API Test Automation
API test automation framework creation using PyTest.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAPIs are an integral part of software development in any small/mid/large scale application. This means that testing of these APIs will dramatically improve the efficiency of the entire application.
There are several benefits to API Testing, including:
- Catch early errors during the development process
- Helpful in providing complete test coverage rather than just UI testing
- Not tightly bound to programming language (API Automation)
- Takes less time to test the application than UI testing
We'll now learn to create an API Test Automation Framework from scratch.
Tech Stack
- Python
- Pytest
- Requests library
- Allure (Reporting)
- Any CI/CD tool
Prerequisites
You'll need a basic understanding of REST API, HTTP methods, and response codes.
Let's get started!
Step 1
Check the version of Python installed on your machine:
Step 2
Install and check the version of pip on your machine: pip.
Step 3
Install requests library
pip install requestsStep 4
Creation of Project Architecture
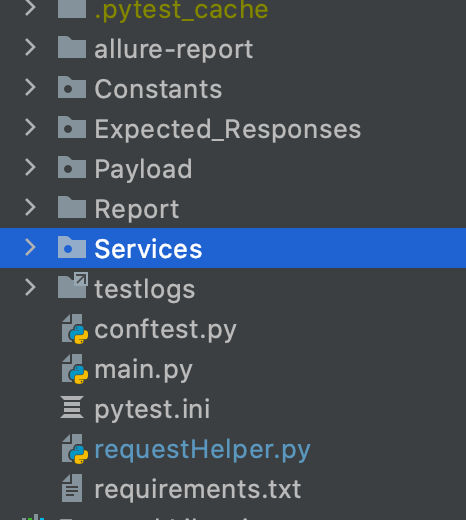
You can follow the above project architecture.
Constants
This package will contain the __init__.py file and Constants.py module, where you can define all your constant values. For example, URL, username, password, tokens, etc.Expected-Responses
This package shall contain the expected responses for each Service request.
You can add multiple packages under Expected-Responses.Payload
This package shall contain the payload in JSON/dict format, which you'll be passing to the request. The payload might contain values that you can import from the Constant.py module created above.Services
This package shall contain the list of service modules. For example:- test_service1.py
- test_service2.py
The test_service1.py module will contain the 'test cases.'
Methods are defined as:
def test_<testcasename>:
They are considered test cases.
For example:
def test_service1(self):
payload_json = json.dumps(payload_service1.data, default=str)
request = HttpRequest()
log.info("the API call is : " + self.URL + "<endpoint>")
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=utf-8", 'token': self.token,
}
response = request.send_request_with_data(self.URL + "<endpoint>",
headers=headers, data=payload_json)
response_code = response.status_code
if response_code != 204:
data = json.loads(response.text)
log.info('The Custom status code is ' + str(data['statusCode']))
assert int(data['statusCode']) == 200
expected_response = json.dumps(service1_expected_response.expected)
expected = json.loads(expected_response)
for key in data.keys():
if key not in expected:
assert False, "Key mismatch"
log.info('The Custom status code is ' + str(data['statusCode']))
assert int(data['statusCode']) == 200- conftest.py
This file contains all the configuration stuff. For example, generation of token for API calls. You'll be able to use the 'token' value throughout your Service calls.
def get_token(request,url):
payload = {
"Key": Constants.KEY,
}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=utf-8"}
requests = HttpRequest()
log.info("The API call is : " + url + "<endpoint>")
response = requests.send_request_with_data(url + "<endpoint>", json=payload,
headers=headers, redirects=False)
response_code = response.status_code
log.info("The status code is " + str(response_code))
response = json.loads(response.text)
token = response['Token']
if request.cls is not None:
request.cls.token = token
request.cls.URL = url
yield token- requestHelpers.py
This module shall contain the helper functions required for the API requests. You can import the request module to create the helper functions. For example,
class HttpRequest(object):
session = None
def __init__(self):
self.session = requests.session()
def send_request_with_data(self, url, data=None, json=None, headers=None, redirects=True):
try:
conn = self.session.post(url, headers=headers, json=json, data=data, verify=False, allow_redirects=redirects, timeout=600)
except Exception as exception:
raise exception
return conn- requirements.txt
This file shall contain all the modules which are a pre-requisite for the creation of this Test automation framework.
pytest
requests
pytest-logger
pytest-html
allure-pytest
Use of Markers:
@pytest.mark.service1Markers can be used to execute specific sets of test cases. For example, if you want to execute the tests specific to service1, then you can apply the custom marker using the above command.
Markers can be executed using the command :
pytest -m "marker_name"You can register your custom markers by creating a pytest.ini file. The contents of the file can be:
[pytest]
markers =
marker1: description
Step 5
Reporting
We'll use the allure reporting tool for our API Automation tests.
Follow the below-mentioned steps to set up the allure reporting:
pip install allure-pytest
For generating report in custom folder
pytest test.py --alluredir=<path_to_custom_folder>
Once the test are executed, you can go to the Custom Report folder and view the report using:
allure serve <Report_folder_name>There's much more to API test automation than just creating the framework architecture. I'll write more about the specific insights of each useful package/module in this framework in the upcoming write-ups.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments