Best Practices in Data Discovery: Building Search for a Data Discovery Platform
Explore major components of a user-friendly UI and look into specific measures that can be employed to increase the quality of search in the Open Data Discovery Platform.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Image by flashmovie from freepik
The efficiency of data discovery depends on the user-friendliness of the UI and the features integrated into it to make it easier for users to look up the data they need. This article explores significant components of a user-friendly UI. In addition, it looks into specific measures that can be employed to increase the quality of search in the Open Data Discovery (ODD) Platform.
The Importance of Search for Users of Data Discovery Solutions
The main goal of any search component is to optimize the way users lookup and retrieve data. Therefore, the better the search feature in a data discovery solution, the better and more efficient the solution will be.
Why so? Because data work takes a lot of time and effort!
Just consider that today data scientists spend around 30% of their time on discovering and validating datasets. Data and ML engineers invest too many resources to ensure that their data is clean and reliable. Fine-tuning, debugging, and maintaining data pipelines and cataloging and curating datasets create data silos that keep engineers away from ML models, analytical dashboards, and other business-critical tasks. More efficient data search and data lineage can help solve some of these data problems, thus reducing the costs of building and maintaining data products for enterprises.
Understanding this, we have designed and built a state-of-the-art search component that enables users of the Open Data Discovery Platform to:
- quickly and easily search for any data
- dramatically reduce the journey from search to data retrieval
- efficiently use the platform for all data needs
All these benefits are critical for data-driven enterprises looking to democratize their data by making it more discoverable, manageable, observable, reliable, and secure.
How It Works in Open Data Discovery Platform
1. A specific visible search field for data
The search field is placed in the most visible areas of the platform, including the home page and on a specific page dedicated to searching for data.
The user can easily navigate to the search field to start a query. They can also activate search queries by pressing “enter” or clicking on the search icon. In addition, all search queries are saved once search results are displayed, thus enabling users to edit their queries.
2. Availability of search suggestions
From a usability perspective, it is critical to suggest potential search queries to users, allowing them to search for the data they need quickly.
The search field begins suggesting search queries on the ODD Platform as the user is typing their query. A special icon indicates the type of data displayed in search results.
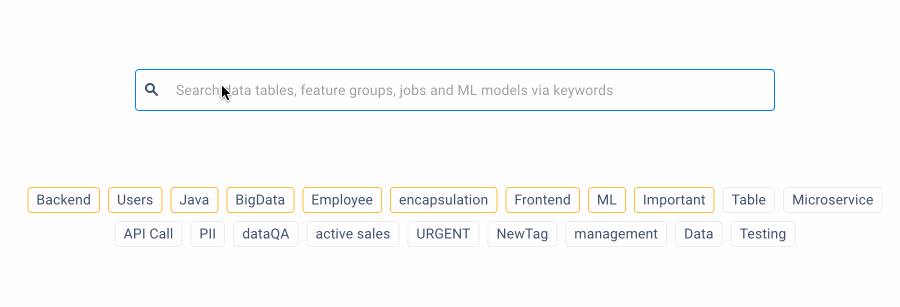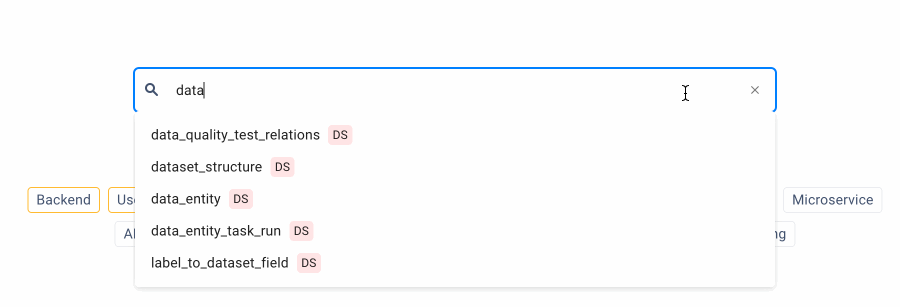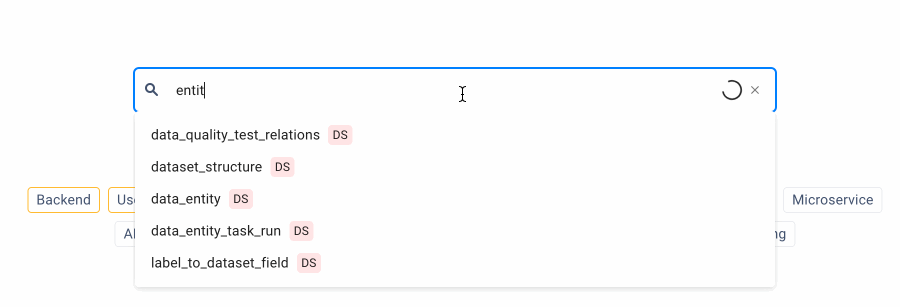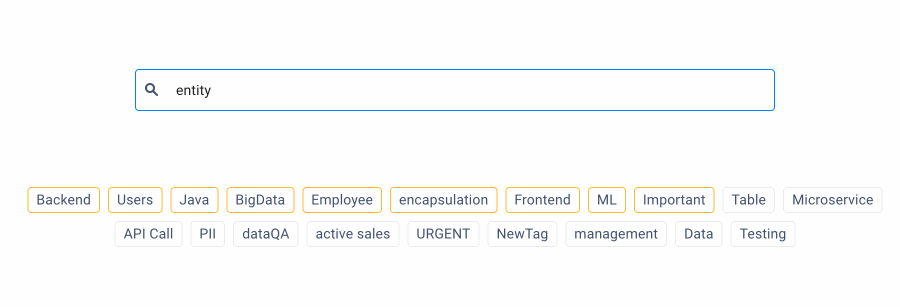
Image by author
3. Search queries and the number of relevant entities displayed on the search results page
The search results page saves all search queries, enabling users to analyze their search history. In addition, the page features relevant entities, displayed by type and filter. It is important to note that, first and foremost, the search is conducted by the entity’s name and by scanning metadata that is stored in the entity’s body. This information can be used to suggest to the user how varied the search can be and how they need to specify it by using filters.
Users can also specify search results by filtering entities by type:
- All — a list of all entities
- My Objects — entities of the user
- Datasets — entities related to “Dataset” type
- Transformers — entities related “Transformers” type
- Data Consumers — entities related to “Data Consumers” type
- Data Inputs — entities related to “Data Inputs” type
- Quality Tests — entities related to “Quality Tests” type
- Groups — entities related to “Data Entity Group” type
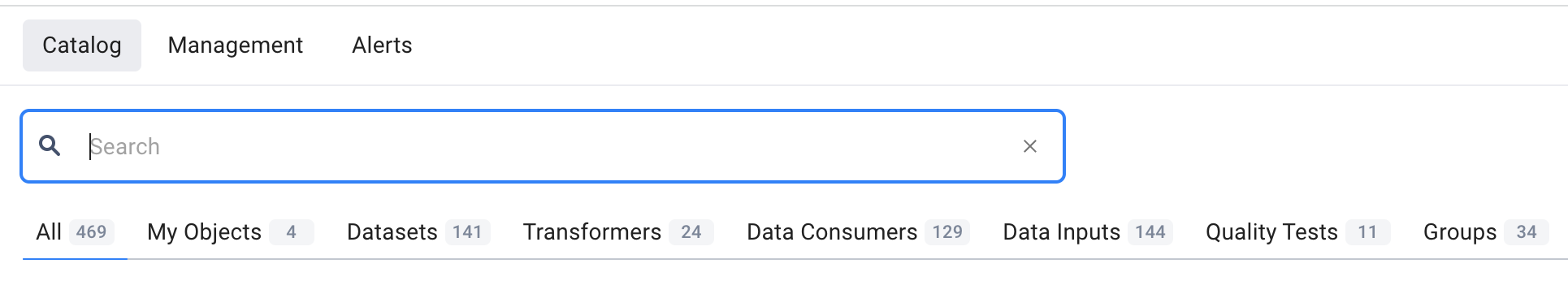
4. Comparison of entities in search results
All characteristics are displayed in table form to make it easier for users to work with search results. When we need to compare multiple entities, their preview features the most essential details. As such, the preview includes various characteristics for varying types of entities.
For All, My Objects and Data Inputs
- Name — the name of a specific entity
- Namespace — a space of names created to group unique identificators logically
- Datasource — the name of the entity’s source
- Owners — the owner of the entity (can be several owners)
- Created — the date of the entity creation
- Last update — the date of the previous update
For Dataset (additional characteristics)
- Use — the number of uses
- Rows — the number of rows
- Columns — the number of columns
For Transformers (additional characteristics)
- Source — a data source for Transformers
- Targets — a target for storing data for Transformers
For Data Consumers (additional characteristics)
- Source — a source of data for Data Consumers
For Data Inputs (additional characteristics)
- Source — a data source for Data Inputs
For Quality Tests (additional characteristics)
- Source — a data source for a specific data test
- Suite URL — a URL for a specific suite of tests
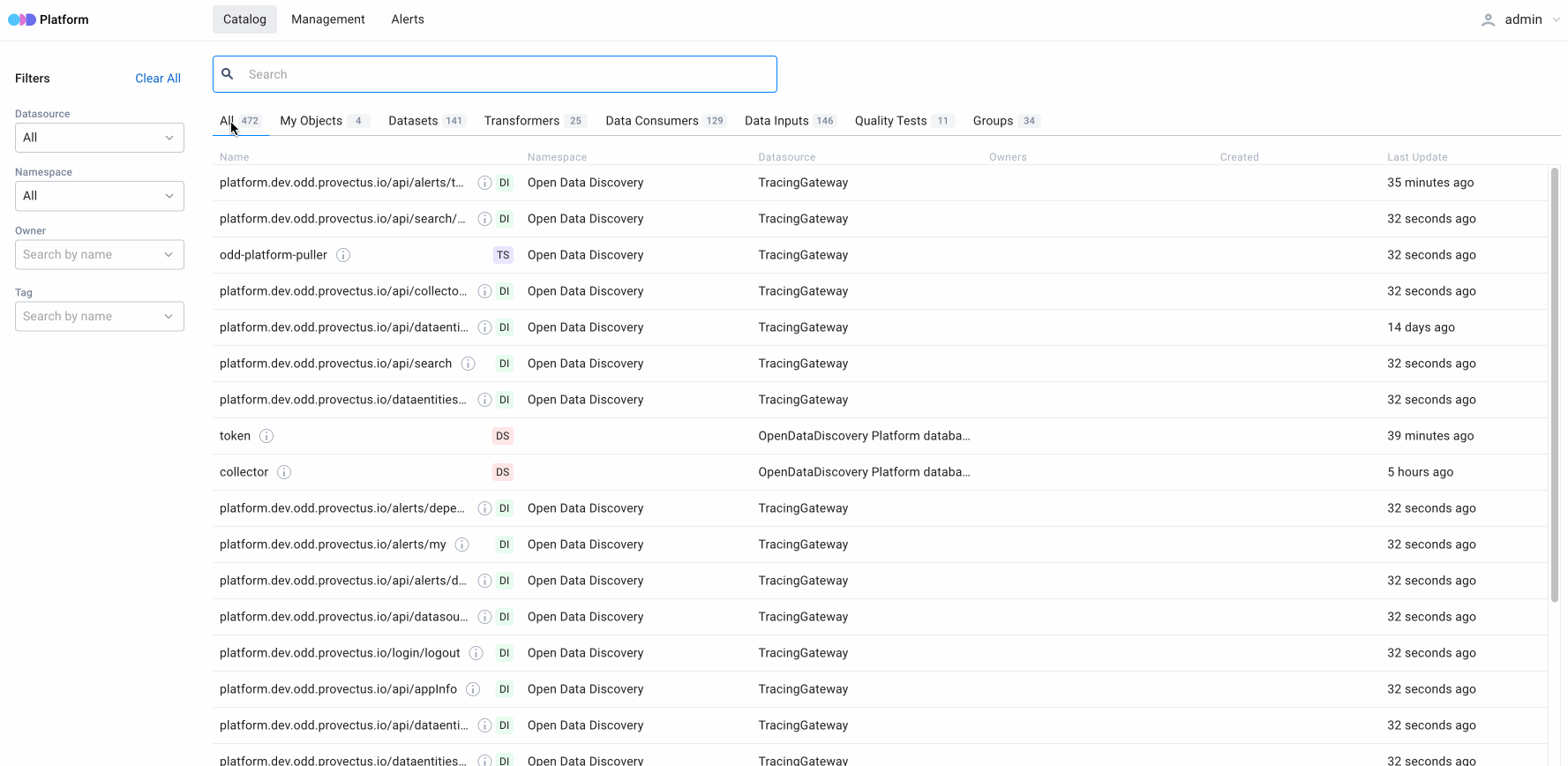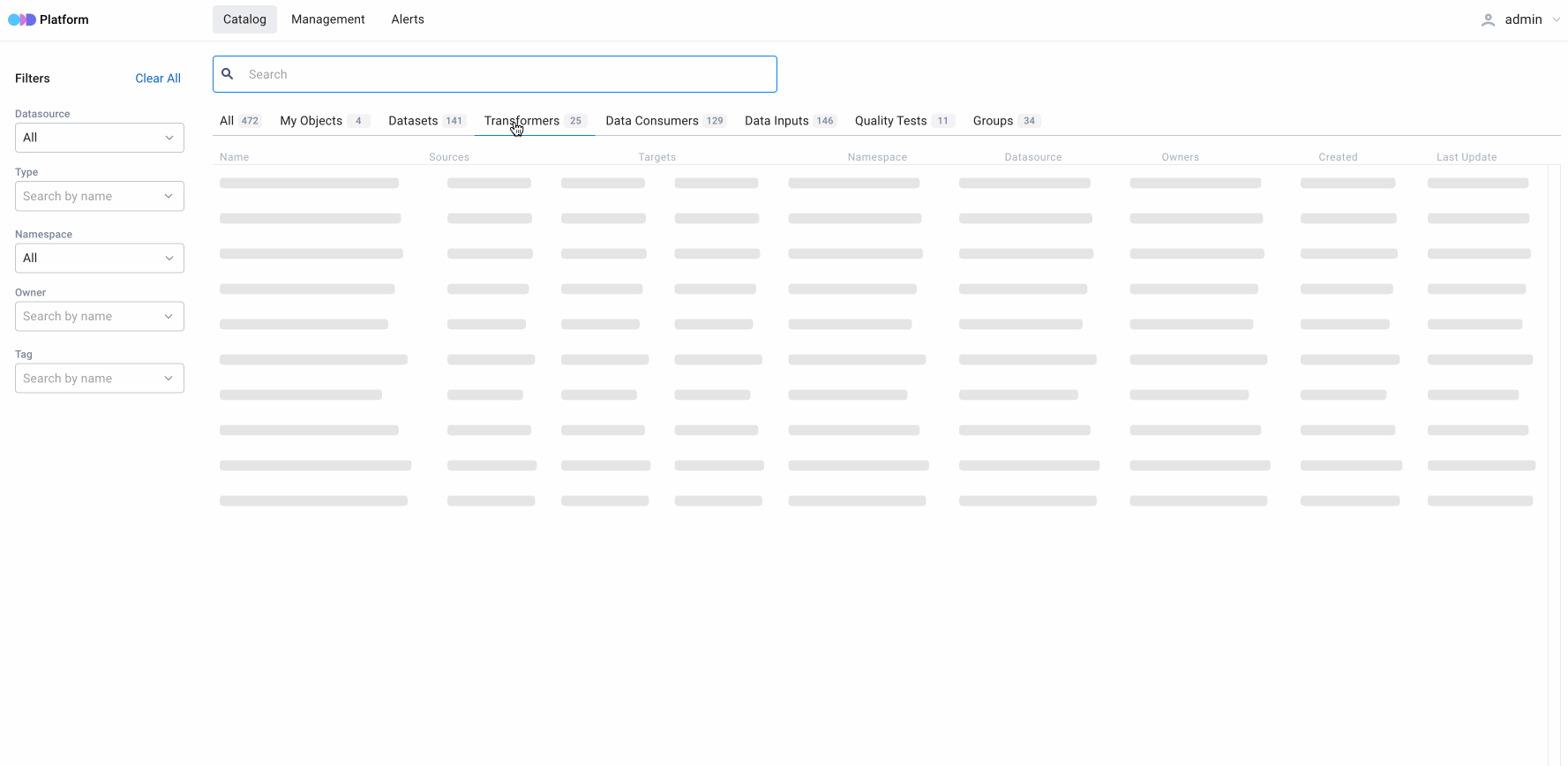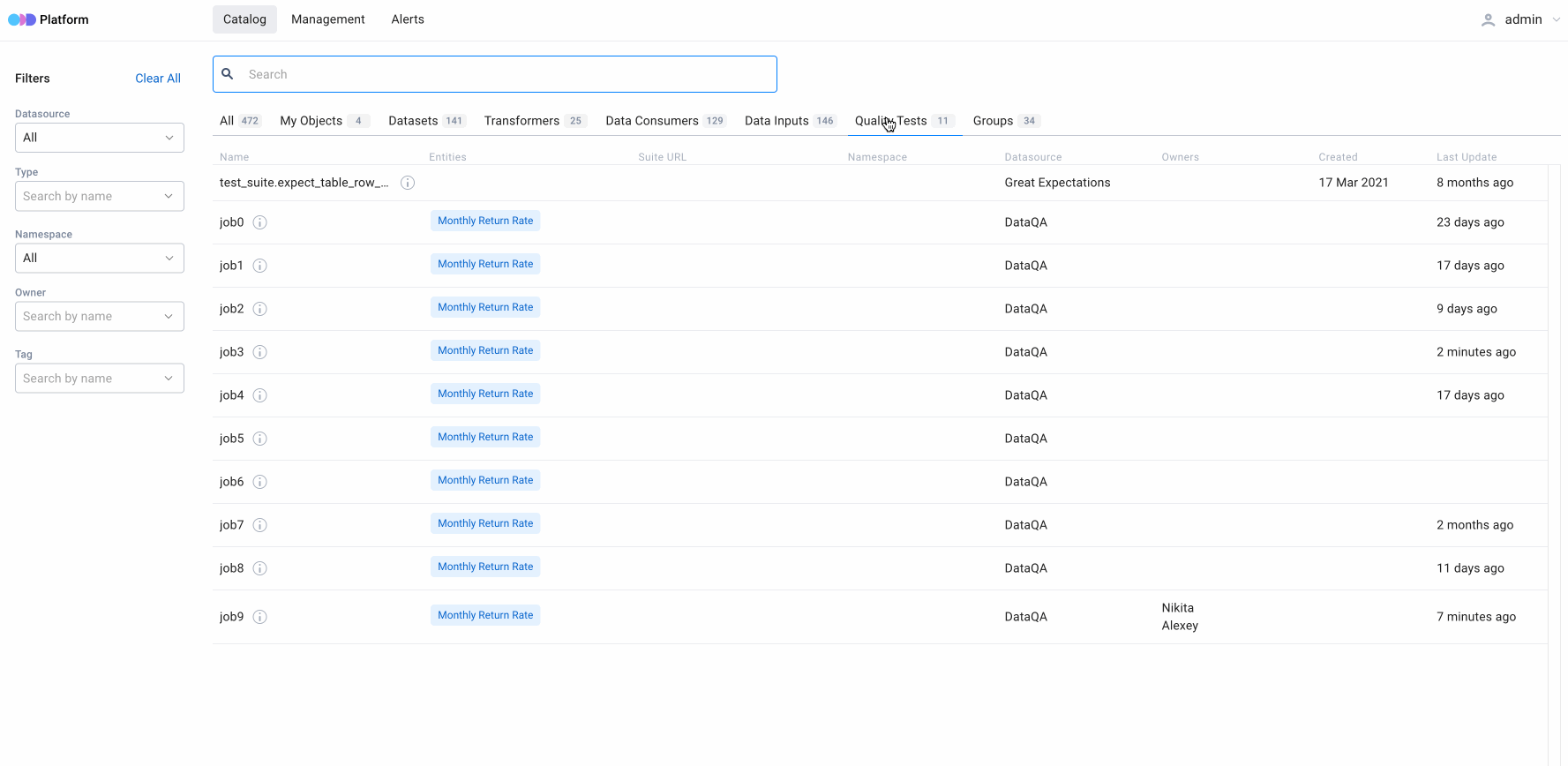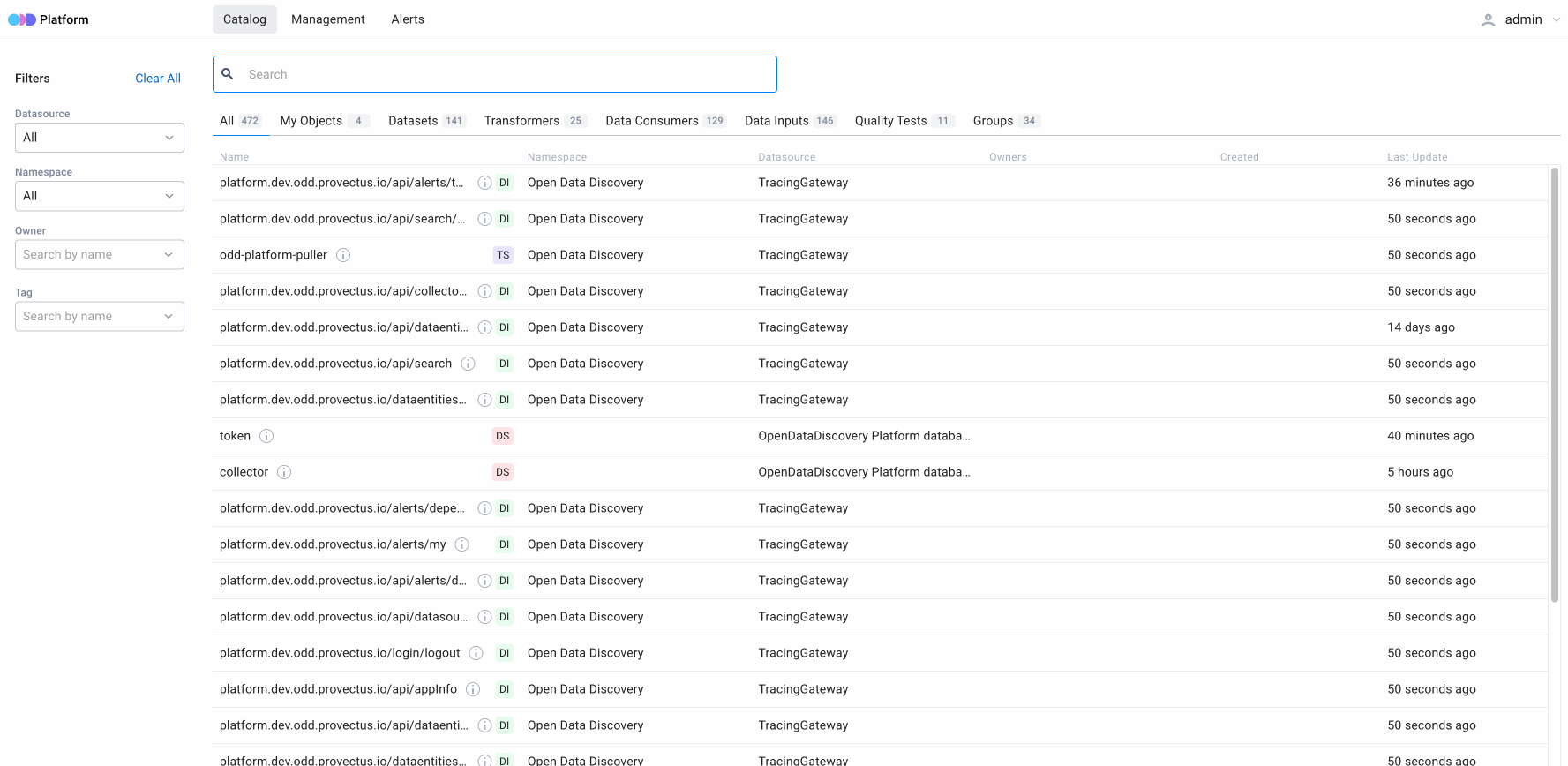
Image by author
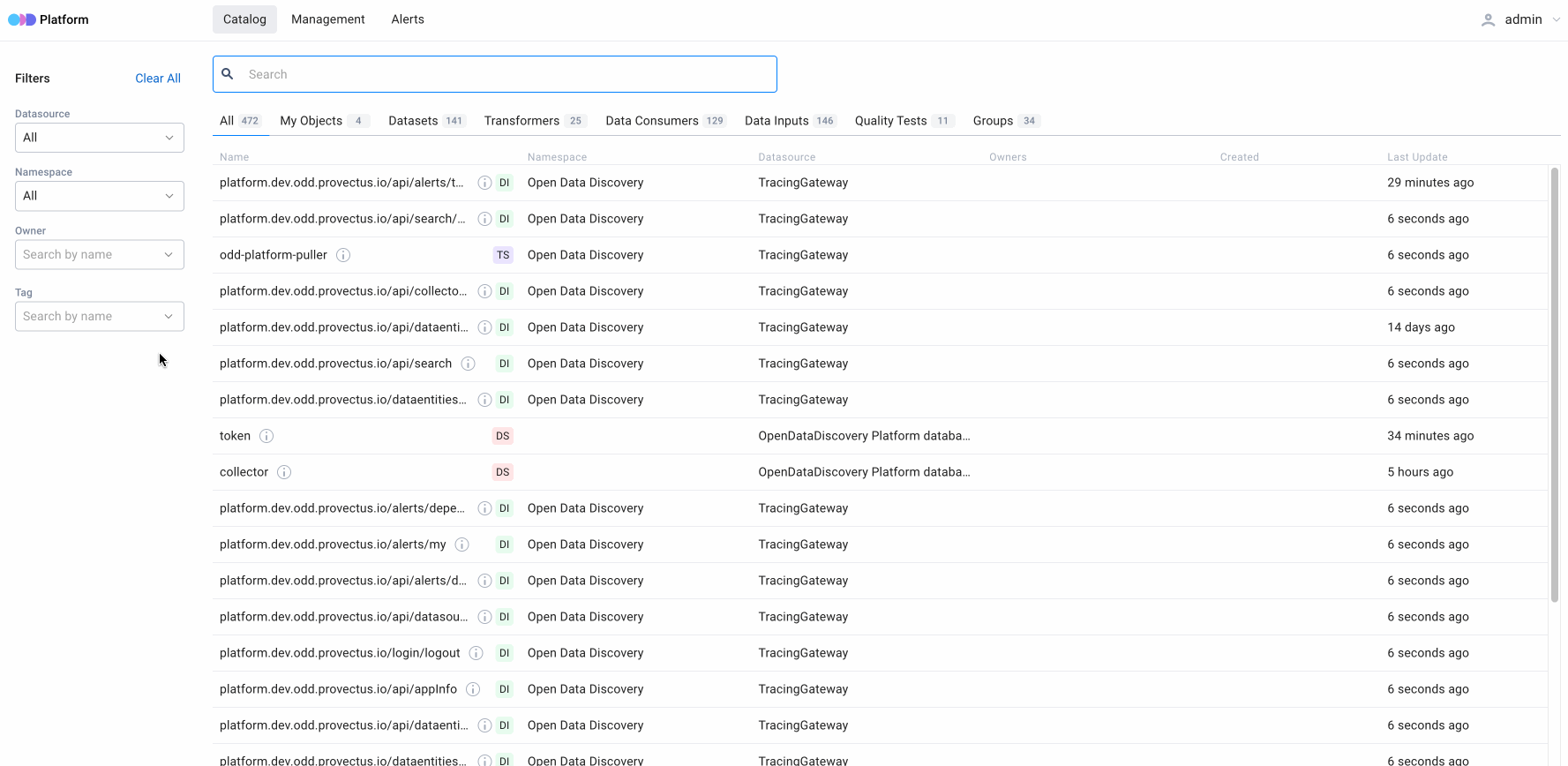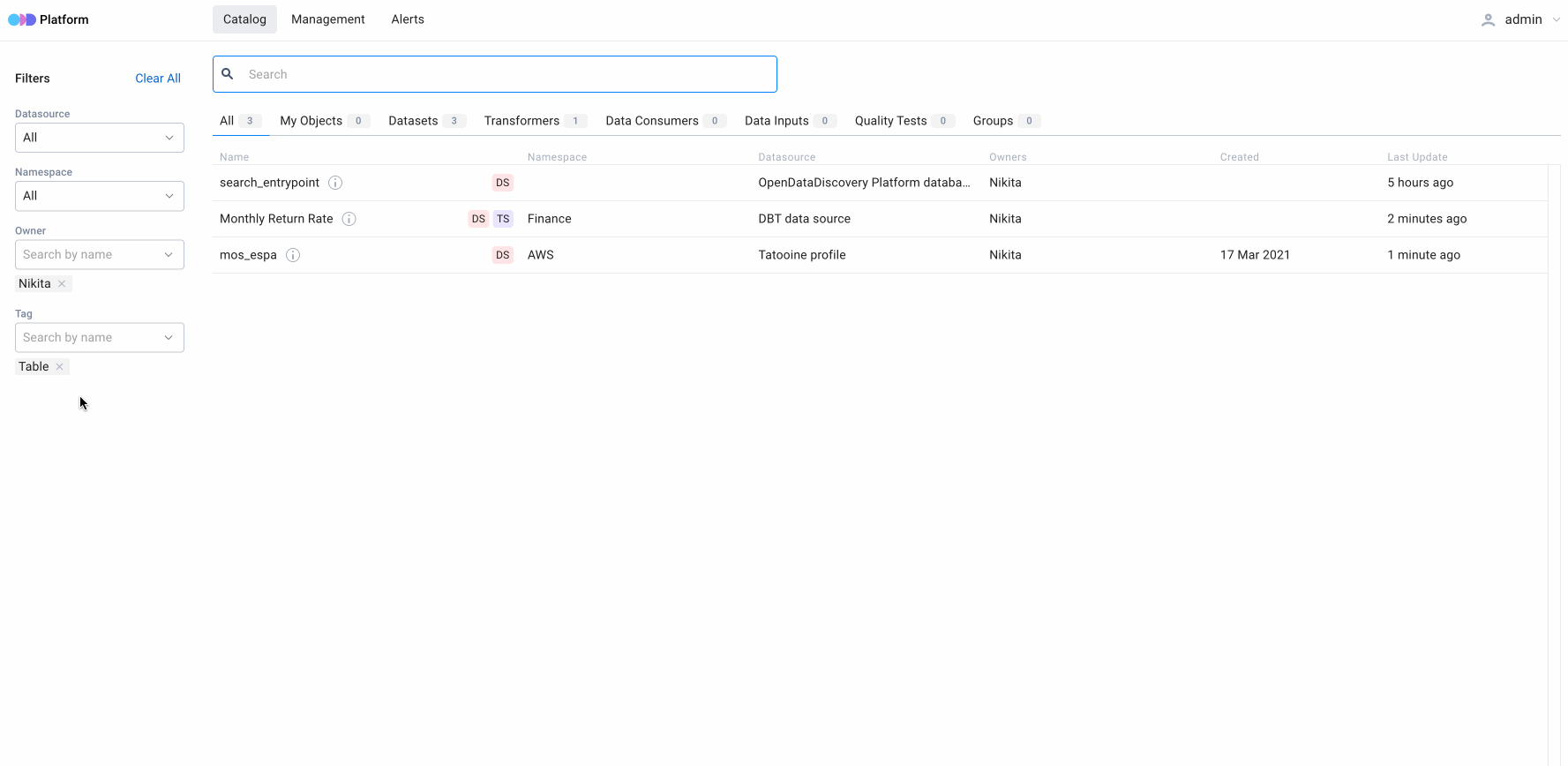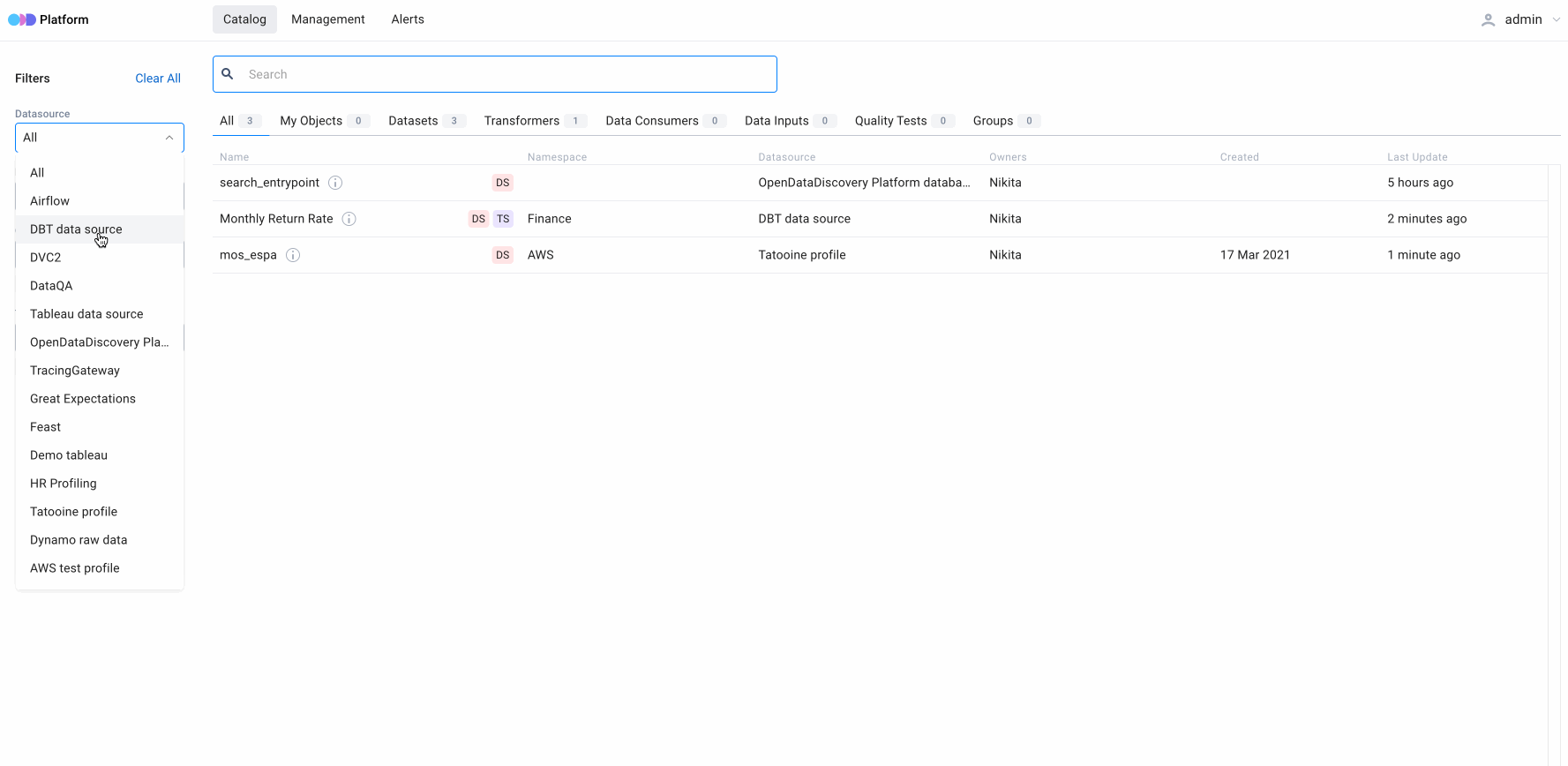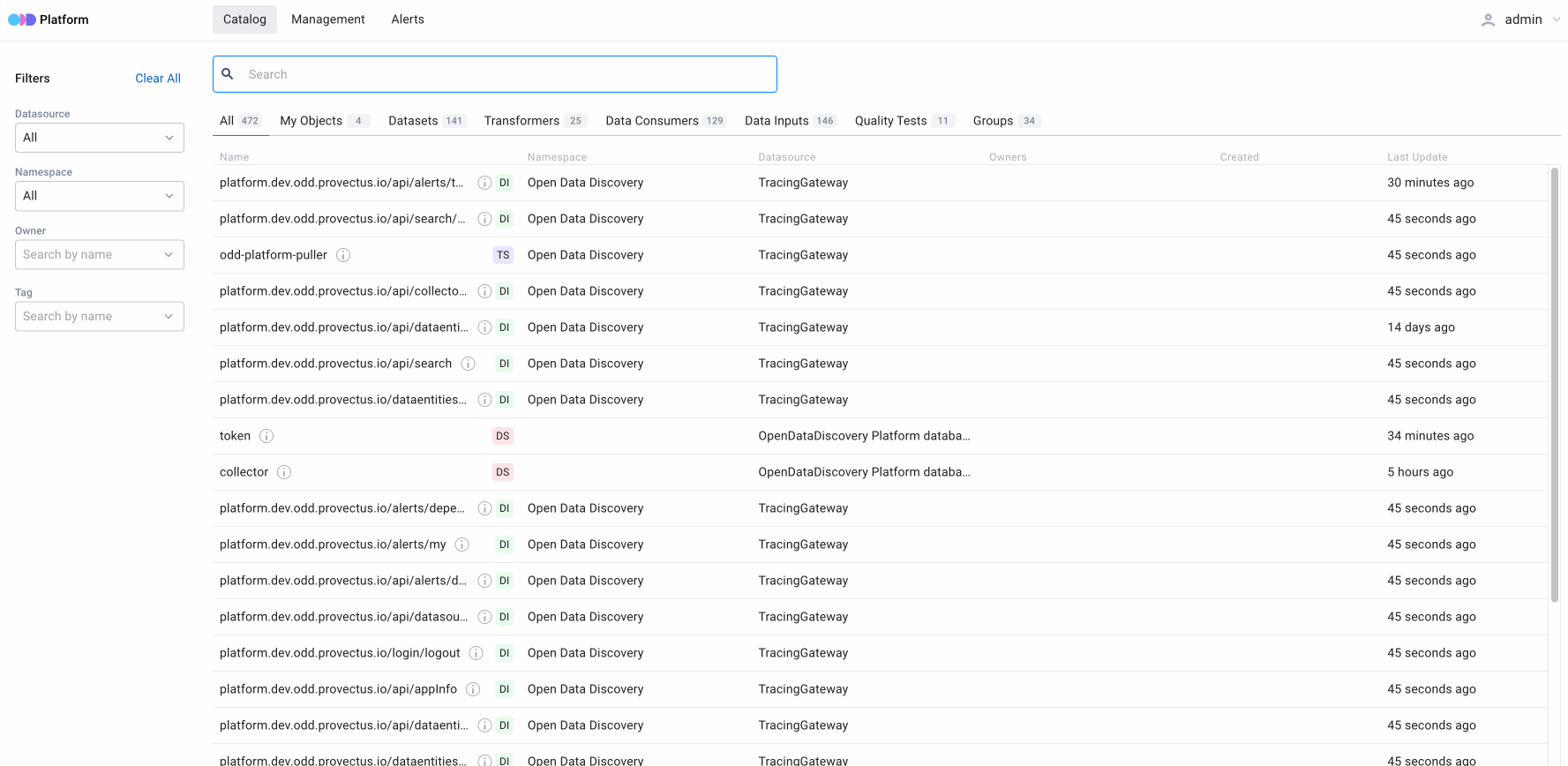
5. Filters for search results
When the user does not know exactly what data they are looking for, it is essential that different parameters can filter search results. This significantly reduces the width of a search to help the user find what they need.
Open Data Discovery Platform can filter search results by specific characteristics of entities, such as:
- Selector for Datasource
- Multiselector for Namespace
- Multiselector for specific types (e.g., table, topic, or file)
- Multiselector for Owner
- Multiselector for Tag — specific tags to tag various entities
Conclusion
The convenience of search plays a critical role in handling data. Not only does it help users to look for essential characteristics of data, but it also ensures that accurate data is chosen to be used in specific applications.
The Open Data Discovery Platform team did their best to design and build a user-friendly search, where search results are conveniently displayed and can be filtered in various ways. At the ODD Platform, any user can effectively search and filter the widest selection of data entities, optimizing the way they conduct their data work. The platform acts as a powerful tool that enables engineering teams to accelerate and facilitate data discovery, minimize data downtimes, and, most importantly, focus on building data products that generate value for businesses.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments