AWS Attribute Based Access Control
In this article, we will explore the concept of ABAC in AWS, its key components, its benefits, and how to implement it within your AWS infrastructure effectively.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAccess control is a critical aspect of any cloud environment, ensuring that only authorized users and entities have appropriate access to resources. Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a robust access control mechanism called Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC). ABAC allows organizations to implement fine-grained access control policies based on various attributes, providing flexibility and enhanced security. In this article, we will explore the concept of ABAC in AWS, its key components, its benefits, and how to implement it within your AWS infrastructure effectively.
ABAC Concept
Tags
A tag refers to a key-value pair that is assigned to a resource in order to store metadata related to that resource. Each tag comprises a label containing a key and value.
Tagging involves the process of attaching metadata to various resources within your AWS environment, serving multiple purposes such as Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC), Cloud Financial Management, and automation tasks like patching specific instances based on tags. We will discuss ABAC and how tags will be used to implement ABAC here.
Principle and Resource Tags for ABAC
Whenever you perform an operation in the AWS console, through an API, or using the CLI, you are essentially sending a request. These requests consist of three key components: Principals, Actions, and Resources.
Tags can be assigned to IAM entities like users and roles, allowing them to be associated with the main element of a request. Principal tags, along with resource tags, are available in the request context while making authorization decisions. This feature facilitates the evaluation of both principal and resource tags to determine access control.
When you assume an IAM role using Security Token Service (STS) or federate identity through an external Identity Provider (IdP) using protocols like SAML or OIDC, you can also assign tags to the temporary session created. These tags, known as principal tags, are accessible within the request context and can be utilized for making authorization decisions.
Therefore, we have not only metadata regarding the objects involved in an authorization request, but also information about the principals participating in the request and the overall context in which the request was initiated. Leveraging this data, IAM policies can be written to allow or deny requests by utilizing policy Conditions that compare the attached metadata of a principal in a request with that of a target resource.
One of the key advantages of Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC) is its ability to significantly reduce the number of policies required to achieve desired goals. This streamlined approach makes it easier for teams to scale and manage access control effectively.
How To Use ABAC
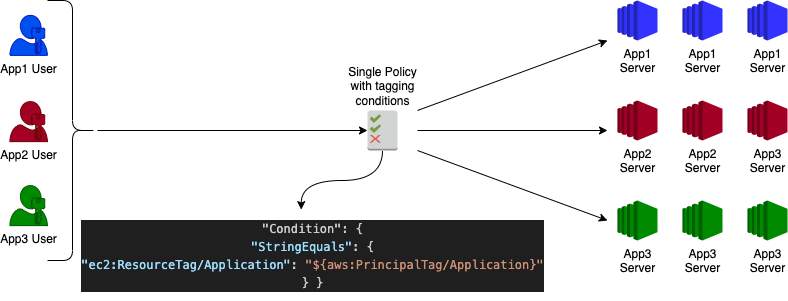
- Create your user or role with the right tagging. Users can be either IAM users or federated users from Microsoft AD or other services like Okta. User tag example, Tag key = Application, Value=app-xx
- Create resources with the right tagging. Almost all AWS resources support tagging. In my example, I am adding tags for EC2 instances. (Application: app-xx)
- Create a policy with a condition that matches the resource tag and principle tag. I have set the action to start or stop instances.
- Please note that permission will be granted to app1-user to app1-server when their application tag values will be matched. i.e, "app-1"
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ec2:DescribeInstances"],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ec2:StartInstances", "ec2:StopInstances"],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"ec2:ResourceTag/application": "${aws:PrincipalTag/application}"
}
}
}
]
}Thus, you don't need an IAM policy for each user/role to manage their own servers. Only one policy will use the condition and provide access to the users to their respective servers.
Restrict Access to Tags
To ensure secure authorization decisions based on resource tags in IAM policies, it is crucial to limit access to tag creation and modification. By enforcing these restrictions, users cannot grant themselves unauthorized access by manipulating resource tags.
Fortunately, IAM policy conditions enable the implementation of such restrictions. AWS offers a globally available context key called aws:TagKeys that allows for the control and restriction of tags used in any request. This feature provides a straightforward method to enforce tag-related restrictions and maintain secure access control.
ABAC Benefits
- ABAC & Consolidated Permission Sets: ABAC simplifies permission management by reducing the number of permission sets needed. No need for separate policies for each action, reducing complexity.
- Seamless Team Support: ABAC automatically grants permissions to new resources based on their properties, adapting access control as teams and resources evolve.
- Employee Attribute Integration: ABAC utilizes employee attributes from AWS SSO, leveraging existing corporate directory attributes for access control decisions and streamlining access management.
- Monitoring Resource Access: AWS CloudTrail enables monitoring of user sessions, tracking user activity, and reviewing logs to observe user attributes, enhancing security and audit capabilities.
Conclusion
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) in AWS provides a powerful mechanism for implementing fine-grained access control and ensuring the security of your cloud infrastructure. By leveraging attributes and policies, organizations can achieve a higher level of control over resource access, enhance security, and meet compliance requirements. Understanding the components of AWS ABAC and following best practices will enable you to effectively implement and manage access control policies in your AWS environment, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your resources.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments