Set up a Spring Boot Application With PostgreSQL
In this article, we will see the steps to set up a Spring boot application with PostgreSQL.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, we will see the steps to set up a Spring Boot application with PostgreSQL. We will have a simple CRUD operation in Postgres Database by exposing the application via Rest API. We will use POSTMAN to test the application.
Setting up Postgres Server
- Download the Postgres server from the link: https://www.postgresql.org/download/
- Run the installer. It will also ask the password for the superuser: postgres
- Click on pgAdmin4.exe located inside the PostgreSQL folder inside Program Files.
Setting up Spring Boot Application
Prerequisite:
Have JDK 1.8 installed
- Download a sample Spring Boot project from https://start.spring.io/
- Update the pom.xml as below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.sample</groupId>
<artifactId>postgress</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>postgress</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>spring-boot-starter-jdbc artifact will give all the spring jdbc related jars
org.postgresql.postgresql will have the dependency of postgres jdbc driver in runtime.
- Create a schema.sql in resource folder. An employee table will be created in server startup. This can be ignored if you don't want the initial database to be configured during server start. Generally, for building a production-ready application, this step can be ignored as tables will be created with scrip directly in the DB.
CREATE TABLE employee
(
employeeName varchar(100) NOT NULL,
employeeId varchar(11) NOT NULL ,
employeeAddress varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
employeeEmail varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (employeeId)
);- Create data.sql in resource folder for loading the first set of employee during startup. Can be skipped otherwise:
insert into employee(employeeId, employeeName , employeeAddress,employeeEmail) values('1','Jack','USA','jack@gmail.com');
- Changes in application.properties to configure the data source with URL, username, and password of the Postgres DB. 5432 is the default port of Postgres. Hibernate will automatically pick up the postgressSQLDialect.
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.jpa.hibernate.show-sql=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=admin
spring.datasource.initialization-mode=always
spring.datasource.initialize=true
spring.datasource.schema=classpath:/schema.sql
spring.datasource.continue-on-error=truespring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto will turn off the hibernate auto-creation of the tables from the entity objects. Generally, Hibernate runs it if there is an Entity defined. But we will be using a native SQL query with JdbcTemplate, hence, we can turn this off as we will not be creating an Entity.
spring.datasource.initialization-mode is marked as always as we want initialization of the database to happen on every startup. This is optional and made for this sample purpose.
spring.datasource.initialize=true will mark the initialization to be true.
spring.datasource.continue-on-error=true will continue application startup in spite of any errors in data initialization.
spring.datasource.schema is the schema path that needs to be initialized.
spring.datasource.url URL of the Postgres DB. It can be a remote DB as well.
spring.datasource.username username for the database.
spring.datasource.password password for the database.
- Create a dao interface and dao implementation.
package com.sample.postgress.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.sample.postgress.entity.Employee;
public interface EmployeeDao {
List<Employee> findAll();
void insertEmployee(Employee emp);
void updateEmployee(Employee emp);
void executeUpdateEmployee(Employee emp);
public void deleteEmployee(Employee emp);
}package com.sample.postgress.dao;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.PreparedStatementCallback;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.GeneratedKeyHolder;
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.KeyHolder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.sample.postgress.entity.Employee;
import com.sample.postgress.mapper.EmployeeRowMapper;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDaoImpl implements EmployeeDao{
public EmployeeDaoImpl(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate template) {
this.template = template;
}
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate template;
@Override
public List<Employee> findAll() {
return template.query("select * from employee", new EmployeeRowMapper());
}
@Override
public void insertEmployee(Employee emp) {
final String sql = "insert into employee(employeeId, employeeName , employeeAddress,employeeEmail) values(:employeeId,:employeeName,:employeeEmail,:employeeAddress)";
KeyHolder holder = new GeneratedKeyHolder();
SqlParameterSource param = new MapSqlParameterSource()
.addValue("employeeId", emp.getEmployeeId())
.addValue("employeeName", emp.getEmployeeName())
.addValue("employeeEmail", emp.getEmployeeEmail())
.addValue("employeeAddress", emp.getEmployeeAddress());
template.update(sql,param, holder);
}
@Override
public void updateEmployee(Employee emp) {
final String sql = "update employee set employeeName=:employeeName, employeeAddress=:employeeAddress, employeeEmail=:employeeEmail where employeeId=:employeeId";
KeyHolder holder = new GeneratedKeyHolder();
SqlParameterSource param = new MapSqlParameterSource()
.addValue("employeeId", emp.getEmployeeId())
.addValue("employeeName", emp.getEmployeeName())
.addValue("employeeEmail", emp.getEmployeeEmail())
.addValue("employeeAddress", emp.getEmployeeAddress());
template.update(sql,param, holder);
}
@Override
public void executeUpdateEmployee(Employee emp) {
final String sql = "update employee set employeeName=:employeeName, employeeAddress=:employeeAddress, employeeEmail=:employeeEmail where employeeId=:employeeId";
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("employeeId", emp.getEmployeeId());
map.put("employeeName", emp.getEmployeeName());
map.put("employeeEmail", emp.getEmployeeEmail());
map.put("employeeAddress", emp.getEmployeeAddress());
template.execute(sql,map,new PreparedStatementCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps)
throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
return ps.executeUpdate();
}
});
}
@Override
public void deleteEmployee(Employee emp) {
final String sql = "delete from employee where employeeId=:employeeId";
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("employeeId", emp.getEmployeeId());
template.execute(sql,map,new PreparedStatementCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps)
throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
return ps.executeUpdate();
}
});
}
}-
findAll() retrieves all the employee and then map the resultset to a Employee Object using RowMapper described below .
-
insertEmployee() will insert an employee using
template.update(sql,param, holder)where param is the SqlParameterSource, which will map the values dynamically in the query marked with a colon. GeneratedKeyHolder will return an auto-generated value when data is inserted. -
executeUpdateEmployee() will update the employee using
template.execute
template.execute(sql,map,new PreparedStatementCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps)
throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
return ps.executeUpdate();
}
}); - EmployeeRowMapper to map the result set retrieved from the select query with the POJO.
package com.sample.postgress.mapper;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import com.sample.postgress.entity.Employee;
public class EmployeeRowMapper implements RowMapper<Employee> {
@Override
public Employee mapRow(ResultSet rs, int arg1) throws SQLException {
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setEmployeeId(rs.getString("employeeId"));
emp.setEmployeeName(rs.getString("employeeName"));
emp.setEmployeeEmail(rs.getString("employeeEmail"));
return emp;
}
}- You can create a controller and a service class as follows:
package com.sample.postgress.controller;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.sample.postgress.entity.Employee;
import com.sample.postgress.service.EmployeeService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/postgressApp")
public class ApplicationController {
@Resource
EmployeeService employeeService;
@GetMapping(value = "/employeeList")
public List<Employee> getEmployees() {
return employeeService.findAll();
}
@PostMapping(value = "/createEmp")
public void createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
employeeService.insertEmployee(emp);
}
@PutMapping(value = "/updateEmp")
public void updateEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
employeeService.updateEmployee(emp);
}
@PutMapping(value = "/executeUpdateEmp")
public void executeUpdateEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
employeeService.executeUpdateEmployee(emp);
}
@DeleteMapping(value = "/deleteEmpById")
public void deleteEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
employeeService.deleteEmployee(emp);
}
}Now, let's use POSTMAN to validate the changes:
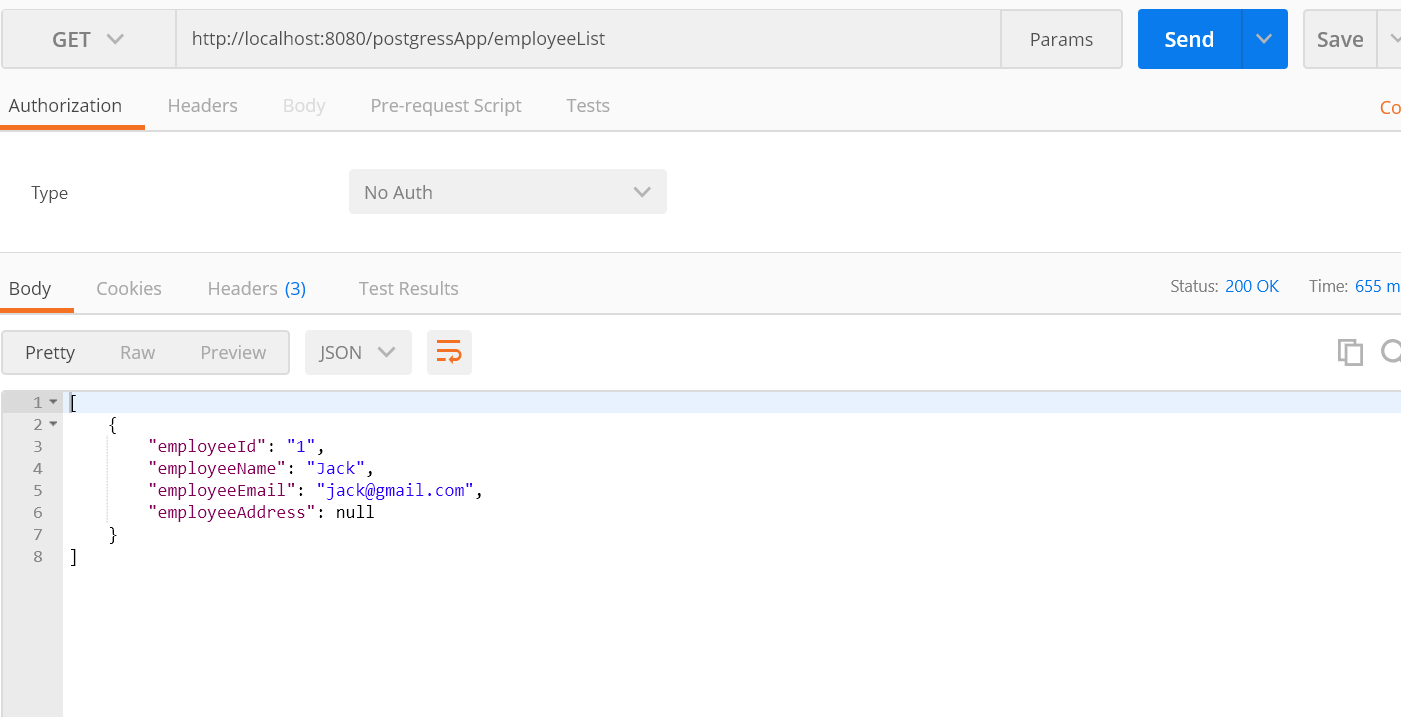
Test 1: Get the list of employees
http://localhost:8080/postgressApp/employeeList
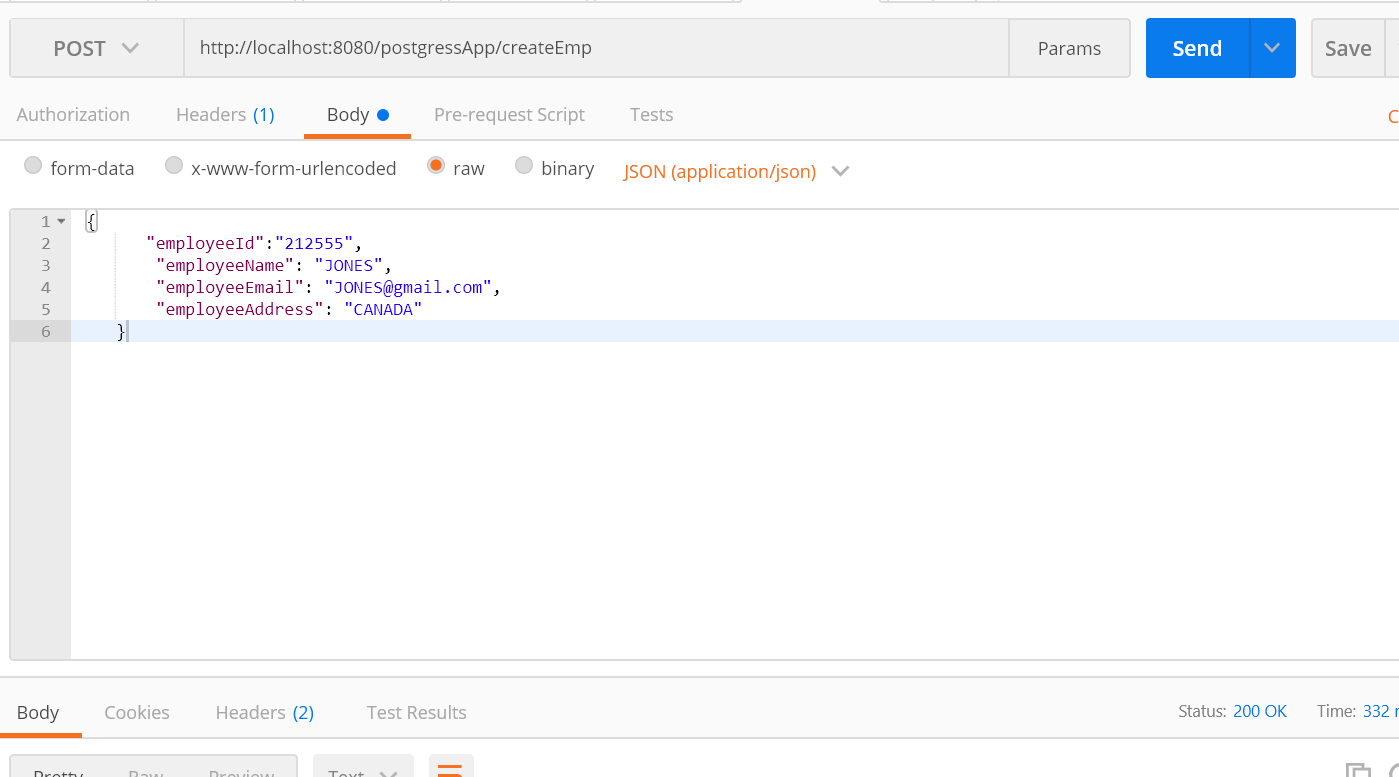
Test 2: Create An employee
http://localhost:8080/postgressApp/createEmp
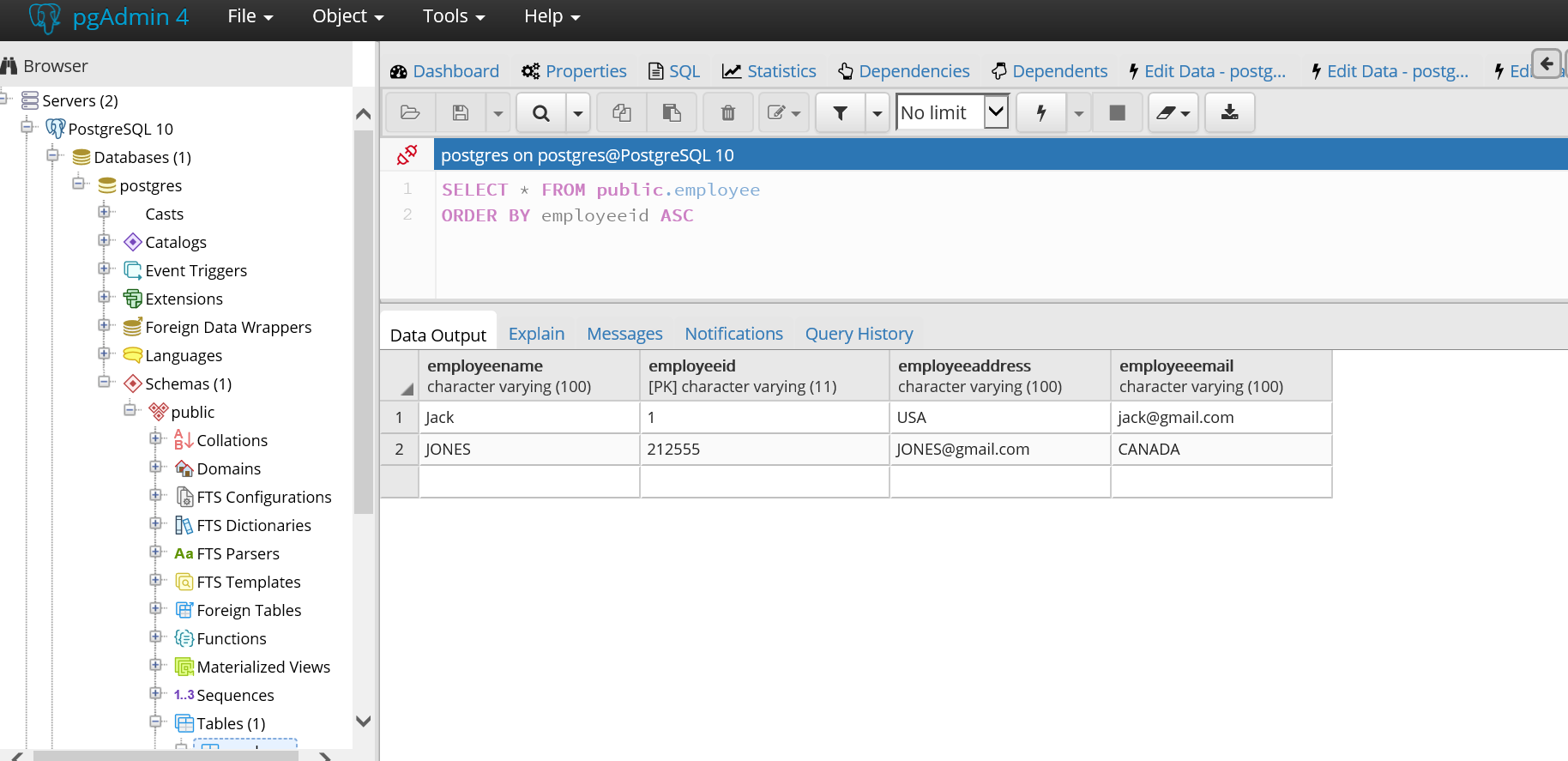
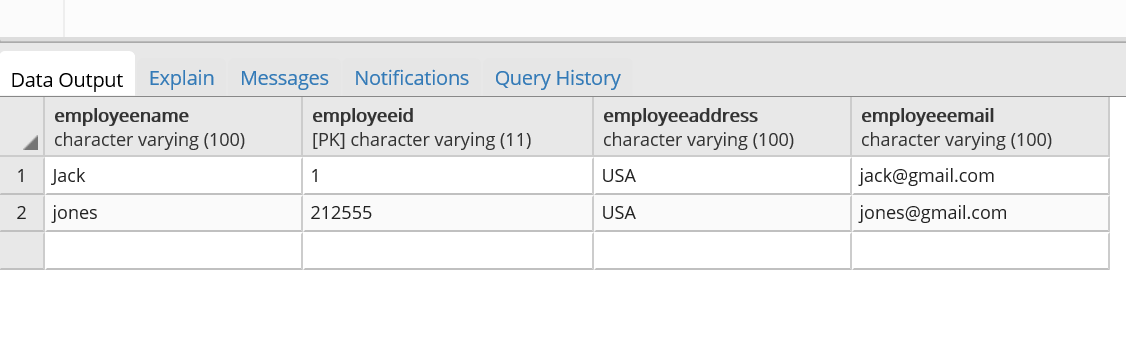
We see an entry got inserted with JONES.
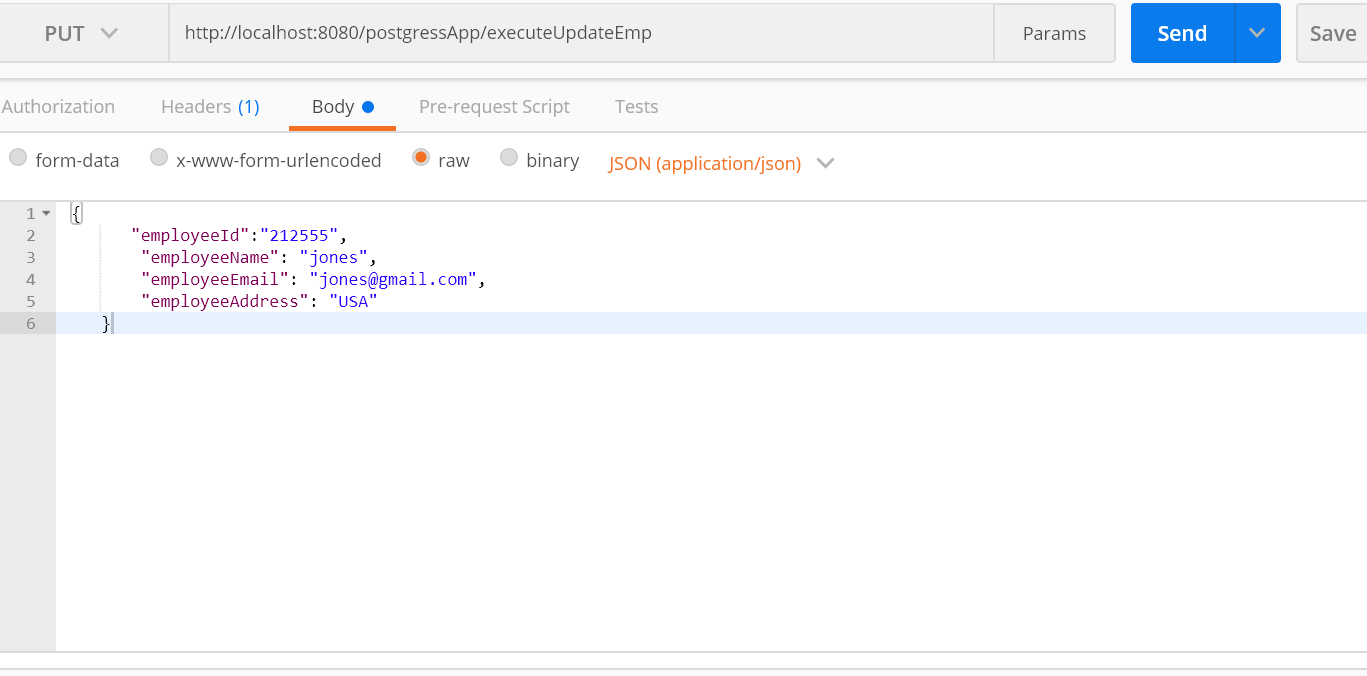
Test 3: Update an Employee
http://localhost:8080/postgressApp/executeUpdateEmp
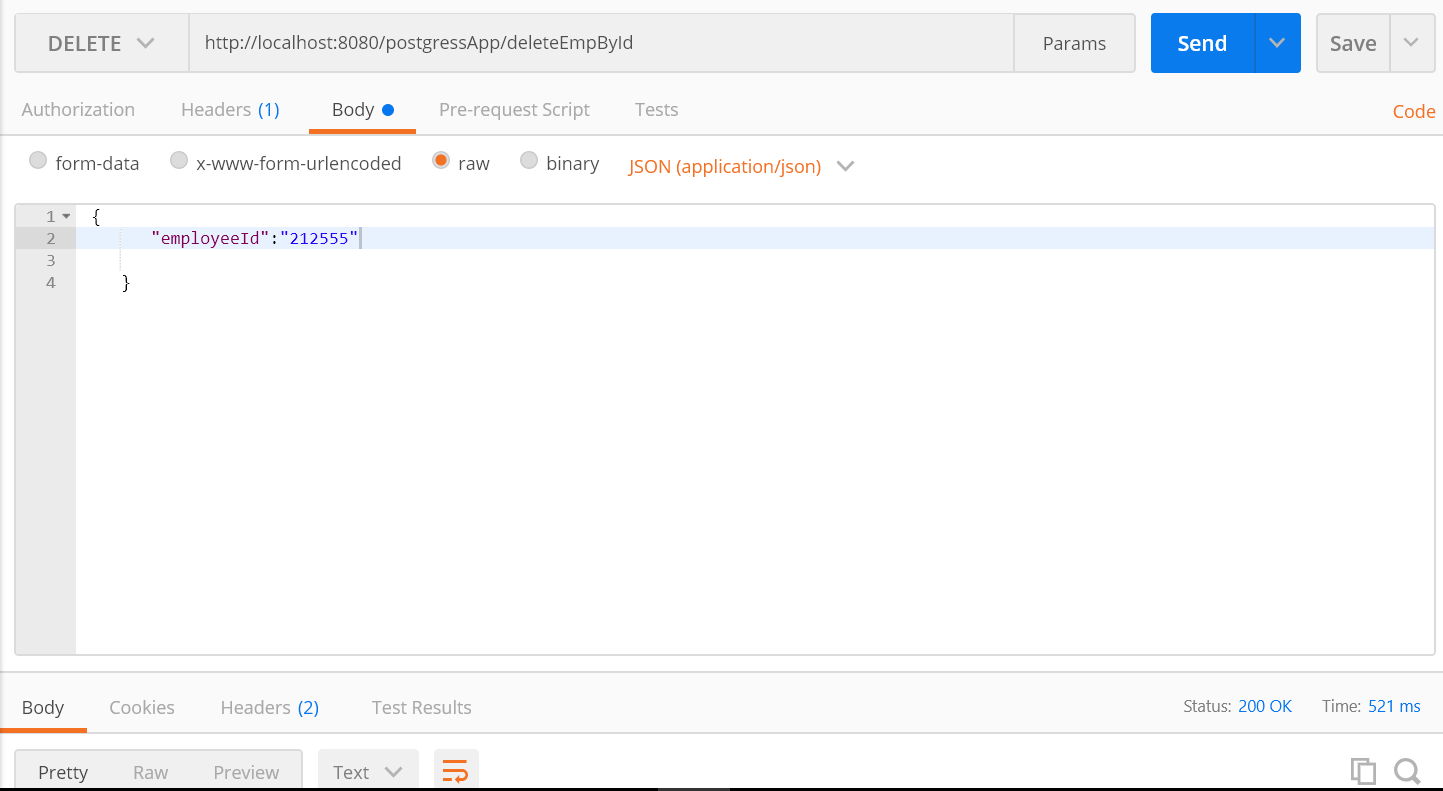
Test 4: Delete Employee
http://localhost:8080/postgressApp/deleteEmpById
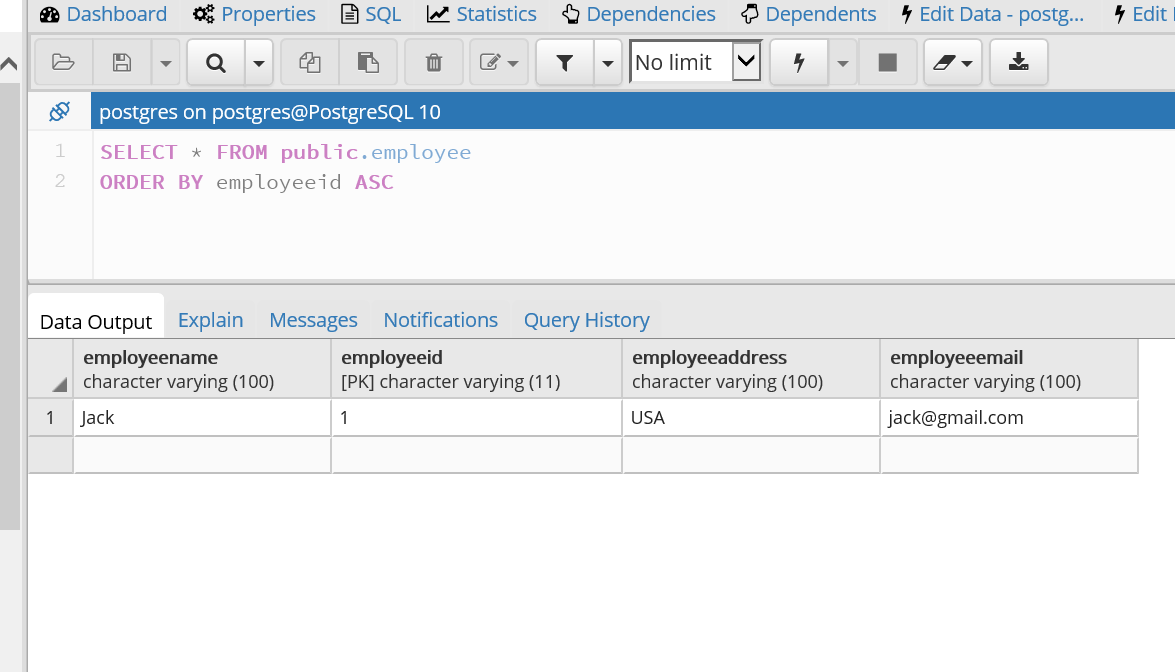
Conclusion
We have learned how to set up a Spring Boot application with Postgres and how to do a CRUD operation. You will find the complete code here.
Happy coding!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments