[Part-1] Text to Action: Build a Smart Calendar AI Assistant
Integrate Google Calendar into your app by setting up OAuth2 authentication and creating an Express endpoint to add events, all in under 50 lines of code.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWelcome to the “Text to Action” series, where we build intelligent systems that transform natural language into real-world actionable outcomes using AI.
To understand the concept better, let’s start simple by building a Smart Calendar AI Assistant. Soon, we’ll tackle more complex challenges — from smart home control to document automation — as we master the art of turning words into actions.
Our goal for this project is to create a working AI system where you can simply type or say, “Create a party event at 5 pm on March 20” and watch it instantly appear in your Google Calendar.
Part 1 focuses on building the backend foundation: an Express.js backend that connects to Google Calendar’s API. This will handle the actual event creation before we add natural language processing in future episodes.
Let’s begin by creating our calendar integration!
This tutorial shows you how to authenticate with OAuth2 and create a simple Express endpoint that adds events to your Google Calendar — perfect for integrating calendar functionality into any application.
Create a simple REST API endpoint that adds events to Google Calendar with minimal code.
Links
- The complete code is available on vivekvells/text-to-calendar-ai
- This tutorial video
What We're Building
A lightweight Express.js API that exposes a single endpoint for creating Google Calendar events. This API will:
- Authenticate with Google using OAuth2
- Add events to your primary calendar
- Return event details and links
Prerequisites
# Install Node.js (v14+) and npm
npm install express googleapis dotenvYou'll need OAuth credentials from the Google Cloud Console.
Project Structure
text-to-calendar/
├── app.js # Our entire application
├── public/ # Static files
│ └── index.html # Simple web interface
└── .env # Environment variablesThe Code: Complete Express Application
// app.js - Google Calendar API with Express
require('dotenv').config();
const express = require('express');
const { google } = require('googleapis');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.static('public'));
// Configure OAuth
const oauth2Client = new google.auth.OAuth2(
process.env.GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID,
process.env.GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET,
process.env.GOOGLE_REDIRECT_URI || 'http://localhost:3000/auth/google/callback'
);
// Load saved tokens if available
try {
const tokens = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('tokens.json'));
oauth2Client.setCredentials(tokens);
} catch (e) { /* No tokens yet */ }
// Auth routes
app.get('/auth/google', (req, res) => {
const authUrl = oauth2Client.generateAuthUrl({
access_type: 'offline',
scope: ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar']
});
res.redirect(authUrl);
});
app.get('/auth/google/callback', async (req, res) => {
const { tokens } = await oauth2Client.getToken(req.query.code);
oauth2Client.setCredentials(tokens);
fs.writeFileSync('tokens.json', JSON.stringify(tokens));
res.redirect('/');
});
// API endpoint to create calendar event
app.post('/api/create-event', async (req, res) => {
try {
// Check if we have the required fields
const { summary, description, startDateTime, endDateTime } = req.body;
if (!summary || !startDateTime || !endDateTime) {
return res.status(400).json({
error: 'Missing required fields: summary, startDateTime, endDateTime'
});
}
// Create the calendar event
const calendar = google.calendar({ version: 'v3', auth: oauth2Client });
const response = await calendar.events.insert({
calendarId: 'primary',
resource: {
summary,
description: description || summary,
start: { dateTime: startDateTime },
end: { dateTime: endDateTime }
}
});
res.status(201).json({
success: true,
eventId: response.data.id,
eventLink: response.data.htmlLink
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error creating event:', error);
res.status(error.code || 500).json({
error: error.message || 'Failed to create event'
});
}
});
// Start server
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${PORT}`));How to Use
1. Set up Environment Variables
Create a .env file:
GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID=your_client_id
GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET=your_client_secret
GOOGLE_REDIRECT_URI=http://localhost:3000/auth/google/callback
PORT=30002. Authenticate With Google
Visit http://localhost:3000/auth/google in your browser to connect to Google Calendar.
3. Create an Event
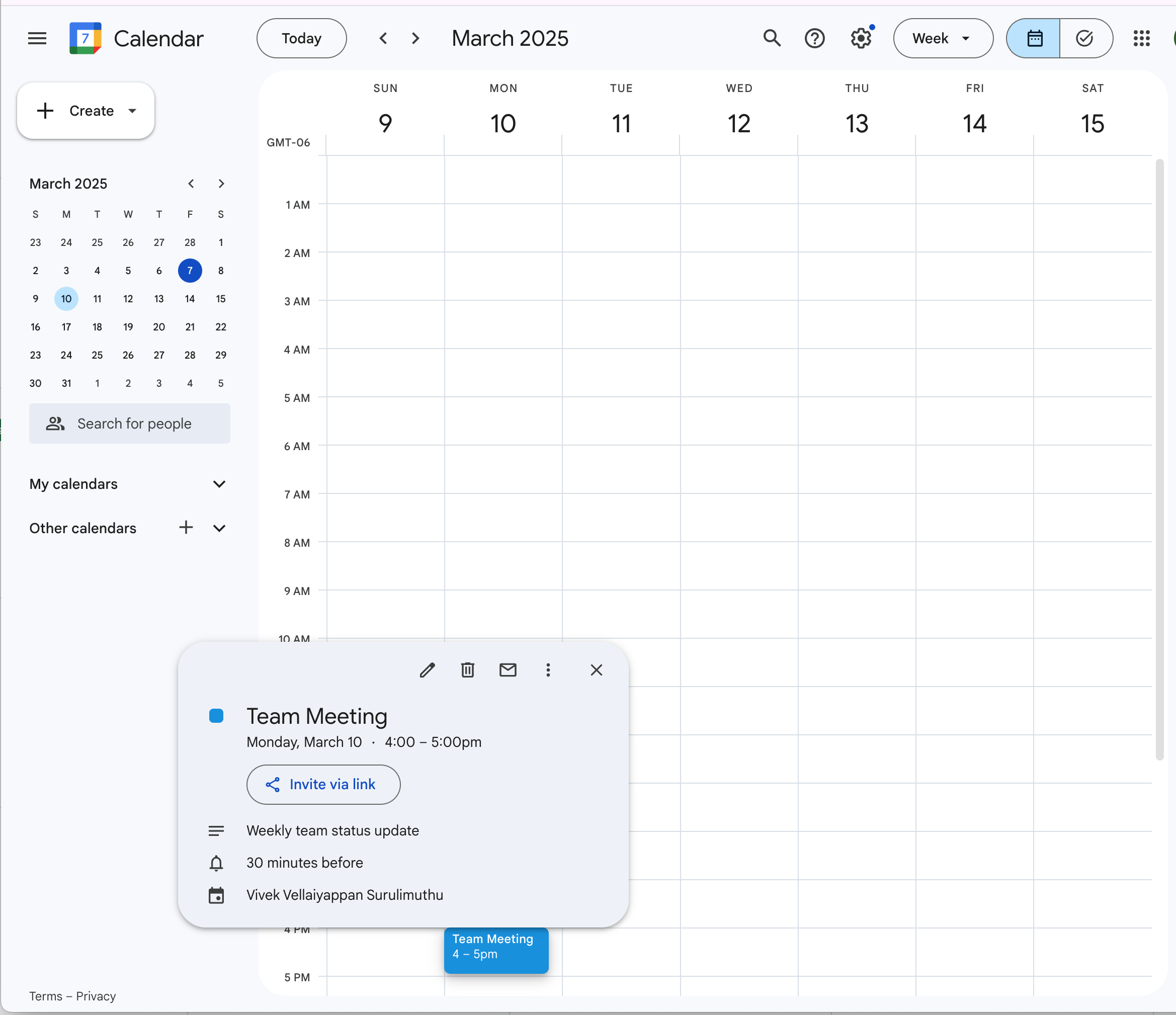
Use a POST request to the API endpoint:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/create-event \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"summary": "Team Meeting",
"description": "Weekly team status update",
"startDateTime": "2025-03-10T14:00:00-07:00",
"endDateTime": "2025-03-10T15:00:00-07:00"
}'Sample response:
{
"success": true,
"eventId": "e0ae1vv8gkop6bcbb5gqilotrs",
"eventLink": "https://www.google.com/calendar/event?eid=ZTBhZTF2djhna29wNmJjYmI1Z3FpbG90cnMgdml2ZWtzbWFpQG0"
}
API Endpoint Details
POST /api/create-event – Create a calendar event
Request:
summary(String, required) – Event titledescription(String) – Event detailsstartDateTime(ISO 8601) – When event startsendDateTime(ISO 8601) – When event ends
Response format:
{
"success": true,
"eventId": "e0ae1vv8gkop6bcbb5gqilotrs",
"eventLink": "https://www.google.com/calendar/event?eid=..."
}OAuth2 Authentication Flow
- User visits
/auth/googleendpoint. - User is redirected to the Google consent screen.
- After granting access, Google redirects to
/auth/google/callback. - The app stores OAuth tokens for future API calls.
- API is now ready to create events.
Troubleshooting
OAuth setup can be tricky. If you encounter issues, refer to the OAUTH_SETUP.md in the repository, which contains a detailed troubleshooting guide for common OAuth errors.
Security Considerations
- Store OAuth tokens securely in production (not in a local file)
- Use HTTPS for all API endpoints in production
- Consider rate limiting to prevent abuse
- Implement proper error handling and validation
Conclusion
With just under 60 lines of core code, we've created a functional API that connects to Google Calendar. This foundation can be extended to support more calendar operations like retrieving, updating, or deleting events.
The complete code is available on text-to-calendar-ai.
The same approach can be applied to integrate with other Google services or third-party APIs that use OAuth2 authentication.
Published at DZone with permission of Vivek Vellaiyappan Surulimuthu. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments