AWS CodeCommit and GitKraken Basics: Essential Skills for Every Developer
AWS CodeCommit can be easily integrated with GitKraken GUI to streamline developer workflow. This enables efficient code management, version control, and more.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeGit is a source code management system that keeps track of the changes made to their codebase and collaborates with other team members. It is commonly used for source code management in software development, but it can track changes to any set of files.
In a version control system, every time a file is modified, a new version is created and saved. This allows users to go back to previous versions of the file, and makes multiple engineers collaborate simultaneously without overwriting each other’s changes.
Git keeps track of changes to a repository, a central location where files are stored. When a user wants to change a file, they first create a copy of the file, make their changes to the copy, and then commit the changes, which saves the modified version of the file to the repository. Other users can then pull the updated version of the file from the repository and merge it into their copies.
Git also includes:
- Features for comparing different file versions.
- Resolving conflicts when multiple people have made changes to the same file.
- Tracking the history of changes to a file over time.
It is a powerful tool widely used in software development and other fields where version control is essential.
Git Workflow
The Git workflow is the series of steps people follow when using Git to manage a project. Here is a general outline of the Git workflow:
- Create a repository: A repository is a central location where all the files for a project are stored. To create a repository, you can use the
git initcommand to initialize an empty repository on your local machine or create a repository on a remote server and clone it to your local machine. - Create a branch: You are creating a snapshot of your project, at that point in time, and diverging from the main development branch. You can then change your codebase on the new branch without affecting the main branch. This allows you to experiment and work on new features without worrying about breaking the main codebase. When you are ready, you can merge your changes back into the main branch to incorporate them into the codebase. To create a new branch, use the command
git branch, and switch to a different branch using thegit checkoutcommand. - Make changes: Once you have a repository set up, you can start changing the files in the repository. When you change a file, Git will recognize that the file has been modified.
- Stage changes: Before you commit your changes, you need to stage them. This involves adding the modified files to a staging area, a list of changes that will be included in the next commit. You can stage changes by using the
git addcommand. - Commit changes: When you are ready to save your changes, you can commit them to the repository. A commit represents the state of the repository at a specific moment in time, and it includes all the staged changes. You can commit your changes by using the
git commitcommand. - Push changes: If you are working with a repository on a remote server, you will need to push your changes to the server for them to be shared with others. You can do this by using the
git pushcommand. - Pull changes: If other people have made changes to the repository and pushed them to the server, you can pull those changes to your local machine by using the
git pullcommand. This will merge the changes into your local repository.
There are many other Git commands available, and you can learn more about them in the Git documentation or by using the git help command.
Branching Strategy
Git branching allows developers to work on multiple features or bug fixes simultaneously within a single Git repository. By using branches, developers can isolate their work from the main codebase and merge their changes back in when they are ready. There are several strategies for using branches in Git, including:
- The Gitflow strategy involves creating long-lived branches for development and releases, as well as short-lived branches for hotfixes and features.
- The Feature Branch strategy involves creating a new branch for each feature or bug fix and merging the branches back into the main codebase when the work is complete.
- The Trunk-Based Development strategy involves working directly on the main codebase (also known as the “trunk”) and using short-lived branches for quick bug fixes or experiments.
The best branching strategy will depend on the specific needs and workflow of your development team.
If you prefer a graphical interface over using the command line, then GitKraken is a free and useful tool. The tool has a user-friendly interface that allows you to perform all the Git operations via the interface and can save time for beginners.
GitKraken
GitKraken is a popular Git client for developers that offers a user-friendly interface and a variety of features to make working with Git easier. It is available on all major platforms and can be used with most version control systems.
One of the key features of GitKraken is its intuitive graphical user interface, which makes it easy to visualize and manage Git repositories. The interface includes a visual representation of the commit history, called thecommit graph, which allows users to see the changes made to the repository over time easily. It also includes a Gitflow feature, which helps users follow best practices when working with Git branches.
In addition to its graphical interface, GitKraken also offers a range of advanced features for developers. It includes tools for code review, such as leaving inline comments on code changes. It supports a range of collaboration features and the ability to assign tasks. It also includes integration with popular tools, like JIRA and Slack, making it easy to connect your Git workflow with other tools you use.
Managing work in progress, pull requests, and branches for issues across multiple repositories can be challenging. That’s why the release of GitKraken Client 9.0 is so exciting. This major version release is expected to improve the development workflow significantly.
Demo
Let’s demonstrate how to use AWS CodeCommit as a version control system and GitKraken as the graphical user interface to manage your Git workflow.
Step 1
Install GitKraken: Download and install GitKraken on your local machine.
Step 2
Set up an AWS account: If you don't have one, you’ll need to create one if you choose to use AWS CodeCommit.
Step 3
Connect GitKraken to your AWS CodeCommit Repository: Before we connect, we need to generate credentials to clone the CodeCommit repo over HTTPS.
Step 4
Go to AWS IAM > Users > Security Credentials > Generate Credentials. 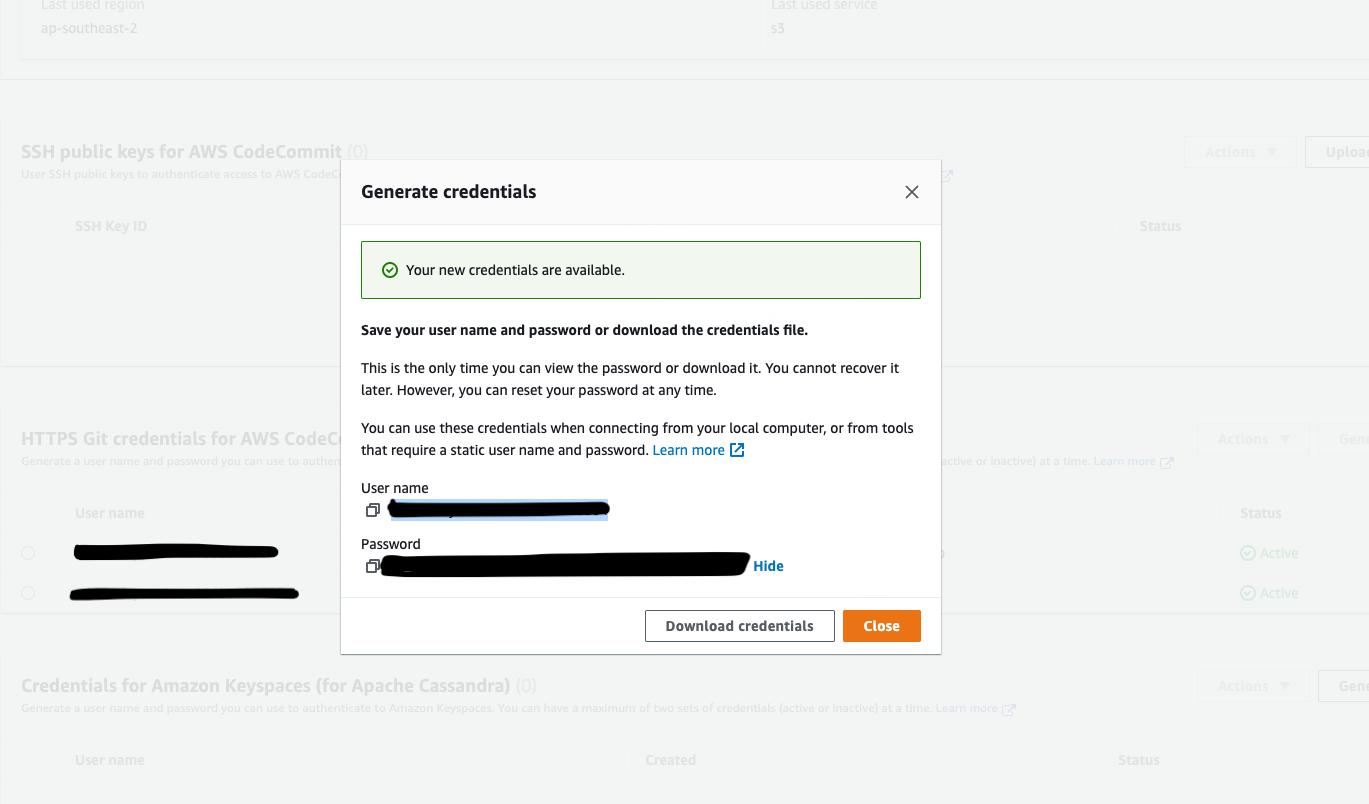
Step 5
Create a CodeCommit repository: Log into the console and navigate to the CodeCommit dashboard. Click the “Create Repository” button and follow the prompts to create a new repository.
Step 6
Clone the repository: In GitKraken, go to File > Clone Repo and enter the URL of your CodeCommit repository. This will download a local copy into your machine. 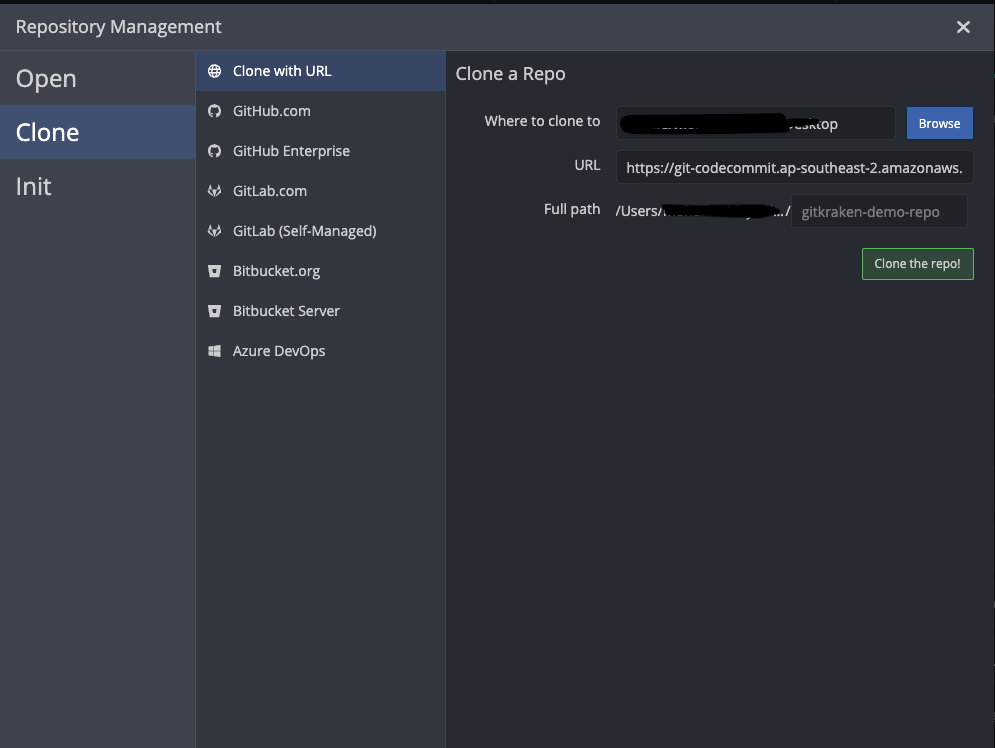
Step 7
Enter the username and password generated in step 4.
Step 8
Make changes and commit: Make any desired changes to the files in your local repository and use GitKraken to stage and commit the changes. 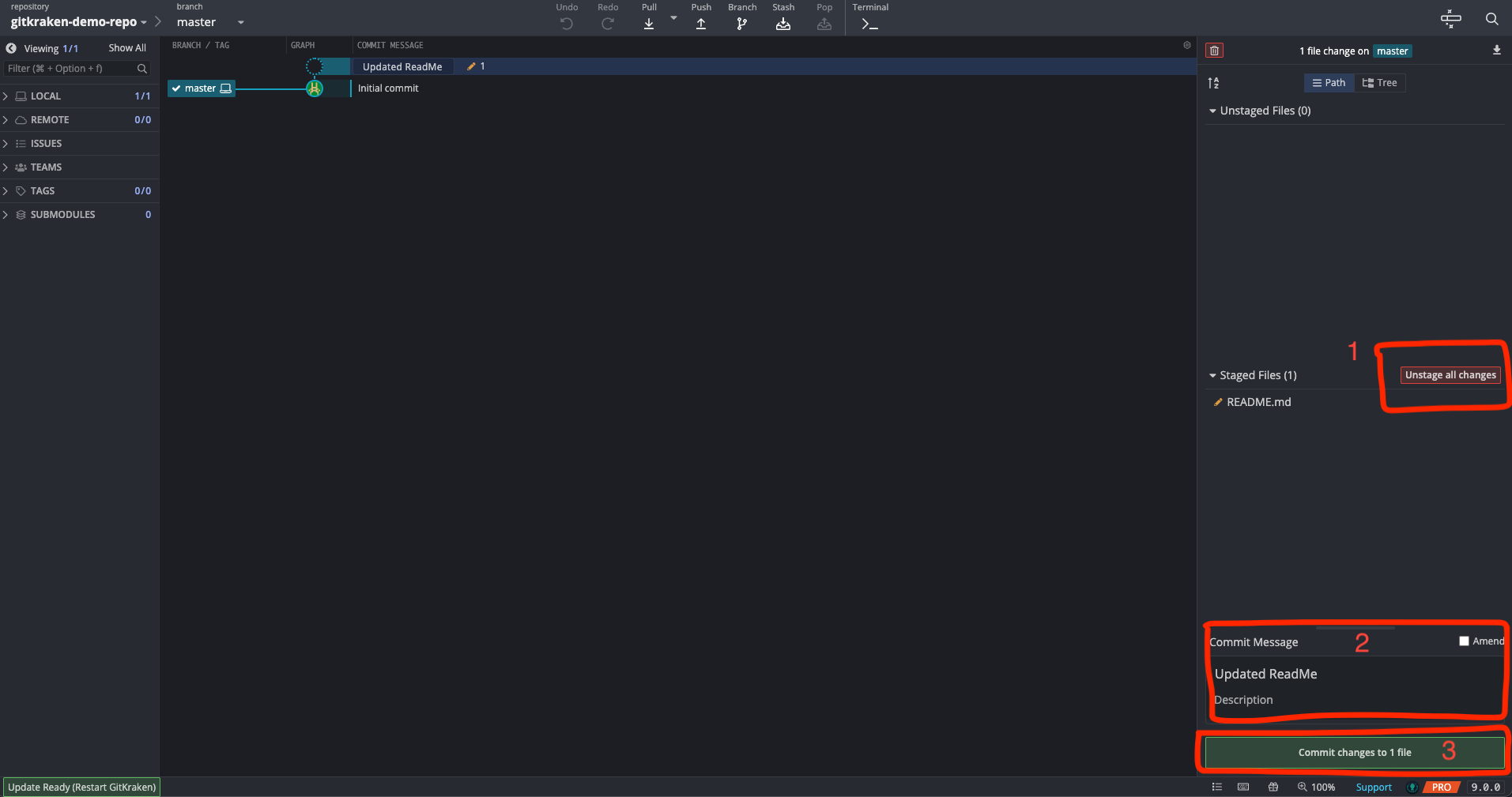
Step 9
Push changes to CodeCommit: Use GitKraken to push your local commits to the CodeCommit repository, which will make them available to other users.
Conclusion
A tool like GitKraken is very helpful if you are switching between various repositories across different accounts. Also, while GUI, like GitKraken, can be useful for users who are new to Git, or prefer a graphical interface, many experienced developers prefer to use commands due to the level of control and flexibility it offers.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments