Applying New JDK 11 String Methods
Want to learn more about the new String methods in JDK11? Click here to learn more about these methods and how to use them.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the posts "New Methods on Java String with JDK 11" and "String#repeat Coming to Java?," I discussed six new methods coming to the Java String with JDK 11. The available early access JDK 11 builds already includes these new methods. In this post, I will demonstrate how to use one of those early access builds.
I am using OpenJDK JDK 11 Early Access Build 20 for compiling and running the examples shown below.
The six methods added to String for JDK 11 in this post via the OpenJDK JDK 11 Early Access Build 20 are:
String.repeat(int)String.lines()String.strip()String.stripLeading()String.stripTrailing()String.isBlank()
The source code for these examples is available on GitHub.
String.repeat(int)
The String.repeat(int) method provides handy functionality that I've wanted to see in Java since experiencing this functionality in Groovy. As its name suggests, this method repeats the String It will run against it as many times as provided by the int parameter. I will frequently use this method in the future when generating simple demonstrations and use it for this post's examples. The next code listing demonstrates the use of String.repeat(int) to easily generate header separators for the demonstration output.
Use of String.repeat(int)
/**
* Write provided {@code String} in header. Note that this
* implementation uses {@code String.repeat(int)}.
*
* @param headerText Title of header.
*/
private static void writeHeader(final String headerText)
{
final String headerSeparator = "=".repeat(headerText.length()+4);
out.println("\n" + headerSeparator);
out.println("= " + headerText + " =");
out.println(headerSeparator);
} The writeHeader(String) method uses String.repeat(int) to easily generate "header separator" lines from the "=" character enough times to cover the provided headerText length, plus 4 additional characters to allow for an extra "=" and extra space on each side of the "header text." The writeHeader(String) method is used by all the other demonstration examples in this post and will be demonstrated via those examples.
String.lines()
The String.lines() method splits the String by its line terminators and returns a Stream of Strings as demarcated by those line terminators.
Use of String.lines()
/**
* Demonstrate method {@code String.lines()} added with JDK 11.
*/
public static void demonstrateStringLines()
{
final String originalString = prepareStringWithLineTerminators();
final String stringWithoutLineSeparators
= originalString.replaceAll("\\n", "\\\\n");
writeHeader("String.lines() on '" + stringWithoutLineSeparators + "'");
final Stream<String> strings = originalString.lines();
strings.forEach(out::println);
} The sample output is shown in the next screen snapshot:
String.strip() / String.stripLeading() / String.stripTrailing()
The String.strip(), String.stripLeading(), and String.stripTrailing() methods trim white space [as determined by Character.isWhiteSpace()] off either the front, back, or both front and back of the targeted String.
Use of String.strip() / String.stripLeading() / String.stripTrailing()
/**
* Demonstrate method {@code String.strip()} added with JDK 11.
*/
public static void demonstrateStringStrip()
{
final String originalString = prepareStringSurroundedBySpaces();
writeHeader("String.strip() on '" + originalString + "'");
out.println("'" + originalString.strip() + "'");
}
/**
* Demonstrate method {@code String.stripLeading()} added with JDK 11.
*/
public static void demonstrateStringStripLeading()
{
final String originalString = prepareStringSurroundedBySpaces();
writeHeader("String.stripLeading() on '" + originalString + "'");
out.println("'" + originalString.stripLeading() + "'");
}
/**
* Demonstrate method {@code String.stripTrailing()} added with JDK 11.
*/
public static void demonstrateStringStripTrailing()
{
final String originalString = prepareStringSurroundedBySpaces();
writeHeader("String.stripTrailing() on '" + originalString + "'");
out.println("'" + originalString.stripTrailing() + "'");
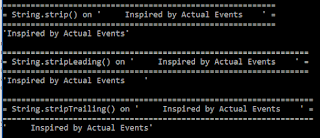
} When the above code is executed, the output looks like that shown in the next screen snapshot:
String.isBlank()
The String.isBlank() method indicates if the targeted String is empty or if it contains only whitespace characters as determined by the Character.isWhitespace(int).
Use of String.isBlank()
/**
* Demonstrate method {@code String.isBlank()} added with JDK 11.
*/
public static void demonstrateStringIsBlank()
{
writeHeader("String.isBlank()");
final String emptyString = "";
out.println("Empty String -> " + emptyString.isBlank());
final String onlyLineSeparator = System.getProperty("line.separator");
out.println("Line Separator Only -> " + onlyLineSeparator.isBlank());
final String tabOnly = "\t";
out.println("Tab Only -> " + tabOnly.isBlank());
final String spacesOnly = " ";
out.println("Spaces Only -> " + spacesOnly.isBlank());
} An example of executing this code is shown in the next screen snapshot.
Some of the methods shown above are called "helper" methods that can be seen on GitHub.
The methods added to JDK 11's String are small additions but will make certain "presentation" tasks related to Java Strings easier than in the past and reduce the need for third-party libraries.
Published at DZone with permission of Dustin Marx, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.




Comments