Building a REST API With AWS Gateway and Python
Build a REST API using AWS Gateway and Python with our easy tutorial. Build secure and robust APIs that developers will love to build applications for.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAWS Gateway is a powerful tool for building APIs that scale to meet the demands of modern web and mobile applications. With AWS Gateway, you can create RESTful APIs that expose your data and business logic to developers who can then build rich, interactive applications that consume your API.
REST API is an industry standard for building scalable, distributed web applications. With AWS Gateway, you can easily build a REST API that supports both GET and POST methods, as well as complex query parameters. You can also add support for other HTTP methods, such as PUT, DELETE, and HEAD.
Using AWS Gateway, you can quickly create APIs that are secure and robust. You can also use it to deploy your code to a production environment with minimal effort. Additionally, AWS Gateway allows for seamless integration with other AWS services, such as S3 and DynamoDB, enabling you to easily add complex functionality to your APIs.
Pre-requisites
Before building a RESTful API with AWS Gateway, you should have the following in place:
- Create an AWS account if you don’t have one already.
- Log in to the AWS Management Console and navigate to the Amazon API Gateway service.
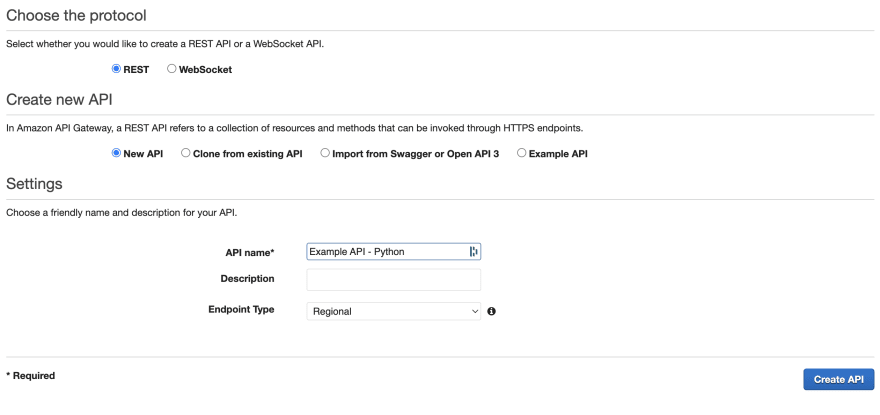
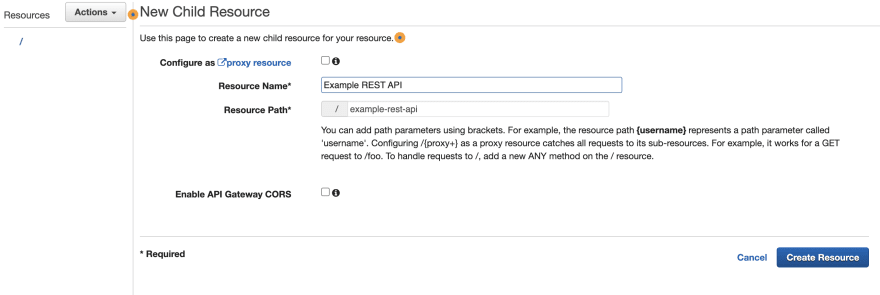
- Click on "Create API" and select "REST API".

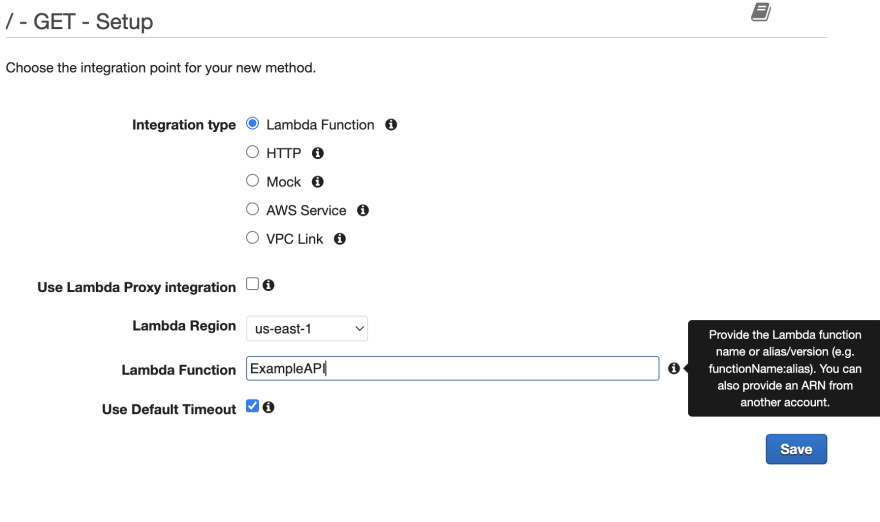
Choose the HTTP verb (e.g. GET, POST, PUT, etc.) and click on the checkmark to create the method.
In the "Integration type" section, select "Lambda Function" and enter the name of the Lambda function you want to use to handle the API requests.
Click on "Save" to create the API.
- Select Node from the Runtime Dropdown.

Code Example
import json
# Example data
data = {
"items": [
{"id": 1, "name": "Item 1", "price": 10.99},
{"id": 2, "name": "Item 2", "price": 15.99},
{"id": 3, "name": "Item 3", "price": 20.99},
]
}
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Determine the HTTP method of the request
http_method = event["httpMethod"]
# Handle GET request
if http_method == "GET":
# Return the data in the response
response = {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(data)
}
return response
# Handle POST request
elif http_method == "POST":
# Retrieve the request's body and parse it as JSON
body = json.loads(event["body"])
# Add the received data to the example data
data["items"].append(body)
# Return the updated data in the response
response = {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(data)
}
return response
# Handle PUT request
elif http_method == "PUT":
# Retrieve the request's body and parse it as JSON
body = json.loads(event["body"])
# Update the example data with the received data
for item in data["items"]:
if item["id"] == body["id"]:
item.update(body)
break
# Return the updated data in the response
response = {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(data)
}
return response
# Handle DELETE request
elif http_method == "DELETE":
# Retrieve the request's body and parse it as JSON
body = json.loads(event["body"])
# Find the item with the specified id in the example data
for i, item in enumerate(data["items"]):
if item["id"] == body["id"]:
# Remove the item from the example data
del data["items"][i]
break
# Return the updated data in the response
response = {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(data)
}
return response
else:
# Return an error message for unsupported methods
response = {
"statusCode": 405,
"body": json.dumps({"error": "Method not allowed"})
}
return responseThis code defines a Lambda function, lambda_handler, that handles different types of HTTP requests (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) on some data. The data is an object containing an array of items, each item has an id, name, and price.
When the function is called, it first determines the HTTP method of the request from the event object. Then it handles the request accordingly:
- GET: returns the data in the response with a status code of 200.
- POST: retrieves the request's body and parses it as JSON, then add the received data to the example data, then returns the updated data in the response with a status code of 200.
- PUT: retrieves the request's body and parses it as JSON, then updates the example data with the received data, then returns the updated data in the response with a status code of 200.
- DELETE: retrieves the request's body and parses it as JSON, then find the item with the specified id in the example data and removes it, then returns the updated data in the response with a status code of 200.
- If the method is not supported, it will return an error message with a status code of 405.
Deploy the API by clicking on "Actions" and selecting "Deploy API".
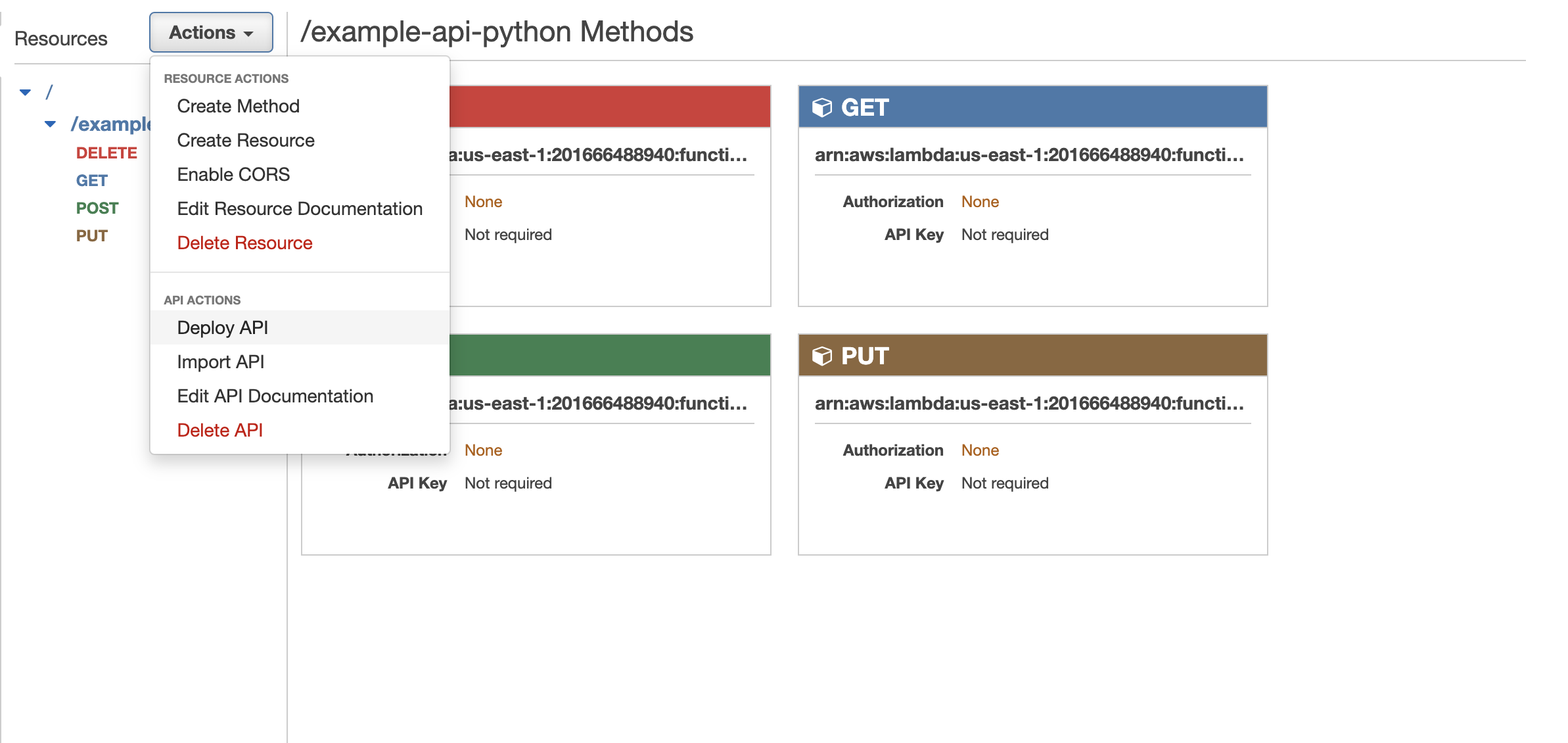
Select a deployment stage (e.g. "prod" or "test") and click on "Deploy".
Use the generated API endpoint to make requests to your API.
Running and Testing the Code in Postman
Now, our API is up and running. You can send a test HTTP request through Postman. By sending a request to your invoke URL, you should see a 200 OK status code. For this test, no request body is needed for the incoming request.
Published at DZone with permission of Derric Gilling. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.




Comments