Building a Database Written in Node.js From the Ground Up
Node is lightweight and scalable, allows us to develop quickly, and npm has incredible packages. Read the tutorial to find out more!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe founding team at HarperDB built the first and only database written in Node.js. A few months back, our CEO Stephen Goldberg was invited to speak at a Women Who Code meetup to share the story of this (what some called crazy) endeavor. Stephen discussed the architectural layers of the database, demonstrated how to build a highly scalable and distributed product in Node.js, and demoed the inner workings of HarperDB. You can watch his talk at the link above, and even read a post from back in 2017, but since we all love Node.js and it’s an interesting topic, I’ll summarize here.
The main (and simplest) reason we chose to build a database in Node is that we knew it really well. We got flak for not choosing to Go, but people now accept that Go and Node are essentially head to head (in popularity and community support). Zach, one of our co-founders, recognized that with the time it would have taken to learn a new language, it would never be worth it.
Pros of Building a Database in Node.js
- We already knew Node.js
- Lightweight
- Rapid development
- Highly scalable
- npm
The HarperDB team has a background in large-scale software development. The initial goal of our database was to create a tool that empowers developers to focus on coding, without having to devote time and effort to database maintenance, while still providing a powerful solution. We wanted people to feel comfortable and confident in the product they were using. Our team has extensive experience in languages other than Node, but we had great success programming in it. (Although coming from Java, Stephen thought Node was horrible at first, but after about 90 days he learned to love it). Node is lightweight, allows us to develop quickly, and npm has incredible packages.
Cons of Building a Database in Node.js
- At the time was not accepted as an “enterprise-grade language.”
- Does not have direct control of Operating System/File System.
- Not as performant as C/C++.
- Did not have native threading (now it does).
We did have some troubles with it being the first database written in Node.js we didn’t have the option to follow in anyone’s footsteps. We’re probably one of the first enterprise products ever built in Node, at least the most data-centric one. People questioned this. One guy told Stephen that he would rather cut his heart out with a spoon than program a database in Node.js. Now people have realized this was a great idea because we have all these incredible features in our product that we didn’t have to build and are inherent in what we do. We did run into challenges around not having direct control of OS in the file system. Also, C/C++ is faster but can be more complicated and not necessarily as scalable horizontally. It really depends if you're looking for vertical or horizontal computing.
Tech Stack
![Tech Stack infographic.]()
This is what our tech stack looks like. We consider our Management Studio to be part of the HarperDB stack, and that is built in React with a Node back end. The green box signifies any application built on top of HarperDB, for example, our Node-RED node can be used to build custom workflows. The HarperDB technology is built entirely in Node.js, which encompasses our interfaces and HarperDB core.
Our product presents itself as a REST API which, under the hood, is essentially just an Express application, that’s the primary interface for how you interact with HarperDB. Our NoSQL parser is a custom solution we built internally. We use AlaSQL for our SQL parsing functionality which you can read more about here, we extend their functionality with custom code on top of that, it’s an amazing npm package for parsing SQL. We offer drivers, like ODBC and JDBC, built by a partner of ours. Finally, we use SocketCluster for distributed computing and clustering which CTO presented at this meetup.
The HarperDB core technology encompasses the “secret sauce.” This is what makes it possible for us to be fully indexed with no data duplication and offer various interface options to a single data model. Within the core, there are numerous npm packages implemented to extend our functionality.
Finally, we have various options for storage media. We bundle LMDB by default as it provides significant performance gains over the other options. HarperDB core contains extensible code that allows us to add additional storage media options in the future.
REST API
- HarperDB is a set of microservices.
- A single endpoint.
- All operations post.
- Stateless/RESTful.
At a former company, our team dealt with the headache of hundreds of APIs with different endpoints, which was simply insane. People might think it’s weird that HarperDB is just one endpoint, but if you look in the body of the code, for every operation you do- all you ever have to change is the body, those first few lines. This is super simple, and when writing a REST-based application you can make it really straightforward. This is something you can take from us and use in any application! Basically, you post a single message to the API, we see what operation you’re performing, and handle it with a standard set of methods. We’ve rewritten a lot of our applications over the last couple of years but this part has stayed mostly the same.
Management Studio
- Built on the HarperDB REST API.
- Written in React Native.
- Allows for control of your HarperDB instances via GUI.
The HarperDB Management Studio is a React front end built on top of our microservices (so we eat our own dog food). One awesome thing about JavaScript is how lightweight it is, regardless of what framework you're using (Node, React, etc), and you can easily couple together these different layers. React is amazing, it’s changed the quality of front-end development and allows us to make our application more accessible. By building on top of this, we’re also testing our own APIs at the same time, which makes it really powerful. Jaxon our VP of Product chose to React for the Studio, while Stephen wrote our back-end reporting in Express.
AlaSQL
- SQL search is built on AlaSQL.
- GitHub link.
- Allows for enhanced SQL.
- Our devs contribute to the project.
We chose AlaSQL for HarperDB's back-end functionality, it has some great things in it that we don’t, and allows us to wire in things like Math.js and GeoJSON, so it’s an incredible package. One amazing benefit of using Node for a language like this is as technology is advancing, most of the cool stuff that you want and need is on npm. If we had to build our own SQL parser, we’d probably still be building HarperDB. It took one of our competitors, FaunaDB, about 4 years just to get to market, but we launched the beta of our product in 6 months, the original version in 12 months, and we just released our cloud product a few months ago (about 3 years later). We’re not saying we’re geniuses, but by developing in Node, we got to stand on the shoulders of people like AlaSQL developers which is what we find amazing about the npm community.
Maths.js
- HarperDB uses math.js functions inside our SQL.
- Allows for enhanced math capability while leveraging the capabilities of the npm community.
Maths.js is another incredible package for things like averages, data science, etc., that we wired into our SQL capability. It’s not hard to use and very powerful in combination with AlaSQL.
![HarperDB infographic.]() Clustering/Replication
Clustering/Replication
- Built on SocketCluster.io.
- Fault-tolerant.
- Peer-to-Peer.
- Table level replication.
- Globally shared schema.
- Distributed Computing.
Another very cool feature of building something in Node.js is that it’s stateless by nature, meaning it does not require holding data in memory that is critical to serving clients across sessions, which is very resource-efficient. Most enterprise-grade applications have background processes and stateful variables that can become highly unstable. Node is stateless, designed for the web, designed to scale horizontally, and to be peer-to-peer. An amazing benefit from using a Node framework is that we were able to wire in SocketCluster to power our clustering and replication. HarperDB uses a simple pub-sub model, so we replicate data by publishing data to different chat rooms which different nodes subscribe to and are able to be distributed horizontally. The node can be horizontally scalable and less resource-intensive than other languages, and its stateless nature makes it incredibly stable.
By putting Node on lots of computers (horizontally scaling), you can make the framework significantly more powerful while driving down costs, having easier development, and being part of an awesome community.
LMDB and File System
- Originally built our exploded data model on the file system.
- Problematic due to the generation of many files taking up inodes and excess disk space, and other issues.
- Rebuilt data model on LMDB.
- Massive performance gain.
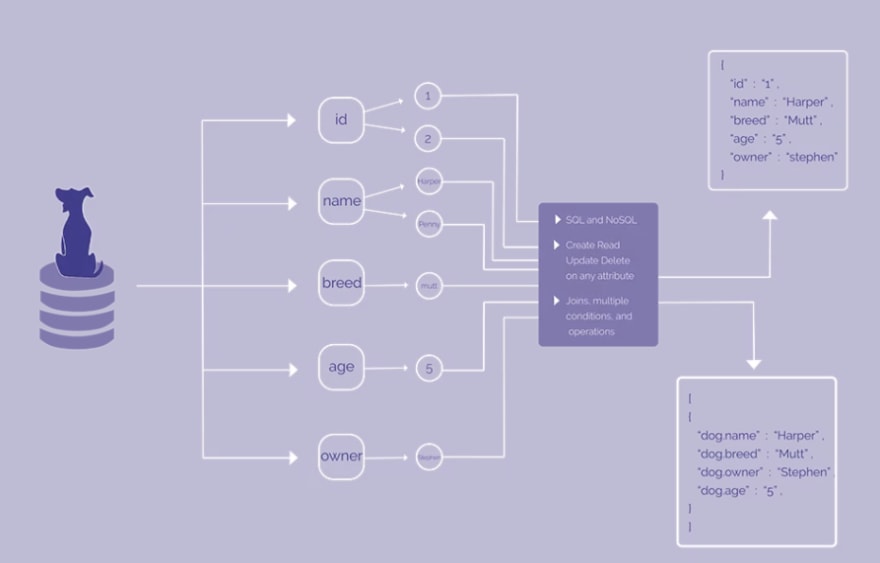
Originally, we were using the file system directly with the above HarperDB data model, this is what makes the product unique. As data comes in, we map it to our data model, it's not a SQL engine or NoSQL engine. We exploded that data into individual attributes and stored them in a folder structure on the file system. We store each thing atomically, and you can query via SQL and NoSQL. We did run into some challenges at scale, so more recently we wired in a package called LMDB, a key-value store that we operate on top of. We were able to implement our exact data model on top of that and it has provided incredible performance gains. In a recent benchmark, we were about 37 times faster than MongoDB, largely thanks to LMDB.
Once again, by leveraging the amazing Node community, we are able to focus on what we’re good at.
You might be able to tell by now that we LOVE Node. Hopefully, this was helpful and you learned something here or simply fueled your love for Node.js. We would love to hear your comments and are always happy to debate if you disagree! :)
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.



 Clustering/Replication
Clustering/Replication
Comments