlying database: This part will provide details on how the cached data will be stored in the underlying database. The database can be MYSQL or any other database. Apache Ignite can also act as a distributed database and can be much more powerful than other databases. However, a large application might have an existing database, and it might be very difficult to replace the existing database with Ignite. Hence, let's consider this scenario.
- Security: In this article, we will add some security to ensure that only certain clients can access data.
- Continuous Query: In this part, we will add continuous querying to ensure that selected clients can access the data and get events when needed.
You may also like: Getting Started With Apache Ignite (Part 1).
Grid Caching
Apache Ignite is also a data caching grid. It can scale horizontally with thousands of nodes. The data in the in-memory cache is stored as key-value pairs. It is an implementation of the JCache (JSR 107) specification. In addition to JCache specifications, it also supports transactions and ensures that data is consistent.
Partitioned Cache
Cache can be partitioned, replicated, or local. In this part, we will go through partitioned cache. A partitioned cache, as name suggests is partitioned across multiple nodes. A partitioned cache is more efficient when compared to replicated cache, as the object added in the cache need not have to be replicated in all cache nodes and is only required to be added to backup cache nodes.
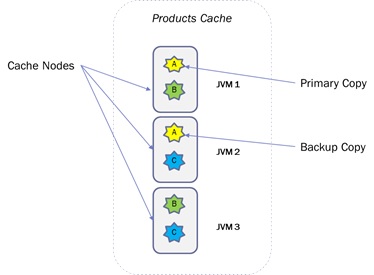
As shown in the above diagram, there are three cache nodes in the product cache, which is a partitioned cache with a single backup copy. The following is the XML configuration of the Product Cache.
<bean class="org.apache.ignite.configuration.CacheConfiguration">
<property name="name" value="ProductsCache" />
<property name="cacheMode" value="PARTITIONED"/>
<property name="backups" value="1" />
<property name="atomicityMode" value="ATOMIC" />
<property name="writeSynchronizationMode" value="FULL_SYNC"/>
</bean>Pre-Requisites
We need to install the following software:
- JDK 13: javac 13.0.1.
- Apache Ignite: 2.7.6.
- Eclipse.
Start Servers
The cache server can be started by following command. I have created a server configuration in server-config.xml file and installed Ignite in the F:\Installed\apache-ignite-2.7.6-bin directory.
F:\Installed\apache-ignite-2.7.6-bin\bin>ignite.bat F:\Installed\apache-ignite-2.7.6-bin\config\learning-config.xmlWe want to create three cache nodes. Hence, we need to execute the above command three times. It will start three servers. You will be able to see the following output on each command prompt.
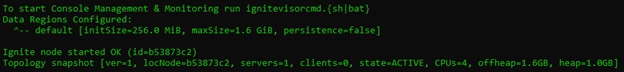
You will be able to see the following output on the console of node one when all other cache server nodes are started. The output clearly shows that there are three servers and there are no clients associated with this cache nodes. In addition, it will also show the total size allocated to this each node.
Visor – Cache Monitoring Tool
Visor tool is a command line tool to monitor Ignite nodes. It can be used to get various statistics about cache nodes, cache, etc. In addition to this, it can be also used for clearing cache, starting new nodes, etc. This tool can be started by executing the following command.
F:\Installed\apache-ignite-2.7.6-bin\bin>ignitevisorcmd.bat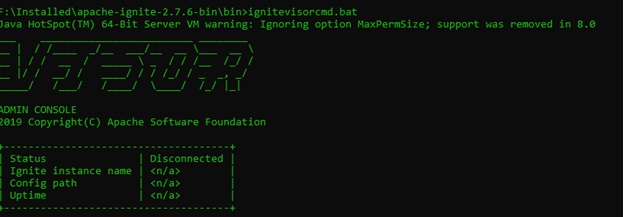
As you can see, the command line tool is not connected to any grid. It can be connected to any grid by executing open command along with the configuration file. This can be used in interactive mode.
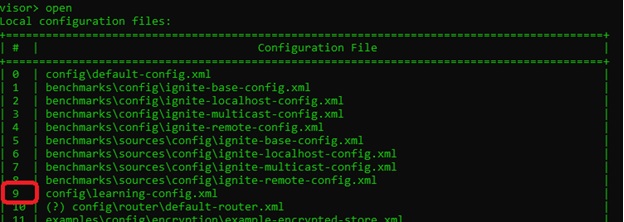
Once connected, we can execute the cache command to view the status of the cache. As you can see, there are three nodes in this grid, and there are no objects stored in this grid as of now.
Cache Client
In our scenario, the cache client is a non-persistence node. This client will be responsible for storing objects and getting objects from the caching grid. In our scenario, the object is a string, but it can be any type of object.
Following is a client code:
public class CacheClient {
public static String cacheName = "ProductsCache";
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println( "Starting Cache Client" );
/*
* Set the mode of the client. This can also be done by creating XML configuration.
*
* In this case, my server and clients are running on same machine. Hence,
* I have not provided network discovery related configuration.
* In most cases, the client node will run on different machine. in this case, we need to
* pass the network configuration like static IP address or multicast IP address.
* in general, I prefer to use multicast IP address to make sure that multiple
* clients & servers are able to connect and there is no dependency on actual IP address.
*
*/
Ignition.setClientMode(true);
Ignite ignite = Ignition.start();
System.out.println("Client Node Started..");
// The Cache name
IgniteCache<String, String> cache = ignite.cache(CacheClient.cacheName);
System.out.println("Got instance of Cache " + CacheClient.cacheName );
// Store keys in cache (values will end up on different cache nodes).
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
cache.put(String.valueOf(i), Integer.toString(i));
System.out.println("Added Objects in Cache" );
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
System.out.println("Got [key=" + i + ", val=" + cache.get(String.valueOf(i)) + ']');
}
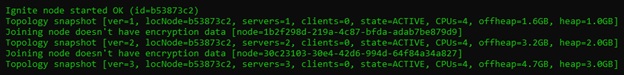
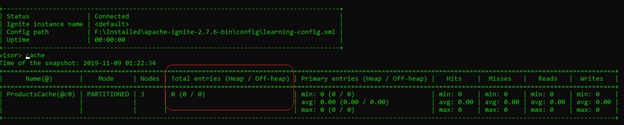
}Once the client node is started, the first node will have the following output on the command prompt. As you can see, there is one client and three servers.
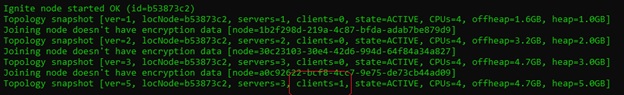
The following will be output on the visor monitoring tool after the execution of the cache command. This shows that there are 100 entries in the cache.
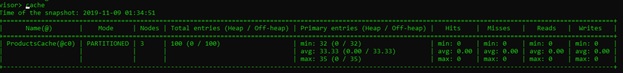
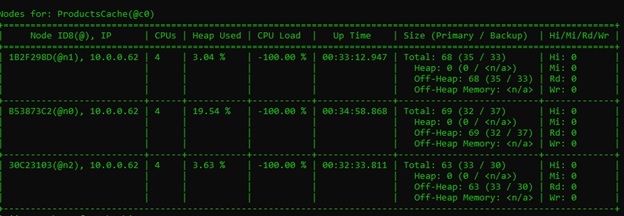
The cache -r -a visor command will provide details on the cache associated with the c0 variable. In this case, it's ProductCache. As you can see, there are three nodes, and each node has a primary and backup copy. We inserted 100 objects in the cache, and each cache has approximately 33 Primary and 33 backup copies.
Further Reading
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments